|
RNAse
Ribonuclease (commonly abbreviated RNase) is a type of nuclease that catalyzes the degradation of RNA into smaller components. Ribonucleases can be divided into endoribonucleases and exoribonucleases, and comprise several sub-classes within the EC 2.7 (for the phosphorolytic enzymes) and 3.1 (for the hydrolytic enzymes) classes of enzymes. Function All organisms studied contain many RNases of two different classes, showing that RNA degradation is a very ancient and important process. As well as clearing of cellular RNA that is no longer required, RNases play key roles in the maturation of all RNA molecules, both messenger RNAs that carry genetic material for making proteins and non-coding RNAs that function in varied cellular processes. In addition, active RNA degradation systems are the first defense against RNA viruses and provide the underlying machinery for more advanced cellular immune strategies such as RNAi. Some cells also secrete copious quantities of non-specific RN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
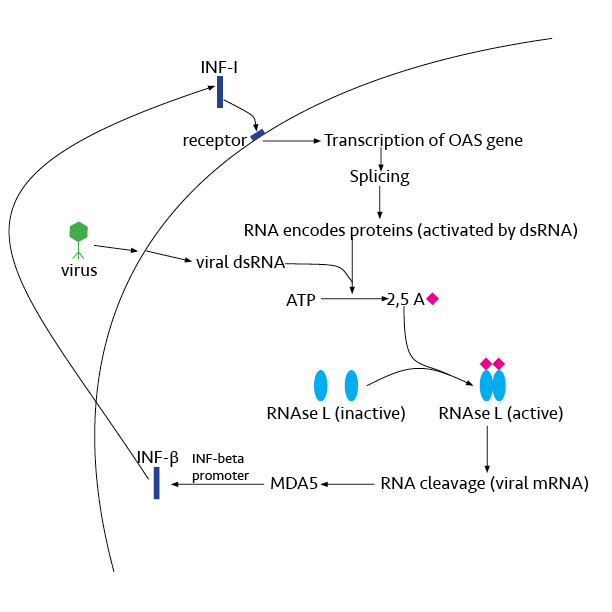
RNase L
Ribonuclease L or RNase L (for ''latent''), known sometimes as ribonuclease 4 or 2'-5' oligoadenylate synthetase-dependent ribonuclease, is an interferon (IFN)-induced ribonuclease which, upon activation, destroys all RNA within the cell (both cellular and viral) as well as inhibiting mRNA export. RNase L is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RNASEL'' gene. This gene encodes a component of the interferon-regulated 2'-5'oligoadenylate (2'-5'A) system that functions in the antiviral and antiproliferative roles of interferons. RNase L is activated by dimerization, which occurs upon 2'-5'A binding, and results in cleavage of all RNA in the cell. This can lead to activation of MDA5, an RNA helicase involved in the production of interferons. Synthesis and activation RNase L is present in very minute quantities during the normal cell cycle. When interferon binds to cell receptors, it activates transcription of around 300 genes to bring about the antiviral state. Among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNase PhyM
Ribonuclease (commonly abbreviated RNase) is a type of nuclease that catalyzes the degradation of RNA into smaller components. Ribonucleases can be divided into endoribonucleases and exoribonucleases, and comprise several sub-classes within the EC 2.7 (for the phosphorolytic enzymes) and 3.1 (for the hydrolytic enzymes) classes of enzymes. Function All organisms studied contain many RNases of two different classes, showing that RNA degradation is a very ancient and important process. As well as clearing of cellular RNA that is no longer required, RNases play key roles in the maturation of all RNA molecules, both messenger RNAs that carry genetic material for making proteins and non-coding RNAs that function in varied cellular processes. In addition, active RNA degradation systems are the first defense against RNA viruses and provide the underlying machinery for more advanced cellular immune strategies such as RNAi. Some cells also secrete copious quantities of non-specific RN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclease
In biochemistry, a nuclease (also archaically known as nucleodepolymerase or polynucleotidase) is an enzyme capable of cleaving the phosphodiester bonds that link nucleotides together to form nucleic acids. Nucleases variously affect single and double stranded breaks in their target molecules. In living organisms, they are essential machinery for many aspects of DNA repair. Defects in certain nucleases can cause genetic instability or immunodeficiency. Nucleases are also extensively used in molecular cloning. There are two primary classifications based on the locus of activity. Exonucleases digest nucleic acids from the ends. Endonucleases act on regions in the ''middle'' of target molecules. They are further subcategorized as deoxyribonucleases and ribonucleases. The former acts on DNA, the latter on RNA. History In the late 1960s, scientists Stuart Linn and Werner Arber isolated examples of the two types of enzymes responsible for phage growth restriction in Escherichi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNase A
Pancreatic ribonuclease family (, ''RNase'', ''RNase I'', ''RNase A'', ''pancreatic RNase'', ''ribonuclease I'', ''endoribonuclease I'', ''ribonucleic phosphatase'', ''alkaline ribonuclease'', ''ribonuclease'', ''gene S glycoproteins'', ''Ceratitis capitata alkaline ribonuclease'', ''SLSG glycoproteins'', ''gene S locus-specific glycoproteins'', ''S-genotype-assocd. glycoproteins'', ''ribonucleate 3'-pyrimidino-oligonucleotidohydrolase'') is a superfamily of pyrimidine-specific endonucleases found in high quantity in the pancreas of certain mammals and of some reptiles. Specifically, the enzymes are involved in endonucleolytic cleavage of 3'-phosphomononucleotides and 3'-phosphooligonucleotides ending in C-P or U-P with 2',3'-cyclic phosphate intermediates. Ribonuclease can unwind the RNA helix by complexing with single-stranded RNA; the complex arises by an extended multi-site cation-anion interaction between lysine and arginine residues of the enzyme and phosphate groups of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA molecules to form polypeptide chains. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small and large ribosomal subunits. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA molecules and many ribosomal proteins (). The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the ''translational apparatus''. Overview The sequence of DNA that encodes the sequence of the amino acids in a protein is transcribed into a messenger RNA (mRNA) chain. Ribosomes bind to the messenger RNA molecules and use the RNA's sequence of nucleotides to determine the sequence of amino acids needed to generate a protein. Amino acids are selected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules, which enter the riboso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRNA
Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA), formerly referred to as soluble ribonucleic acid (sRNA), is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes). In a cell, it provides the physical link between the genetic code in messenger RNA (mRNA) and the amino acid sequence of proteins, carrying the correct sequence of amino acids to be combined by the protein-synthesizing machinery, the ribosome. Each three-nucleotide codon in mRNA is complemented by a three-nucleotide anticodon in tRNA. As such, tRNAs are a necessary component of translation, the biological synthesis of new proteins in accordance with the genetic code. Overview The process of translation starts with the information stored in the nucleotide sequence of DNA. This is first transformed into mRNA, then tRNA specifies which three-nucleotide codon from the genetic code corresponds to which amino acid. Each mRNA codon is recognized by a particular type of tRNA, which docks to it along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribozyme
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to Catalysis, catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demonstrated that RNA can be both genetic material (like DNA) and a biological catalyst (like protein enzymes), and contributed to the RNA world hypothesis, which suggests that RNA may have been important in the evolution of prebiotic self-replicating systems. The most common activities of natural or Directed evolution, ''in vitro'' evolved ribozymes are the cleavage (or Ligation (molecular biology), ligation) of RNA and DNA and peptide bond formation. For example, the smallest ribozyme known (GUGGC-3') can aminoacylate a GCCU-3' sequence in the presence of PheAMP. Within the ribosome, ribozymes function as part of the large subunit ribosomal RNA to link amino acids during Translation (biology), protein synthesis. They also participate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNase P
Ribonuclease P (, ''RNase P'') is a type of ribonuclease which cleaves RNA. RNase P is unique from other RNases in that it is a ribozyme – a ribonucleic acid that acts as a catalyst in the same way that a protein-based enzyme would. Its function is to cleave off an extra, or precursor, sequence of RNA on tRNA molecules. Further, RNase P is one of two known multiple turnover ribozymes in nature (the other being the ribosome), the discovery of which earned Sidney Altman and Thomas Cech the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1989: in the 1970s, Altman discovered the existence of precursor tRNA with flanking sequences and was the first to characterize RNase P and its activity in processing of the 5' leader sequence of precursor tRNA. Its best characterised enzyme activity is the generation of mature 5′-ends of tRNAs by cleaving the 5′-leader elements of precursor-tRNAs. Cellular RNase Ps are ribonucleoproteins. The RNA from bacterial RNase P retains its catalytic activity in the ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Commission Number
The Enzyme Commission number (EC number) is a numerical classification scheme for enzymes, based on the chemical reactions they catalyze. As a system of enzyme nomenclature, every EC number is associated with a recommended name for the corresponding enzyme-catalyzed reaction. EC numbers do not specify enzymes but enzyme-catalyzed reactions. If different enzymes (for instance from different organisms) catalyze the same reaction, then they receive the same EC number. Furthermore, through convergent evolution, completely different protein folds can catalyze an identical reaction (these are sometimes called non-homologous isofunctional enzymes) and therefore would be assigned the same EC number. By contrast, UniProt identifiers uniquely specify a protein by its amino acid sequence. Format of number Every enzyme code consists of the letters "EC" followed by four numbers separated by periods. Those numbers represent a progressively finer classification of the enzyme. Preliminary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNase III
Ribonuclease III (RNase III or RNase C) (BREND3.1.26.3 is a type of ribonuclease that recognizes dsRNA and cleaves it at specific targeted locations to transform them into mature RNAs. These enzymes are a group of endoribonucleases that are characterized by their ribonuclease domain, which is labelled the RNase III domain. They are ubiquitous compounds in the cell and play a major role in pathways such as RNA precursor synthesis, RNA Silencing, and the ''pnp'' autoregulatory mechanism. Types of RNase III The RNase III superfamily is divided into four known classes: 1, 2, 3, and 4. Each class is defined by its domain structure.Liang Y-H, Lavoie M, Comeau M-A, Elela SA, Ji X. Structure of a Eukaryotic RNase III Post-Cleavage Complex Reveals a Double- Ruler Mechanism for Substrate Selection. Molecular cell. 2014;54(3):431-444. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.006. Class 1 RNase III *Class 1 RNase III enzymes have a homodimeric structure whose function is to cleave dsRNA into multipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |