|
Raw Image Format
A camera raw image file contains unprocessed or minimally processed data from the image sensor of either a digital camera, a motion picture film scanner, or other image scanner. Raw files are so named because they are not yet processed, and contain large amounts of potentially redundant data. Normally, the image is processed by a raw converter, in a wide- gamut internal color space where precise adjustments can be made before conversion to a viewable file format such as JPEG or PNG for storage, printing, or further manipulation. There are dozens of raw formats in use by different manufacturers of digital image capture equipment. Rationale Raw image files are sometimes described as "digital negatives". Like transparency film and unlike negative film, raw image pixels contain positive exposure measurements. The raw datasets are more like undeveloped film: a raw image can be developed by software in a non-reversible manner to reach a complete image that resolves ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sony α
Sony α (the lower case to Greek language, Greek letter Alpha (letter), alpha, often transliterated as ''Sony Alpha'') is a brand of digital camera. This line has been active since 2006, building upon the Konica Minolta camera technologies, whose assets were acquired by Sony. Overview Sony Alpha was introduced on 5 June 2006. It builds on existing Konica Minolta technologies including the Minolta AF SLR lens mount, whose assets were acquired by Sony after the end of Konica Minolta's photography operations in early 2006. Sony also has an 11.08% ownership stake in Japanese lens manufacturer Tamron, which is known to have partnered with Konica Minolta and Sony in the design and manufacture of many zoom lenses. Prior to the acquisition by Sony, the ''α'' branding had already been used on the Japanese market by Minolta for their AF camera system (marketed as "Dynax" in Europe, and "Maxxum" in North America). Sony adopted the name "Minolta A-mount system, A-mount system" f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
File Format Conversion
Data conversion is the conversion of computer data from one format to another. Throughout a computer environment, data is encoded in a variety of ways. For example, computer hardware is built on the basis of certain standards, which requires that data contains, for example, parity bit checks. Similarly, the operating system is predicated on certain standards for data and file handling. Furthermore, each computer program handles data in a different manner. Whenever any one of these variables is changed, data must be converted in some way before it can be used by a different computer, operating system or program. Even different versions of these elements usually involve different data structures. For example, the changing of bits from one format to another, usually for the purpose of application interoperability or of the capability of using new features, is merely a data conversion. Data conversions may be as simple as the conversion of a text file from one character encoding sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database. Before digital storage and retrieval of data have become widespread, index cards were used for data storage in a wide range of applications and environments: in the home to record and store recipes, shopping lists, contact information and other organizational data; in business to record presentation notes, project research and notes, and contact information; in schools as flash c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Content Management System
A content management system (CMS) is computer software used to manage the creation and modification of digital content ( content management).''Managing Enterprise Content: A Unified Content Strategy''. Ann Rockley, Pamela Kostur, Steve Manning. New Riders, 2003. It is typically used for enterprise content management (ECM) and web content management (WCM). ECM typically supports multiple users in a collaborative environment, by integrating document management, digital asset management, and record retention. Alternatively, WCM is the collaborative authoring for websites and may include text and embed graphics, photos, video, audio, maps, and program code that display content and interact with the user. ECM typically includes a WCM function. Structure A CMS typically has two major components: a content management application (CMA), as the front-end user interface that allows a user, even with limited expertise, to add, modify, and remove content from a website without the interve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
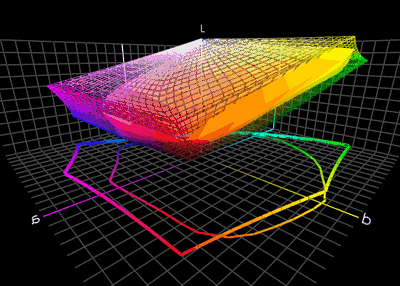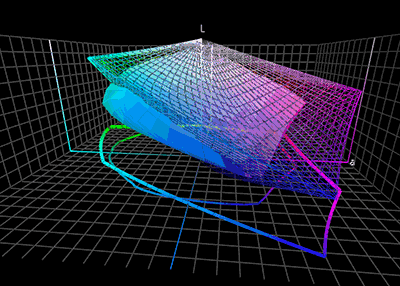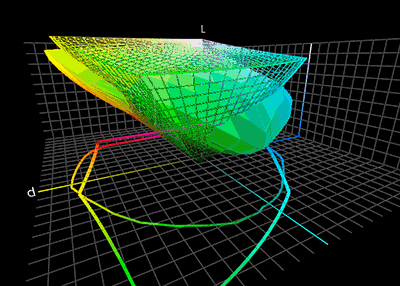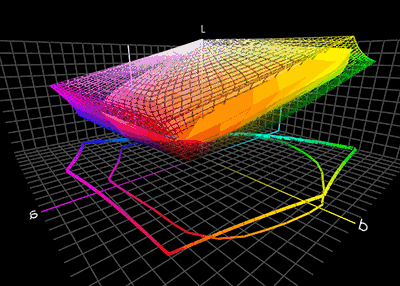
ICC Profile
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium (ICC). Profiles describe the color attributes of a particular device or viewing requirement by defining a mapping between the device source or target color space and a ''profile connection space'' (PCS). This PCS is either CIELAB (L*a*b*) or CIEXYZ. Mappings may be specified using tables, to which interpolation is applied, or through a series of parameters for transformations. Every device that captures or displays color can be profiled. Some manufacturers provide profiles for their products, and there are several products that allow an end-user to generate their own color profiles, typically through the use of a tristimulus colorimeter or a spectrophotometer (sometimes called a spectrocolorimeter). The ICC defines the format precisely but does not define algorithms or processing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Filter Array
In digital imaging, a color filter array (CFA), or color filter mosaic (CFM), is a mosaic of tiny color filters placed over the pixel sensors of an image sensor to capture color information. The term is also used in reference to Electronic paper, e paper devices where it means a mosaic of tiny color filters placed over the grey scale display panel to reproduce color images. Image sensor overview Color filters are needed because the typical photosensors detect light intensity with little or no wavelength specificity and therefore cannot separate color information. Since sensors are made of semiconductors, they obey solid-state physics. The color Filter (optics), filters filter the light by wavelength range, such that the separate filtered intensities include information about the color of light. For example, the Bayer filter (shown by the image) gives information about the intensity of light in red, green, and blue (RGB) wavelength regions. The raw image data captured by the ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including: * Descriptive metadata – the descriptive information about a resource. It is used for discovery and identification. It includes elements such as title, abstract, author, and keywords. * Structural metadata – metadata about containers of data and indicates how compound objects are put together, for example, how pages are ordered to form chapters. It describes the types, versions, relationships, and other characteristics of digital materials. * Administrative metadata – the information to help manage a resource, like resource type, and permissions, and when and how it was created. * Reference metadata – the information about the contents and quality of Statistical data type, statistical data. * Statistical metadata – also called process data, may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endianness
file:Gullivers_travels.jpg, ''Gulliver's Travels'' by Jonathan Swift, the novel from which the term was coined In computing, endianness is the order in which bytes within a word (data type), word of digital data are transmitted over a data communication medium or Memory_address, addressed (by rising addresses) in computer memory, counting only byte Bit_numbering#Bit significance and indexing, significance compared to earliness. Endianness is primarily expressed as big-endian (BE) or little-endian (LE), terms introduced by Danny Cohen (computer scientist), Danny Cohen into computer science for data ordering in an Internet Experiment Note published in 1980. Also published at The adjective ''endian'' has its origin in the writings of 18th century Anglo-Irish writer Jonathan Swift. In the 1726 novel ''Gulliver's Travels'', he portrays the conflict between sects of Lilliputians divided into those breaking the shell of a boiled egg from the big end or from the little end. By analogy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software. Each pixel is a Sampling (signal processing), sample of an original image; more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original. The Intensity (physics), intensity of each pixel is variable. In color imaging systems, a color is typically represented by three or four component intensities such as RGB color model, red, green, and blue, or CMYK color model, cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. In some contexts (such as descriptions of camera sensors), ''pixel'' refers to a single scalar element of a multi-component representation (called a ''photosite'' in the camera sensor context, although ''wikt:sensel, sensel'' is sometimes used), while in yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiometric
Radiometry is a set of techniques for measuring electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. Radiometric techniques in optics characterize the distribution of the radiation's power in space, as opposed to photometric techniques, which characterize the light's interaction with the human eye. The fundamental difference between radiometry and photometry is that radiometry gives the entire optical radiation spectrum, while photometry is limited to the visible spectrum. Radiometry is distinct from quantum techniques such as photon counting. The use of radiometers to determine the temperature of objects and gasses by measuring radiation flux is called pyrometry. Handheld pyrometer devices are often marketed as infrared thermometers. Radiometry is important in astronomy, especially radio astronomy, and plays a significant role in Earth remote sensing. The measurement techniques categorized as ''radiometry'' in optics are called ''photometry'' in some astronomical applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Range
Dynamics (from Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' " power") or dynamic may refer to: Physics and engineering * Dynamics (mechanics), the study of forces and their effect on motion Brands and enterprises * Dynamic (record label), an Italian record label in Genoa Mathematics * Dynamical system, a concept describing a point's time dependency ** Topological dynamics, the study of dynamical systems from the viewpoint of general topology * Symbolic dynamics, a method to model dynamical systems Social science * Group dynamics, the study of social group processes especially * Population dynamics, in life sciences, the changes in the composition of a population * Psychodynamics, the study of psychological forces driving human behavior * Social dynamics, the ability of a society to react to changes * Spiral Dynamics, a social development theory Other uses * Dynamics (music), the softness or loudness of a sound or note * DTA Dynami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Image
A latent image is an invisible image produced by the exposure to light of a photosensitive material such as photographic film. When photographic film is developed, the area that was exposed darkens and forms a visible image. In the early days of photography, the nature of the invisible change in the silver halide crystals of the film's emulsion coating was unknown, so the image was said to be "latent" until the film was treated with photographic developer. In more physical terms, a latent image is a small cluster of metallic silver atoms formed in or on a silver halide crystal due to reduction of interstitial silver ions by photoelectrons (a photolytic silver cluster). If intense exposure continues, such photolytic silver clusters grow to visible sizes. This is called ''printing out'' the image. On the other hand, the formation of a visible image by the action of photographic developer is called ''developing out'' the image. The size of a silver cluster in the latent ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |