|
Qäwrighul Culture
The Qäwrighul culture (after the Tarim Basin cemetery of Qäwrighul , also named 古墓溝 Gumugou in Chinese) is a late Bronze Age culture which flourished along the Kongque River in Xinjiang from ca. 2100 BC to 1500 BC, and is one of the cultures of the Tarim mummies. It is considered as part of the Xiaohe culture, with its Xiaohe cemetery slightly to the south. Characteristics The Qäwrighul culture is primarily known for its cemeteries. It is considered as the oldest of the Tarim mummies burial sites, going back to 2135–1939 BCE for its lowest layers. The best attested of these are the cemeteries of Qäwrighul itself, in which at least forty-two burials have been uncovered. Qäwrighul tombs are divided into two types. The first type of Qäwrighul tomb is characterized by shaft graves. These included evidence of wooden planking. Sometimes, wooden poles were erected on the western and eastern ends of the chamber. The deceased in these tombs were buried in an extended po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Xinjiang, Northwestern China occupying an area of about and one of the largest basins in Northwest China.Chen, Yaning, et al. "Regional climate change and its effects on river runoff in the Tarim Basin, China." Hydrological Processes 20.10 (2006): 2207–2216.online 426 KB) Located in China's Xinjiang region, it is sometimes used synonymously to refer to the southern half of the province, that is, Southern Xinjiang or Nanjiang (), as opposed to the northern half of the province known as Dzungaria or Beijiang. Its northern boundary is the Tian Shan mountain range and its southern boundary is the Kunlun Mountains on the edge of the Tibetan Plateau. The Taklamakan Desert dominates much of the basin. The historical Uyghur name for the Tarim Basin is Altishahr (Uyghur language, Traditional Uyghur: , ), which means 'six cities' in Uyghur language, Uyghur. The region was also called ''Little Bukhara'' or ''Little Bukharia''. Geography and relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asian People
East Asian people (also East Asians) are the people from East Asia, which consists of China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. The total population of all countries within this region is estimated to be 1.677 billion and 21% of the world's population in 2020. However, large East Asian diasporas, such as the Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Mongolian diasporas, as well as diasporas of other East Asian ethnic groups, mean that the 1.677 billion does not necessarily represent an accurate figure for the number of East Asian people worldwide. The major ethnic groups that form the core of traditional East Asia are the Han Chinese, Koreans, and Yamato. Other ethnic groups of East Asia include the Ainu, Bai, Daur, Manchus, Mongols, Qiang, Ryukyuans, and Tibetans. Culture The major East Asian language families that form the traditional linguistic core of East Asia are the Sinitic, Japonic, and Koreanic families. Other language families include the Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thames & Hudson
Thames & Hudson (sometimes T&H for brevity) is a publisher of illustrated books in all visually creative categories: art, architecture, design, photography, fashion, film, and the performing arts. It also publishes books on archaeology, history, and popular culture. Headquartered in London, it has a sister company in New York City, and subsidiaries in Melbourne, Singapore, and Hong Kong. In Paris it has a sister company, Éditions Thames & Hudson, and a subsidiary called Interart which distributes English-language books. The Thames & Hudson group currently employs approximately 150 staff in London and approximately 65 more around the world. The publishing company was founded in 1949 by Walter and Eva Neurath, who aimed to make the world of art and the research of top scholars available to a wider public. The company's name reflects its international presence, particularly in London and New York. It remains an independent, family-owned company, and is one of the largest publishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor & Francis
Taylor & Francis Group is an international company originating in the United Kingdom that publishes books and academic journals. Its parts include Taylor & Francis, CRC Press, Routledge, F1000 (publisher), F1000 Research and Dovepress. It is a division of Informa, a United Kingdom-based publisher and conference company. Overview Founding The company was founded in 1852 when William Francis (chemist), William Francis joined Richard Taylor (editor), Richard Taylor in his publishing business. Taylor had founded his company in 1798. Their subjects covered agriculture, chemistry, education, engineering, geography, law, mathematics, medicine, and social sciences. Publications included the ''Philosophical Magazine''. Francis's son, Richard Taunton Francis (1883–1930), was sole partner in the firm from 1917 to 1930. Acquisitions and mergers In 1965, Taylor & Francis launched Wykeham Publications and began book publishing. T&F acquired Hemisphere Publishing in 1988, and the compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brill Publishers
Brill Academic Publishers () is a Dutch international academic publisher of books, academic journals, and Bibliographic database, databases founded in 1683, making it one of the oldest publishing houses in the Netherlands. Founded in the South Holland city of Leiden, it maintains its headquarters there, while also operating offices in Boston, Paderborn, Vienna, Singapore, and Beijing. Since 1896, Brill has been a public limited company (). Brill is especially known for its work in subject areas such as Oriental studies, classics, religious studies, Jewish studies, Islamic studies, Asian studies, international law, and human rights. The publisher offers traditional print books, academic journals, primary source materials online, and publications on microform. In recent decades, Brill has expanded to Electronic publishing, digital publishing with ebooks and online resources including databases and specialty collections varying by discipline. History Founding by Luchtmans, 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
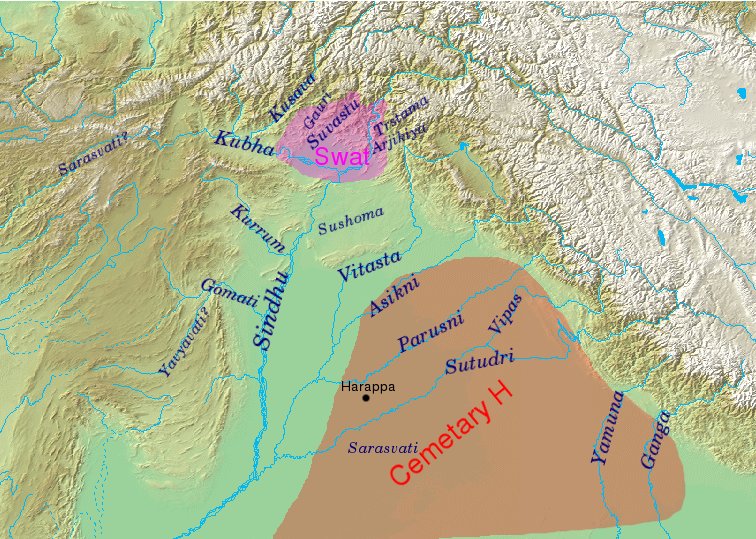
Swat Culture
The Gandhara grave culture of present-day Pakistan is known by its "protohistoric graves", which were spread mainly in the middle Swat River valley and named the Swat Protohistoric Graveyards Complex, dated in that region to –800 BCE. The Italian Archaeological Mission to Pakistan (MAIP) holds that there are no burials with these features after 800 BCE. More recent studies by Pakistani scholars, such as Muhammad Zahir, consider that these protohistoric graves extended over a much wider geography and continued in existence from the 8th century BCE until the historic period. The core region was in the middle of the Swat River course and expanded to the valleys of Dir, Kunar, Chitral, and Peshawar. Protohistoric graves were present in north, central, and southern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province as well as in north-western tribal areas, including Gilgit-Baltistan province, Taxila, and Salt Range in Punjab, Pakistan, along with their presence in Indian Kashmir, Ladakh, and Uttarakhan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tazabagyab Culture
The Tazabagyab culture is from the late Bronze Age, ca. 1850 BC to 1500 BC,Garner, Jennifer, (2020)"Metal sources (tin and copper) and the BMAC" in ''The World of the Oxus Civilization, Chapter 28, Routledge, Table 28.1:'' "Andronovo-Tazabag'jab, 1850-1500 BC (after Parzinger and Boroffka 2003: 280, fig. 1)" and flourished in the lower Zeravshan valley, as well as along the lower Amu Darya towards the south shore of the Aral Sea; this last region is known as Khwarazm or Khorezm. Earlier it was thought to be from ca. 1500 BC to 1100 BC and regarded a southern offshoot of the Andronovo culture, composed of Indo-Iranians, but Stanislav Grigoriev, in a recent study asserts that Tazabagyab is not part of the Andronovo cultural horizon.Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo Problem: Studies of Cultural Genesis in the Eurasian Bronze Age" in Open Archaeology 2021 (7), p.5: "...In western literature, for example, the Tazabagyab culture of the southern Aral Sea region is sometimes viewed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishkent Culture
The Bishkent culture or Beshkent culture is a Bronze Age archaeological culture of southern Tajikistan, recently dated to c. 2800 – 2400 BC. It is primarily known from its cemeteries, which appear to have been used by mobile pastoralists, but currently considered to be a small group of people moving towards Tajikistan from Swat valley or Baluchistan, just as it was found in the early necropolis of Tulkhar. According to J. P. Mallory, "the Bishkent culture has been seen as a possible contributor to the Swat culture, which in turn is often associated with early Indo-Aryan movements into northwest India." See also * Vakhsh culture * Chust culture * Yaz culture The Yaz culture (named after the type site Yaz-Tappe, Yaz Tepe, or Yaz Depe, near Baýramaly, Turkmenistan) was an early Iron Age culture of Margiana, Bactria and Sogdia (–500 BC, or –330 BC). It emerges at the top of late Bronze Age sites ... References Sources * * Archaeological cultures of South Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vakhsh Culture
The Vakhsh culture is a Bronze Age culture which took place around 2500-1650 BC, as shown by radiocarbon dates, and flourished along the lower Vakhsh River in southern Tajikistan, earlier thought to be from ca. 1700 BC to 1500 BC. Earlier research seemed to show that Vakhsh culture had appeared somewhat later than the Bishkent culture, with which it shares many similarities. Settlements Evidence of settlements in the Vakhsh culture is scant. They made stone walls and mud-brick constructions. Houses on the site at Kangurt Tut in the Vaksh valley contained storage pits for grain and hearths. The grain storages had barley and wheat. Faunal remains have revealed dogs, deer, camels, donkeys, horses, sheep and goats.Mallory, J. P., & Douglas Q. Adams, (1997)"Vaksh Culture" in Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture, Taylor & Francis, p. 617. Burials The Vaksh culture is known chiefly for its burials. These were catacomb graves covered entirely over with a mound, and entrance shafts blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaz Culture
The Yaz culture (named after the type site Yaz-Tappe, Yaz Tepe, or Yaz Depe, near Baýramaly, Turkmenistan) was an early Iron Age culture of Margiana, Bactria and Sogdia (–500 BC, or –330 BC). It emerges at the top of late Bronze Age sites ( BMAC), sometimes as mud-brick platforms and sizeable houses associated with irrigation systems. Ceramics were mostly hand-made, but there was increasing use of wheel-thrown ware. Bronze and iron arrowheads, also iron sickles and carpet knives among other artifacts have been found. With the farming citadels and absence of burials it has been regarded as a likely archaeological reflection of early East Iranian culture as described in the Avesta. So far, no burials related to the culture have been found, and this is taken as possible evidence of the Zoroastrian practice of exposure or sky burial. Overview Yaz I In the region of Southern Central Asia, the Bronze Age Oxus civilization (or BMAC) was characteristic for irrigation and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chust Culture
The Chust culture is a late Bronze Age and early Iron Age culture which flourished in the Fergana Valley of eastern Uzbekistan from ca. 1500 BC to 900 BC. Settlements of the Chust culture varied in size between small dwelling sites to large settlements over 10 ha in size. Some sites occupy hilltop locations, while others indicate the presence of defensive structures. Domestic structures are not well known, with some built of mud-bricks. Large pits appear frequently in Chust sites. These were probably intended for the storage of grain. Barley, wheat and particularly millet have been recovered, along with agricultural tools such as sickles and hoes. Domestic animals that were part of the Chust culture include camels, asses, horses, cattle, sheep, goat and probably pig. Wild animals that appeared in their territories include onagers, gazelles and saiga antilope. Chust pottery was hand-made. They created both bronze objects and later iron objects. Objects made of bronze include sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qijia Culture
The Qijia culture (2400 BC – 1600 BC) was an early Bronze Age culture distributed around the upper Yellow River region of Gansu (centered in Lanzhou) and eastern Qinghai, China. It is regarded as one of the earliest bronze cultures in China. The Qijia Culture is named after the Qijiaping Site (齐家坪) in Gansu Province. Prior to Qijia culture, in the same area there existed Majiayao culture that was also familiar with metalwork. At the end of the third millennium B.C., Qijia culture succeeded Majiayao culture at sites in three main geographic zones: Eastern Gansu, Middle Gansu, and Western Gansu/Eastern Qinghai. The Qijia culture benefited from the warm and humid climatic conditions from the Late Glacial to the Middle Holocene, which led to flourishing agricultural production and rapid population growth. These conditions changed with the aridification of the Late Holocene, provoking material and cultural decline. Research Johan Gunnar Andersson discovered the initial si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |