|
Quote Stuffing
In finance, quote stuffing refers to a form of market manipulation employed by high-frequency traders (HFT) that involves quickly entering and withdrawing a large number of orders in an attempt to flood the market. This can create confusion in the market and trading opportunities for high-speed algorithmic traders. The term is relatively new to the financial market lexicon and was coined by Nanex in studies on HFT behavior during the 2010 Flash Crash. By quote stuffing, trading systems delay price quotes while the stuffing is occurring, simply by placing and canceling orders at a rate that substantially surpasses the bandwidth of market data feed lines. The orders pile up in buffers, and the delay (increased latency) lasts until the buffer drains. Trading systems slow down a direct exchange feed whenever they want, and the phantom orders do not need to be in a particular stock; they can be in any of the securities that cohabit the particular price (market data) feed. For exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Manipulation
In economics and finance, market manipulation occurs when someone intentionally alters the supply or demand of a security to influence its price. This can involve spreading misleading information, executing misleading trades, or manipulating quotes and prices. Market manipulation is prohibited in most countries, in particular, it is prohibited in the United States under Section 9(a)(2) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, in the European Union under Article 12 of the ''Market Abuse Regulation'', in Australia under Section 1041A of the Corporations Act 2001, and in Israel under Section 54(a) of the securities act of 1968. In the US, market manipulation is also prohibited for wholesale electricity markets under Section 222 of the Federal Power Act and wholesale natural gas markets under Section 4A of the Natural Gas Act. Examples Pools Agreements, often written, among a group of traders to delegate authority to a single manager to trade in a specific stock for a work per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spoofing (finance)
Spoofing is a disruptive algorithmic trading activity employed by traders to outpace other market participants and to manipulate markets. Spoofers feign interest in trading futures, stocks, and other products in financial markets creating an illusion of the demand and supply of the traded asset. In an order driven market, spoofers post a relatively large number of limit orders on one side of the limit order book to make other market participants believe that there is pressure to sell (limit orders are posted on the offer side of the book) or to buy (limit orders are posted on the bid side of the book) the asset. Spoofing may cause prices to change because the market interprets the one-sided pressure in the limit order book as a shift in the balance of the number of investors who wish to purchase or sell the asset, which causes prices to increase (more buyers than sellers) or prices to decline (more sellers than buyers). Spoofers bid or offer with intent to cancel before the orders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denial Of Service
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyberattack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to a network. Denial of service is typically accomplished by flooding the targeted machine or resource with superfluous requests in an attempt to overload systems and prevent some or all legitimate requests from being fulfilled. The range of attacks varies widely, spanning from inundating a server with millions of requests to slow its performance, overwhelming a server with a substantial amount of invalid data, to submitting requests with an illegitimate IP address. In a distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack), the incoming traffic flooding the victim originates from many different sources. More sophisticated strategies are required to mitigate this type of attack; simply attempting to block a single source is insuffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Crash
In modern finance, a flash crash is a very rapid, deep, and volatile fall in Security (finance), security prices occurring within a very short time period followed by a quick recovery. Flash crashes are frequently blamed by media on trades executed by black-box trading, combined with high-frequency trading, whose speed and interconnectedness can result in the loss and recovery of billions of dollars in a matter of minutes and seconds, but in reality occur because almost all participants have pulled their liquidity and temporarily paused their trading in the face of a sudden increase in risk. Occurrences Examples of flash crashes that have occurred: * 2010 flash crash, May 6, 2010, flash crash * AP Tweet Flash Crash of 2013, April 23, 2013, flash crash * Frankenshock, or Flash Crash Swiss franc, Swiss Franc on January 15, 2015 * Flash Crash of the Pound sterling, British Pound on October 6, 2016 *Flash Crash of Japanese yen, Japanese Yen on January 2, 2019 * Flash Crash of Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Bug
A software bug is a design defect ( bug) in computer software. A computer program with many or serious bugs may be described as ''buggy''. The effects of a software bug range from minor (such as a misspelled word in the user interface) to severe (such as frequent crashing). In 2002, a study commissioned by the US Department of Commerce's National Institute of Standards and Technology concluded that "software bugs, or errors, are so prevalent and so detrimental that they cost the US economy an estimated $59 billion annually, or about 0.6 percent of the gross domestic product". Since the 1950s, some computer systems have been designed to detect or auto-correct various software errors during operations. History Terminology ''Mistake metamorphism'' (from Greek ''meta'' = "change", ''morph'' = "form") refers to the evolution of a defect in the final stage of software deployment. Transformation of a ''mistake'' committed by an analyst in the early stages of the softw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Manipulation
In economics and finance, market manipulation occurs when someone intentionally alters the supply or demand of a security to influence its price. This can involve spreading misleading information, executing misleading trades, or manipulating quotes and prices. Market manipulation is prohibited in most countries, in particular, it is prohibited in the United States under Section 9(a)(2) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, in the European Union under Article 12 of the ''Market Abuse Regulation'', in Australia under Section 1041A of the Corporations Act 2001, and in Israel under Section 54(a) of the securities act of 1968. In the US, market manipulation is also prohibited for wholesale electricity markets under Section 222 of the Federal Power Act and wholesale natural gas markets under Section 4A of the Natural Gas Act. Examples Pools Agreements, often written, among a group of traders to delegate authority to a single manager to trade in a specific stock for a work per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-frequency Trading
High-frequency trading (HFT) is a type of algorithmic trading in finance characterized by high speeds, high turnover rates, and high order-to-trade ratios that leverages high-frequency financial data and electronic trading tools.Lin, Tom C. W. "The New Financial Industry" (March 30, 2014). 65 Alabama Law Review 567 (2014); Temple University Legal Studies Research Paper No. 2014-11; . While there is no single definition of HFT, among its key attributes are highly sophisticated algorithms, co-location, and very short-term investment horizons in trading securities. HFT uses proprietary trading strategies carried out by computers to move in and out of positions in seconds or fractions of a second. In 2016, HFT on average initiated 10–40% of trading volume in equities, and 10–15% of volume in foreign exchange and commodities. High-frequency traders move in and out of short-term positions at high volumes and high speeds aiming to capture sometimes a fraction of a cent in profit on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
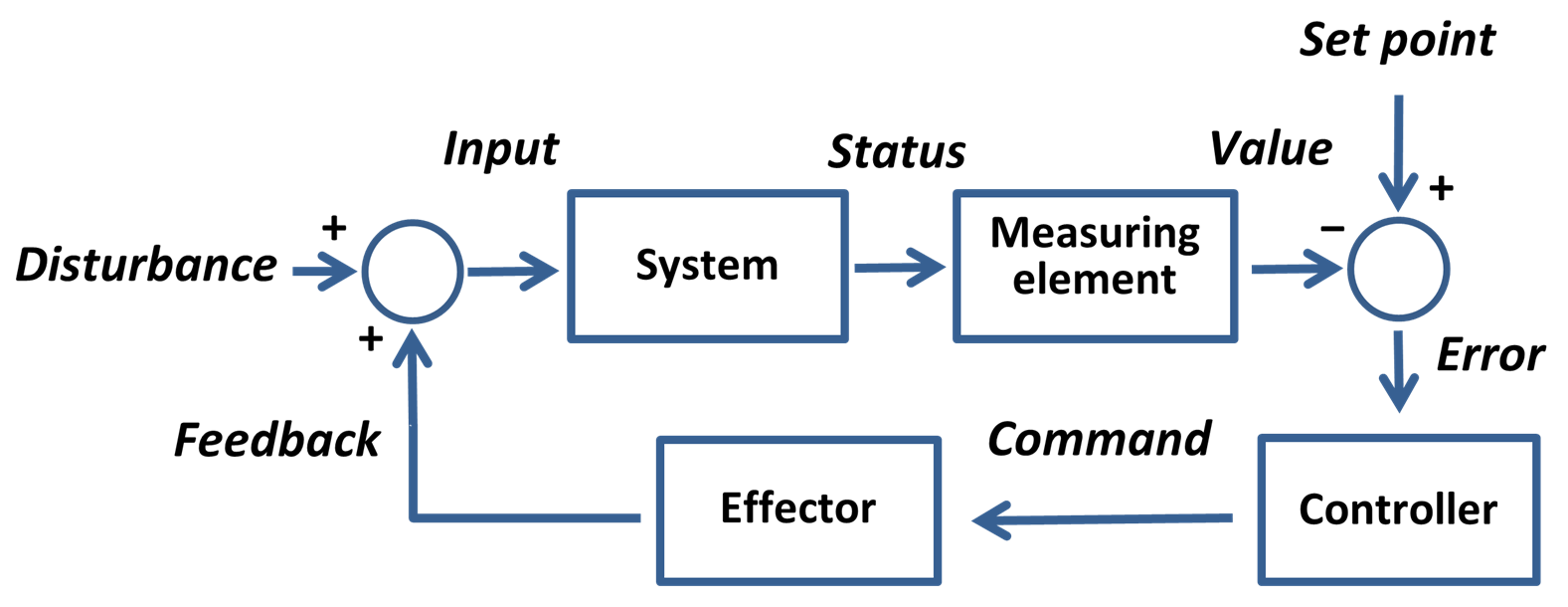
Feedback Loop
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled carefully when applied to feedback systems: History Self-regulating mechanisms have existed since antiquity, and the idea of feedback started to enter economic theory in Britain by the 18th century, but it was not at that time recognized as a universal abstraction and so did not have a name. The first ever known artificial feedback device was a float valve, for maintaining water at a constant level, invented in 270 BC in Alexandria, Egypt. This device illustrated the principle of feedback: a low water level opens the valve, the rising water then provides feedback into the system, closing the valve when the required level is reached. This then reoccurs in a circular fashion as the water level fluctuates. Centrifugal governors were u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading is a method of executing orders using automated pre-programmed trading instructions accounting for variables such as time, price, and volume. This type of trading attempts to leverage the speed and computational resources of computers relative to human traders. In the twenty-first century, algorithmic trading has been gaining traction with both retail and institutional traders. A study in 2019 showed that around 92% of trading in the Forex market was performed by trading algorithms rather than humans. It is widely used by investment banks, pension funds, mutual funds, and hedge funds that may need to spread out the execution of a larger order or perform trades too fast for human traders to react to. However, it is also available to private traders using simple retail tools. The term algorithmic trading is often used synonymously with automated trading system. These encompass a variety of trading strategies, some of which are based on formulas and results ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investors
An investor is a person who allocates financial capital with the expectation of a future return (profit) or to gain an advantage (interest). Through this allocated capital the investor usually purchases some species of property. Types of investments include equity, debt, securities, real estate, infrastructure, currency, commodity, token, derivatives such as put and call options, futures, forwards, etc. This definition makes no distinction between the investors in the primary and secondary markets. That is, someone who provides a business with capital and someone who buys a stock are both investors. An investor who owns stock is a shareholder. Types of investors There are two types of investors: retail investors and institutional investors. A ''retail investor'' is also known as an ''individual investor''. There are several sub-types of institutional investor: * Pension plans making investments on behalf of employees * Businesses that make investments, either dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feedback Loops
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled carefully when applied to feedback systems: History Self-regulating mechanisms have existed since antiquity, and the idea of feedback started to enter economic theory in Britain by the 18th century, but it was not at that time recognized as a universal abstraction and so did not have a name. The first ever known artificial feedback device was a float valve, for maintaining water at a constant level, invented in 270 BC in Alexandria, Egypt. This device illustrated the principle of feedback: a low water level opens the valve, the rising water then provides feedback into the system, closing the valve when the required level is reached. This then reoccurs in a circular fashion as the water level fluctuates. Centrifugal governors were used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority
The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) is a private American corporation that acts as a self-regulatory organization (SRO) that regulates member brokerage firms and exchange markets. FINRA is the successor to the National Association of Securities Dealers, Inc. (NASD) as well as to the member regulation, enforcement, and arbitration operations of the New York Stock Exchange. The U.S. government agency that acts as the ultimate regulator of the U.S. securities industry, including FINRA, is the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Overview The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority is the largest independent regulator for all securities firms doing business in the United States. FINRA's mission is to protect investors by making sure the United States securities industry operates fairly and honestly. As of October 2023, FINRA oversaw 3,394 brokerage firms, 149,887 branch offices and approximately 612,457 registered securities representatives. FINRA ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |