|
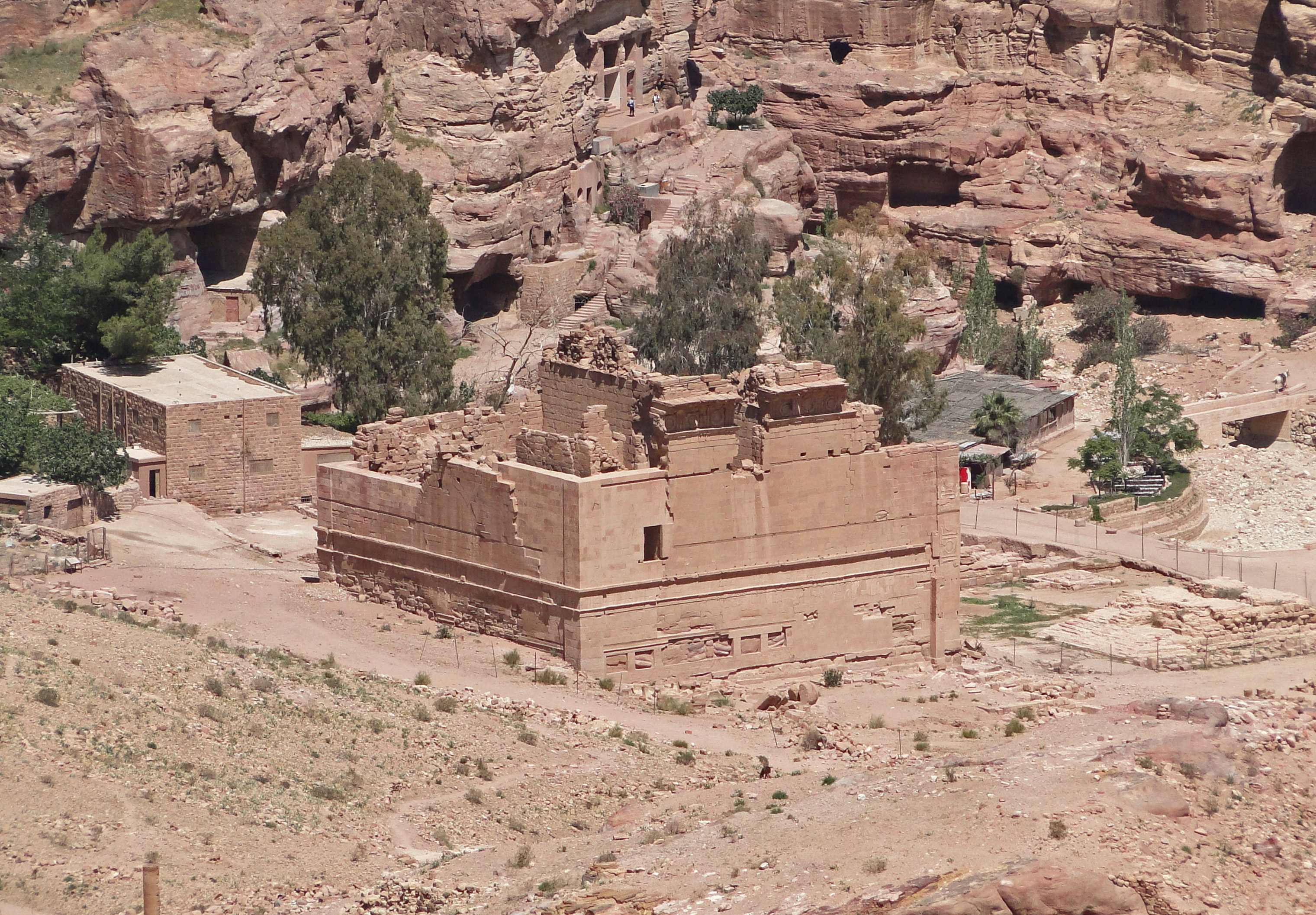
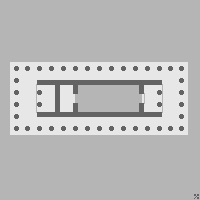
Qasr Al-Bint
The Qasr al-Bint is a religious temple in the Nabataean city of Petra. It faces the Wadi Musa and is located to the northwest of the Great Temple and the southwest of the Temple of the Winged Lions. One of the best preserved ancient structures surviving in Petra today, it stands near the monumental gate and was a key focal point on the colonnaded street, as well as a focus of religious worship. Name The full modern Arabic name of the ruin is Qasr al-Bint Fir'aun, or "the palace of Pharaoh's daughter". This name derives from a local folktale according to which the virtuous daughter of a wicked Pharaoh determined to decide between her suitors by setting them the task of providing a water supply for her palace. Two suitors completed the task simultaneously by directing water to the palace from different springs in the hills surrounding it. The princess accepted the more modest of the two suitors who ascribed his success to God. Associated deity The deity to whom the Qasr al Bint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qasr Al-Bint 03
Qasr (, plural ''qusur''), is a term derived from Latin ''castrum''. It often occurs in toponyms. Qasr, Qusur/Qusour can refer to: ''Qasr''-type structures * Desert castles: List of sites, includes several whose modern name does not contain the word qasr Individual ''qusur'' and places named after such * * * ('small qasr') * ('qasrs') * * * Particular types of ''qusur'' *Alcázar, also ''Alcácer'' or ''Alcàsser'': cognate Spanish term used in Iberia and former colonies. *Alcazar (other) *Desert castles, category of Umayyad ''qusur'', whose names usually have the form ''Qasr XY'' *Ksar, North African form of ''qasr'' ** See also * Glossary of Arabic toponyms: Qasr. Contains similar information to this page. *Kasbah A kasbah (, also ; , , Maghrebi Arabic: ), also spelled qasbah, qasba, qasaba, or casbah, is a fortress, most commonly the citadel or fortified quarter of a city. It is also equivalent to the term in Spanish (), which is derived from the same .../al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashlar
Ashlar () is a cut and dressed rock (geology), stone, worked using a chisel to achieve a specific form, typically rectangular in shape. The term can also refer to a structure built from such stones. Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, and is generally rectangular (cuboid). It was described by Vitruvius as ''opus isodomum'' or trapezoidal. Precisely cut "on all faces adjacent to those of other stones", ashlar is capable of requiring only very thin joints between blocks, and the visible face of the stone may be Quarry-faced stone, quarry-faced or feature a variety of treatments: tooled, smoothly polished or rendered with another material for decorative effect. One such decorative treatment consists of small grooves achieved by the application of a metal comb. Generally used only on softer stone ashlar, this decoration is known as "mason's drag". Ashlar is in contrast to rubble masonry, which employs irregularly shaped stones, sometimes minimally worked or selected for simi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manar Al-Athar
Manar al-Athar is a photo archive based at the Faculty of Classics at the University of Oxford which aims to provide high-quality open-access images of archaeological sites and buildings. The archive's collection focuses on areas of the Roman Empire which later came under Islamic rule, namely the Levant, North Africa, Turkey, Georgia and Armenia. As of June 2022, the archive holds more than 83,000 unique images. Particular strengths include Late antiquity, as well as the transition from paganism to Christianity and later to Islam. The archive licenses its images under a Creative Commons CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 license; the images can be used for any non-commercial purpose, including in academic publications, and are jointly labelled in English and Arabic to encourage usage by academics and students around the world. History Manar al-Athar was founded in 2012 by Judith McKenzie, archaeologist and Associate Professor of Late Antique Egypt and the Holy Land at the University of Oxf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Khazneh
Al-Khazneh (; , "The Treasury"), also known as Khazneh el-Far'oun (treasury of the pharaoh), is one of the most elaborate rock-cut tombs in Petra, a city of the Nabatean Kingdom inhabited by the Arabs in ancient times. As with most of the other buildings in this ancient town, including the Monastery (Arabic: Ad Deir), this structure was carved out of a sandstone rock face. It is thought that Al-Khazneh was built as a mausoleum and crypt at the beginning of the 1st century AD during the reign of Aretas IV Philopatris. It is one of the most popular tourist attractions in both Jordan and the region. Name Al-Khazneh means "The Treasury" in Arabic, a name derived from legends regarding the decorative stone urn high on the second level, which in reality is solid sandstone. It came to be called "Al-Khazneh" in the early 19th century by the area's Bedouins as they had believed it contained treasures. One legend is that the Ancient Egypt, Egyptian Pharaoh and some of his armies escaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminus Post Quem
A ''terminus post quem'' ('limit after which', sometimes abbreviated TPQ) and ''terminus ante quem'' ('limit before which', abbreviated TAQ) specify the known limits of dating for events or items.. A ''terminus post quem'' is the earliest date the event may have happened or the item was in existence, and a ''terminus ante quem'' is the latest. An event may well have both a ''terminus post quem'' and a ''terminus ante quem'', in which case the limits of the possible range of dates are known at both ends, but many events have just one or the other. Similarly, a ''terminus ad quem'' 'limit to which' is the latest possible date of a non-punctual event (period, era, etc.), whereas a ''terminus a quo'' 'limit from which' is the earliest. The concepts are similar to those of upper and lower bounds in mathematics. These terms are often used in archaeological and historical studies, such as dating layers in excavated sites, coins, historical events, authors, inscriptions or texts where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedrus Libani
''Cedrus libani'', commonly known as cedar of Lebanon, Lebanon cedar, or Lebanese cedar (), is a species of large evergreen conifer in the genus ''Cedrus'', which belongs to the Pinaceae, pine family and is native species, native to the mountains of the Eastern Mediterranean basin. Known for its longevity, height, and durable wood, it has held profound significance for millennia. The tree features in ancient Akkadian literature, Mesopotamian and Israelites, Israelite literature, notably in the in the Hebrew Bible, according which the tree was used in the construction of the Solomon's Temple, Jerusalem Temple by Solomon, who received the trees from Hiram I, Hiram of Tyre. Today, it is the national emblem of Lebanon and is widely used as an ornamental tree in parks and gardens. Description ''Cedrus libani'' can reach in height, with a massive monopodial columnar Trunk (botany), trunk up to in diameter.Farjon 2010, p. 258 The trunks of old, open-grown trees often Tree fork, fork ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Order
The Corinthian order (, ''Korinthiakós rythmós''; ) is the last developed and most ornate of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order, which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects, other than the capitals of the columns, though this changed in Roman architecture. A Corinthian capital may be seen as an enriched development of the Ionic capital, though one may have to look closely at a Corinthian capital to see the Ionic volutes ("helices"), at the corners, perhaps reduced in size and importance, scrolling out above the two ranks of Acanthus (ornament), stylized acanthus leaves and stalks ("cauliculi" or ''caulicoles''), eight in all, and to notice that smaller volutes scroll inwards to meet each other on each side. The leaves may be quite stiff, schematic and dry, or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cella
In Classical architecture, a or naos () is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek or Roman temple. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings: of a hermit's or monk's cell, and (since the 17th century) of a biological cell in plants or animals. Greek and Roman temples In ancient Greek and Roman temples, the ''cella'' was a room at the center of the building, usually containing a cult image or statue representing the particular deity venerated in the temple. In addition, the ''cella'' might contain a table to receive supplementary votive offerings, such as votive statues of associated deities, precious and semi-precious stones, helmets, spear and arrow heads, swords, and war trophies. No gatherings or sacrifices took place in the ''cella'', as the altar for sacrifices was always located outside the building along the axis and temporary altars for other deities were built next to it. The accumulated offerings made Greek and Roman temples virtual treasuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adyton
In Classical architecture, the ''adyton'' ( , 'innermost sanctuary, shrine', ) or (Latin) was a restricted area within the ''cella'' of a Greek temple, Greek or Roman temple. The ''adyton'' was frequently a small area at the farthest end of the cella from the entrance; at Delphi it measured just . The ''adyton'' often would house the cult image of the deity. ''Adyta'' were spaces reserved for oracles, priestesses, priests, or acolytes, and not for the general public. ''Adyta'' were found frequently associated with temples of Apollo, as at Didyma, Bassae, Clarus, Delos, and Delphi, although they were also said to have been natural phenomena (see the story of Nyx (mythology), Nyx). Those sites often had been dedicated to deities whose worship preceded that of Apollo and may go back to prehistoric eras, such as Delphi, but who were supplanted by the time of Classical Greek culture. In modern scholarship, the term may denote the innermost sacred space of a temple in the Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar Kokhba Revolt
The Bar Kokhba revolt (132–136 AD) was a major uprising by the Jews of Judaea (Roman province), Judaea against the Roman Empire, marking the final and most devastating of the Jewish–Roman wars. Led by Simon bar Kokhba, the rebels succeeded in establishing an independent Jewish state that lasted for several years. The revolt was ultimately crushed by the Romans, resulting in the near-depopulation of Judea through large-scale killings, mass enslavement, and the displacement of many Jews from the region. Resentment toward Roman rule in Judaea and nationalistic aspirations remained high following the destruction of Jerusalem during the First Jewish–Roman War, First Jewish Revolt in 70 AD. The immediate triggers of the Bar Kokhba revolt included Emperor Hadrian's decision to build ''Aelia Capitolina''—a Colonia (Roman), Roman colony dedicated to Jupiter (god), Jupiter—on the ruins of Jerusalem, extinguishing hopes for the Temple's reconstruction, as well as a possible ban o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataeans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ) were an ancient Arabs, Arab people who inhabited northern Arabian Peninsula, Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' () to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BC, with Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by contemporary Greco-Roman accounts, the Nabataeans were annexed into the Roman Empire by Emperor Trajan in 106 AD. Nabataeans' individual culture, easily identified by their characteristic finely potted painted ceramics, was adopted into the larger Greco-Roman culture. They converted to Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babatha
Babatha bat Shimʿon, also known as Babata (; – after 132) was a Jewish woman who lived in the town of Maḥoza at the southeastern tip of the Dead Sea in what is now Jordan at the beginning of the 2nd century. In 1960, archaeologist Yigael Yadin discovered a leather pouch containing her documents in what came to be known as the Cave of Letters, near the Dead Sea. The documents found include such legal contracts concerning marriage ( ketuba), property transfers, and guardianship. These documents, ranging from 96 to 134, depict a vivid picture of life for an upper-middle class Jewish woman during that time. They also provide an example of the Roman bureaucracy and legal system under which she lived. Life Babatha was born in approximately 104 CE, probably in Mahoza. The town was part of the Nabataean Kingdom until 106, when the kingdom was conquered by the Roman Empire and turned into the province of Arabia Petraea. Maḥoza was predominantly Nabatean but had a sizable Jewi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |