|
Q10 (temperature Coefficient)
The ''Q''10 temperature coefficient is a measure of temperature sensitivity based on the chemical reactions. The ''Q''10 is calculated as: : Q_=\left( \frac \right )^ where; : ''R'' is the rate : ''T'' is the temperature in Celsius degrees or kelvin. : Rewriting this equation, the assumption behind ''Q''10 is that the reaction rate ''R'' depends exponentially on temperature: : R_2 = R_1 ~Q_^ ''Q''10 is a unitless quantity, as it is the factor by which a rate changes, and is a useful way to express the temperature dependence of a process. For most biological systems, the ''Q''10 value is ~ 2 to 3. In muscle performance The temperature of a muscle has a significant effect on the velocity and power of the muscle contraction, with performance generally declining with decreasing temperatures and increasing with rising temperatures. The ''Q''10 coefficient represents the degree of temperature dependence a muscle exhibits as measured by contraction rates. A ''Q''10 of 1.0 indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q10TemperatureCoefficientPlot
Q1 or Q-1 may refer to: Transport Air * Radioplane Q-1, an American experimental unmanned aircraft of the 1950s * The primary United States Air Force designation for a series of unmanned aerial vehicles built by General Atomics, which includes the MQ-1 Predator and the MQ-1C Warrior Road * Q1 (New York City bus) * Rossion Q1, a sports car from US car maker 1g Racing/Rossion Automotive Rail * LNER Thompson Class Q1, a class of steam locomotives of the London and North Eastern Railway, UK * PRR Q1, a steam locomotive of the Pennsylvania Railroad, USA * SECR Q1 class, a steam locomotive of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway, UK * SR Q1 class, a steam locomotive of the Southern Railway, UK Science and technology * First quartile in descriptive statistics * DIGITAL Q1, a digital camera model (Fujifilm) * Samsung Q1, an Ultra Mobile Personal Computer (UMPC) * Q1 microcomputer, an early offering in the history of personal computers * The Universe, which has Wikidat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celsius
The degree Celsius is the unit of temperature on the Celsius temperature scale "Celsius temperature scale, also called centigrade temperature scale, scale based on 0 ° for the melting point of water and 100 ° for the boiling point of water at 1 atm pressure." (originally known as the centigrade scale outside Sweden), one of two temperature scales used in the International System of Units (SI), the other being the closely related Kelvin scale. The degree Celsius (symbol: °C) can refer to a specific point on the Celsius temperature scale or to a difference or range between two temperatures. It is named after the Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius (1701–1744), who proposed the first version of it in 1742. The unit was called ''centigrade'' in several languages (from the Latin ''centum'', which means 100, and ''gradus'', which means steps) for many years. In 1948, the International Committee for Weights and Measures renamed it to honor Celsius and also to rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By definition, the Celsius scale (symbol °C) and the Kelvin scale have the exact same magnitude; that is, a rise of 1 K is equal to a rise of 1 °C and vice versa, and any temperature in degrees Celsius can be converted to kelvin by adding 273.15. The 19th century British scientist Lord Kelvin first developed and proposed the scale. It was often called the "absolute Celsius" scale in the early 20th century. The kelvin was formally added to the International System of Units in 1954, defining 273.16 K to be the triple point of water. The Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Rankine scales were redefined in terms of the Kelvin scale using this definition. The 2019 revision of the SI now defines the kelvin in terms of energy by setting the Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q10 Graphs
Q1 or Q-1 may refer to: Transport Air * Radioplane Q-1, an American experimental unmanned aircraft of the 1950s * The primary United States Air Force designation for a series of unmanned aerial vehicles built by General Atomics, which includes the MQ-1 Predator and the MQ-1C Warrior Road * Q1 (New York City bus) * Rossion Q1, a sports car from US car maker 1g Racing/Rossion Automotive Rail * LNER Thompson Class Q1, a class of steam locomotives of the London and North Eastern Railway, UK * PRR Q1, a steam locomotive of the Pennsylvania Railroad, USA * SECR Q1 class, a steam locomotive of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway, UK * SR Q1 class, a steam locomotive of the Southern Railway, UK Science and technology * First quartile in descriptive statistics * DIGITAL Q1, a digital camera model (Fujifilm) * Samsung Q1, an Ultra Mobile Personal Computer (UMPC) * Q1 microcomputer, an early offering in the History of personal computers#Q1, history of personal computers * The Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF, AFib or A-fib) is an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) characterized by fibrillation, rapid and irregular beating of the Atrium (heart), atrial chambers of the heart. It often begins as short periods of abnormal cardiac cycle, beating, which become longer or continuous over time. It may also start as other forms of arrhythmia such as atrial flutter that then transform into AF. Episodes can be asymptomatic. Symptomatic episodes may involve heart palpitations, syncope (medicine), fainting, Presyncope, lightheadedness, Unconsciousness, loss of consciousness, or shortness of breath. Atrial fibrillation is associated with an increased risk of heart failure, dementia, and stroke. It is a type of supraventricular tachycardia. Atrial fibrillation frequently results from bursts of tachycardia that originate in muscle bundles extending from the Atrium (heart), atrium to the pulmonary veins. Pulmonary vein isolation by catheter ablation, trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhenius Equation
In physical chemistry, the Arrhenius equation is a formula for the temperature dependence of reaction rates. The equation was proposed by Svante Arrhenius in 1889, based on the work of Dutch chemist Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff who had noted in 1884 that the Van 't Hoff equation for the temperature dependence of equilibrium constants suggests such a formula for the rates of both forward and reverse reactions. This equation has a vast and important application in determining the rate of chemical reactions and for calculation of Activation energy, energy of activation. Arrhenius provided a physical justification and interpretation for the formula.Keith J. Laidler, Laidler, K. J. (1987) ''Chemical Kinetics'', Third Edition, Harper & Row, p. 42 Currently, it is best seen as an empirical relationship.Kenneth Connors, Chemical Kinetics, 1990, VCH Publishers It can be used to model the temperature variation of Mass diffusivity, diffusion coefficients, population of Vacancy defect, crystal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrhenius Plot
In chemical kinetics, an Arrhenius plot displays the logarithm of a reaction rate constant, ordinate axis) plotted against reciprocal of the temperature abscissa). Arrhenius plots are often used to analyze the effect of temperature on the rates of chemical reactions. For a single rate-limited thermally activated process, an Arrhenius plot gives a straight line, from which the activation energy and the pre-exponential factor can both be determined. The Arrhenius equation can be given in the form: k = A \exp\left(\frac\right) = A \exp\left(\frac\right) where: * k = rate constant * A = pre-exponential factor * E_\text = (molar) activation energy * R = gas constant, (R=k_\text N_\text, where N_\text is the Avogadro constant). * E_\text' = activation energy (for a single reaction event) * k_\text = Boltzmann constant * T = absolute temperature The only difference between the two forms of the expression is the quantity used for the activation energy: the former would have the unit j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotonic (exercise Physiology)
In an isotonic contraction, tension remains the same, whilst the muscle's length changes. Isotonic contractions differ from isokinetic contractions in that in isokinetic contractions the muscle speed remains constant. While superficially identical, as the muscle's force changes via the length-tension relationship during a contraction, an isotonic contraction will keep force constant while velocity changes, but an isokinetic contraction will keep velocity constant while force changes. A near isotonic contraction is known as Auxotonic contraction. There are two types of isotonic contractions: (1) concentric and (2) eccentric. In a concentric contraction, the muscle tension rises to meet the resistance, then remains the same as the muscle shortens. In eccentric, the muscle lengthens due to the resistance being greater than the force the muscle is producing. Concentric This type is typical of most exercise. The external force on the muscle is less than the force the muscle is gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isometric Exercise
An isometric exercise is an exercise involving the static contraction of a muscle without any visible movement in the angle of the joint. The term "isometric" combines the Greek words ''isos'' (equal) and ''-metria'' (measuring), meaning that in these exercises the length of the muscle and the angle of the joint do not change, though contraction strength may be varied. This is in contrast to ''isotonic contractions'', in which the contraction strength does not change, though the muscle length and joint angle do. The three main types of isometric exercise are isometric presses, pulls, and holds. They may be included in a strength training regime in order to improve the body's ability to apply power from a static position or, in the case of isometric holds, improve the body's ability to maintain a position for a period of time. Considered as an action, isometric presses are also of fundamental importance to the body's ability to prepare itself to perform immediately subsequent pow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
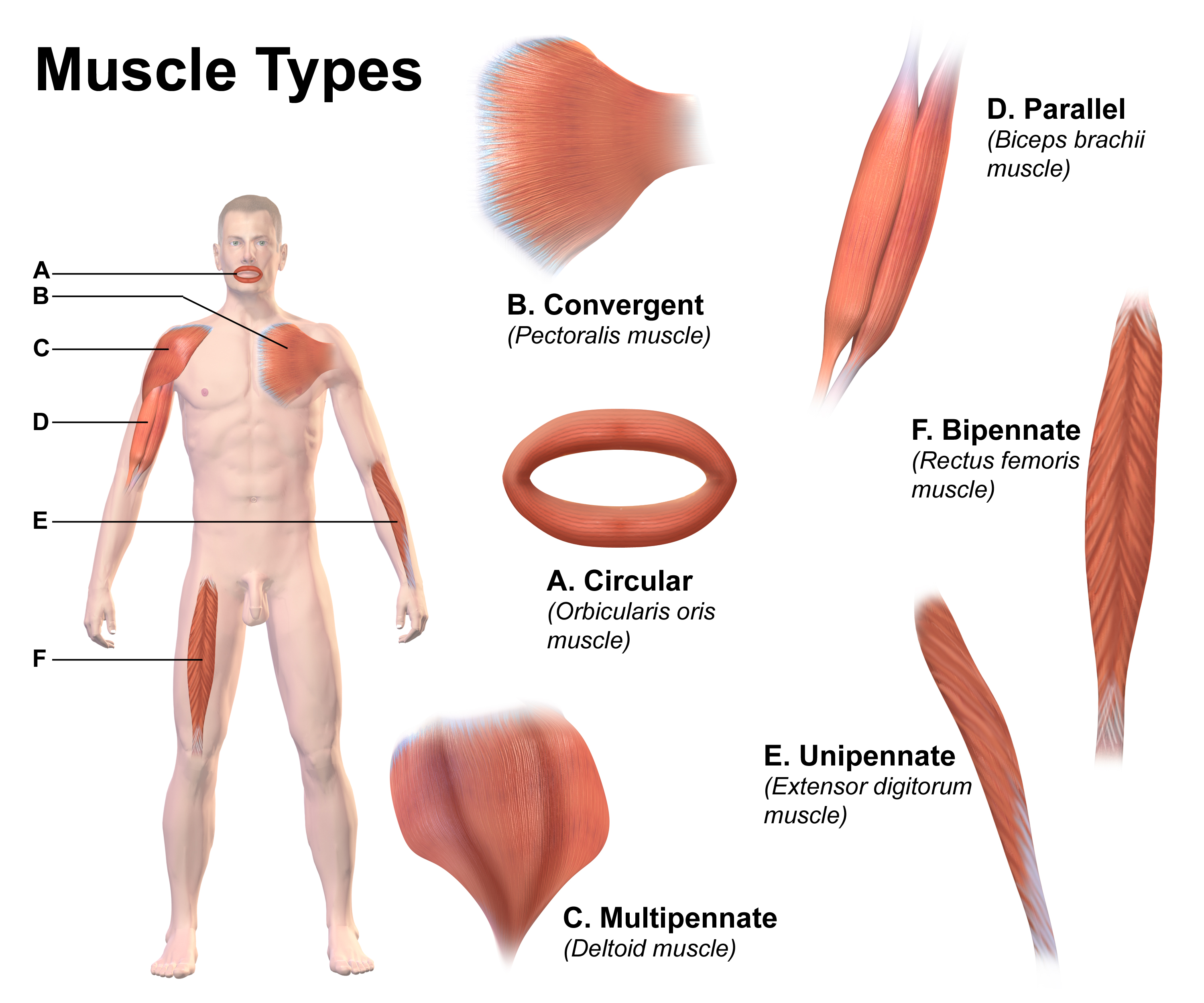
Skeletal Striated Muscle
Skeletal muscle (commonly referred to as muscle) is one of the three types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. They are part of the somatic nervous system, voluntary muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The skeletal muscle cells are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are also known as ''muscle fibers''. The tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated muscle tissue, striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. A skeletal muscle contains multiple muscle fascicle, fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the cell fusion, fusion of developmental myoblasts in a process known as myogenesis resulting in long multinucleated cells. In these cells, the cell nucleus, nuclei, termed ''myonuclei'', are located along the inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetanic Contraction
A tetanic contraction (also called tetanized state, tetanus, or physiologic tetanus, the latter to differentiate from the disease called tetanus) is a sustained muscle contraction evoked when the motor nerve that innervates a skeletal muscle emits action potentials at a very high rate. During this state, a motor unit has been maximally stimulated by its motor neuron and remains that way for some time. This occurs when a muscle's motor unit is stimulated by multiple impulses at a sufficiently high frequency. Each stimulus causes a twitch. If stimuli are delivered slowly enough, the tension in the muscle will relax between successive twitches. If stimuli are delivered at high frequency, the twitches will overlap, resulting in tetanic contraction. A tetanic contraction can be either ''unfused (incomplete) or fused (complete)''. An unfused tetanus is when the muscle fibers do not completely relax before the next stimulus because they are being stimulated at a fast rate; however there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Metrics
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance (ecology), abundance, biomass (ecology), biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; ecological succession, successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |