|
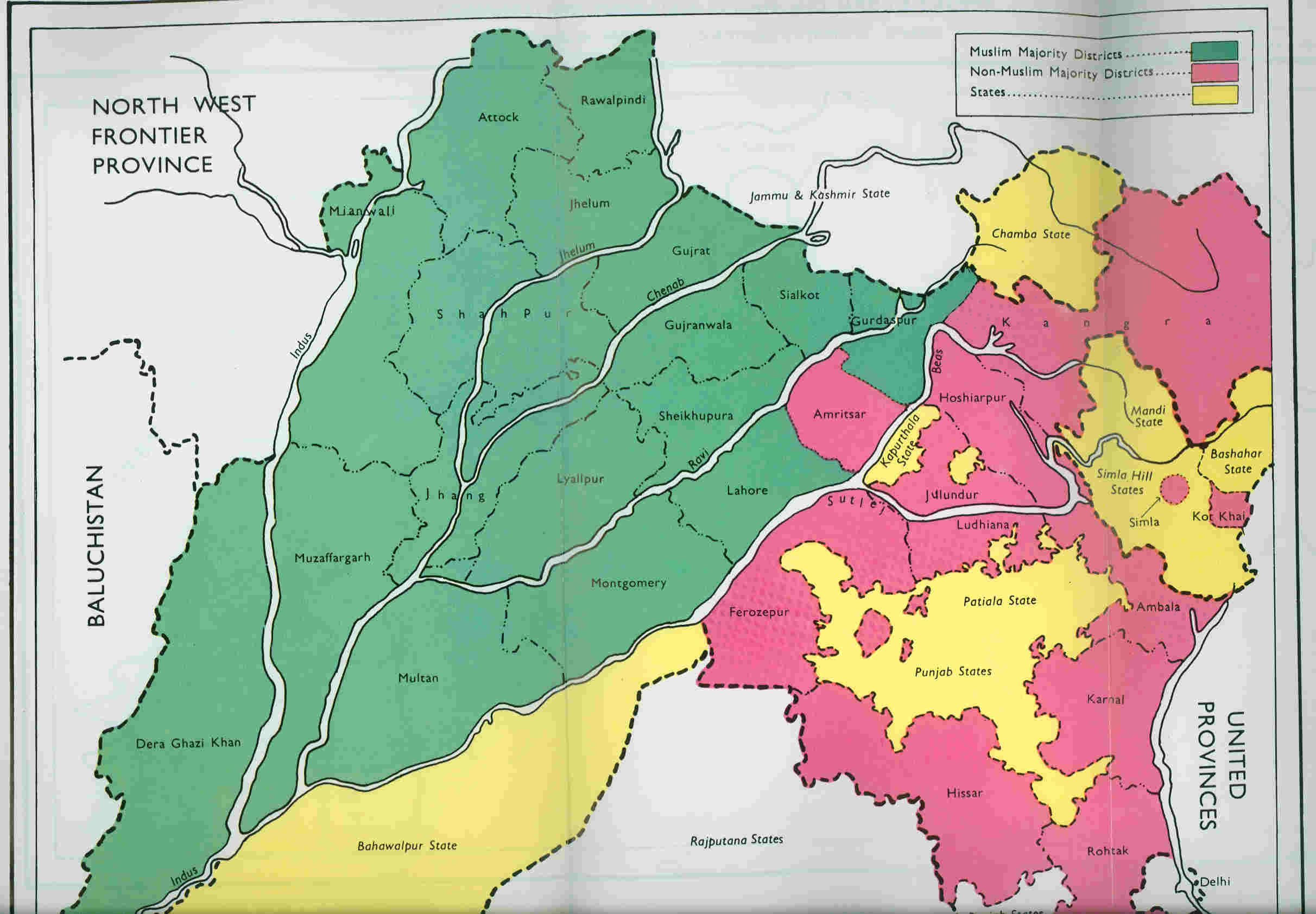
Punjab (British India)
The Punjab Province, officially the Province of the Punjab, was a province of British India, with its capital in Lahore and summer capitals in Murree and Simla. At its greatest extent, it stretched from the Khyber Pass to Delhi; and from the Babusar Pass and the borders of Tibet to the borders of Sind. Established in 1849 following Punjab's annexation, the province was partitioned in 1947 into West and East Punjab; and incorporated into Pakistan and India, respectively. Most of the Punjab region was annexed by the East India Company on 29 March 1849 following the company's victory at the battle of Gujrat in northern Punjab, a month prior. The Punjab was the last major region of the Indian subcontinent to fall to British imperialism. Immediately following its annexation, the Punjab was annexed into the Bengal Presidency and administered separately by a board of administration led by the head of province. After 1853, the board was replaced by a chief commissioner a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidencies And Provinces Of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods: *Between 1612 and 1757, the East India Company set up Factory (trading post), "factories" (trading posts) in several locations, mostly in coastal India, with the consent of the Mughal Empire, Mughal emperors, Maratha Empire or local rulers. Its rivals were the merchant trading companies of Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, and France. By the mid-18th century three ''Presidency towns'': Madras, Bombay and Calcutta, had grown in size. *During the period of Company rule in India, 1757–1858, the Company gradually acquired sovereignty over large parts of India, now called "Presidencies". However, it also increasingly came under British government ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India, Eighth Schedule language, the status and cultural heritage of which are recognised by the Constitution of India. Quote: "The Eighth Schedule recognizes India's national languages as including the major regional languages as well as others, such as Sanskrit and Urdu, which contribute to India's cultural heritage. ... The original list of fourteen languages in the Eighth Schedule at the time of the adoption of the Constitution in 1949 has now grown to twenty-two." Quote: "As Mahapatra says: "It is generally believed that the significance for the Eighth Schedule lies in providing a list of languages from which Hindi is directed to draw the appropriate forms, style and expressions for its enrichment" ... Being recognized in the Constitution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Company Rule
Company rule in India (also known as the Company Raj, from Hindi , ) refers to regions of the Indian subcontinent under the control of the British East India Company (EIC). The EIC, founded in 1600, established its first trading post in India in 1612, and gradually expanded its presence in the region over the following decades. During the Seven Years' War, the East India Company began a process of rapid expansion in India, which resulted in most of the subcontinent falling under its rule by 1857, when the Indian Rebellion of 1857 broke out. After the rebellion was suppressed, the Government of India Act 1858 resulted in the EIC's territories in India being administered by the Crown instead. The India Office managed the EIC's former territories, which became known as the British Raj. The range of dates is taken to have commenced either in 1757 after the Battle of Plassey, when the Nawab of Bengal Siraj ud-Daulah was defeated and replaced with Mir Jafar, who had the support o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of India
The partition of India in 1947 was the division of British India into two independent dominion states, the Dominion of India, Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan. The Union of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan is the Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The Partition (politics), partition involved the division of two provinces, Bengal and the Punjab Province (British India), Punjab, based on district-wise Hindu or Muslim majorities. It also involved the division of the British Indian Army, the Royal Indian Navy, the Indian Civil Service, the History of rail transport in India, railways, and the central treasury, between the two new dominions. The partition was set forth in the Indian Independence Act 1947 and resulted in the dissolution of the British Raj, or Crown rule in India. The two self-governing countries of India and Pakistan legally came into existence at midnight on 14–15 August 1947. The partiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
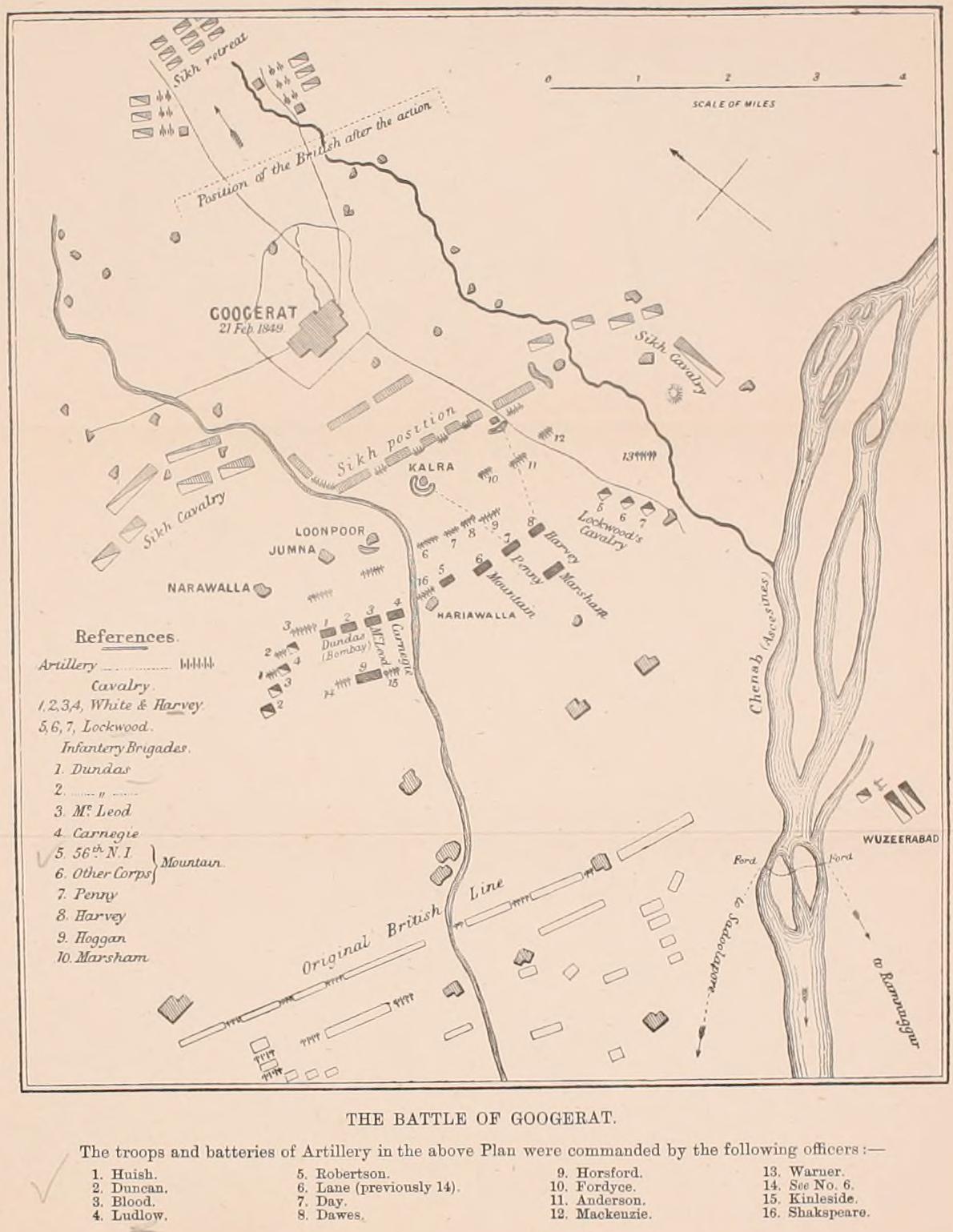
Battle Of Gujrat
The Battle of Gujrat was a decisive battle in the Second Anglo-Sikh War, fought on 21 February 1849, between the forces of the East India Company, and a Sikh army in rebellion against the company's control of the Sikh Empire, represented by the child Maharaja Duleep Singh who was in British custody in Lahore. The Sikh army was defeated by the British regular and Bengal Army forces of the British East India Company. After it capitulated a few days later, the Punjab was annexed to the East India Company's territories and Duleep Singh was deposed. Outbreak and course of the war After the British victory in the First Anglo-Sikh War, the Punjab was indirectly governed by a British representative at the Durbar (court) in Lahore and Agents in several of the regions. The Sikh Army, the Khalsa, was kept in being and used to keep order in the Punjab and North West Frontier Region. The Khalsa regarded itself as betrayed rather than defeated in the first war, and several of its Sarda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjab Provincial Assembly (British India)
The Punjab Provincial Assembly was the legislature of the province of Punjab (British India), Punjab in British India. Established by British authorities under Government of India Act 1935, the assembly had executive powers and members directly elected from 175 constituencies by first past the post system. Speakers Deputy Speakers Prime minister Seats Distribution All 175 constituencies were reserved on the bases of religion. It was as follows:- ^Special constituencies (non-territory constituency) were further divided into Categories and sub-categories as follow:- * Women - 4 **General - 1 **Mohammadans - 2 **Sikhs - 1 * European - 1 * Anglo-Indian - 1 * Indian Christian - 2 * Punjab Commerce and Industry - 1 * Landholders - 5 **General - 1 **Mohammadans - 3 **Sikhs - 1 * Trade and Labour Unions - 3 * University - 1 First Assembly After the passing of Government of India act 1935, Provincial assembly was set up in Punjab. It consisted 175 constituencies. Out of these 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjab Legislative Council (British India)
The Punjab Legislative Council was the Unicameralism, unicameral legislature of Punjab (British India), British Punjab, a province of the British Raj. It was established in 1921 by the British authorities under Government of India Act 1919, the council had nominal powers and a membership of mainly pro-British politicians and government officials. Voting was largely boycotted until the Government of India Act 1935 increased representation and the powers of the assembly. It was dissolved in 1936 and was succeeded by Punjab Provincial Assembly (British India), Punjab Provincial Assembly. The First World War gave the momentum to the growing demand for self-government in British India. Therefore, the new constitutional reforms, under the Montagu–Chelmsford Reforms were introduced by British Government. The scheme was implemented through the Government of India Act 1919. The first Council was constituted on 8 January 1921 for the first time. The election for first Council was held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malik Khizar Hayat Tiwana
Sir Malik Khizar Hayat Tiwana (7 August 1900 – 20 January 1975) was a British Indian statesman, landowner, army officer, and politician belonging to the Punjab Unionist Party. He served as the prime minister of the Punjab Province of British India between 1942 and 1947. He opposed the Partition of India and the ideology of Muslim League. The Muslim League plotted to oust Tiwana from office and after this, Punjab was plunged into communal violence supported by the Muslim League. Early life Khizar Hayat Tiwana was born at Chak Muzaffarabad, in the Shahpur District of the Punjab Province during British Raj in 1900. He was born into the feudal Tiwana family of Shahpur. He was owner of 1,800 Murabba (45,000 acres) of agriculture land. His father Sir Umar Hayat Khan was also a wealthy landowner and soldier who was an elected member of the Council of the Secretary of State for India. Sir Umar Hayat was a close friend to King George V. He was educated at Aitchison College in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikandar Hayat Khan
'' Khan Bahadur'' Major Sir Sikandar Hayat Khan, (5 June 1892 – 26 December 1942), also written Sikandar Hyat-Khan or Sikandar Hyat Khan, was an Indian politician and statesman from the Punjab who served as the Premier of the Punjab, among other positions. Early life Sikandar Hayat Khan was born in Multan, Punjab, British Raj in a Punjabi family of the Khattar tribe . His father was Nawab Muhammad Hayat Khan, a civil servant and close associate of Sir Syed Ahmed Khan, and his grandfather was Sardar Karam Khan, who died in battle fighting for the British against the Sikhs in the Second Anglo-Sikh War. He was educated at Oriental Collegiate High School in Aligarh and later at Aligarh Muslim University, and was sent to study medicine at King's College London in the United Kingdom but was recalled home by his family circa 1915. During the First World War, he initially worked as a War Recruitment Officer in his native Attock District and later served as one of the first Indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premier Of The Punjab
The Premier of the Punjab was the head of government and the Leader of the House in the Legislative Assembly of Punjab Province in British India. The position was dissolved upon the Partition of India in 1947. History The office was created under the Government of India Act 1935. The Unionist Party was the principal legislative force in the province. It received support from legislators of the Punjab Muslim League, the Indian National Congress and the Sikh Akali Dal at various periods. The Unionist government implemented agrarian reforms in Punjab by using legal and administrative measures to relieve farmers and peasants of crippling debt. Similar steps were taken by the Prime Minister of Bengal. The Unionists opposed the Quit India movement and supported the Allies during World War II. The Unionists were constitutionalists who favored cooperation with the British to achieve independence from the Raj. The Unionists signed the Lucknow Pact with the All India Muslim League (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evan Meredith Jenkins
Sir Evan Meredith Jenkins (2 February 1896 – 19 November 1985) was a British colonial administrator and the last governor of the Punjab Province (British India), Punjab Province of British India. Life He was a son of John Lewis Jenkins, Sir John Lewis Jenkins and his wife Florence Mildred, second daughter of Sir Arthur Trevor, and a brother of David Jenkins, Baron Jenkins. He was educated at Rugby School and Balliol College, Oxford. He joined the Indian Civil Service in 1920 and held various posts in the Punjab commission and Central Secretariat. In 1937 he was appointed List of Chief Commissioners of Delhi, Chief Commissioner of Delhi and in 1943 he was made secretary to the List of governors-general of India, Viceroy and Governor-General of India. He served as the last List of governors of Punjab (British India), Governor of the Punjab in British India from 8 April 1946 to August 1947. Due to boycotts engulfing the Punjab, on 2 March 1947 Malik Khizar Hayat Tiwana resigne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Montgomery Lawrence
Brigadier-General Sir Henry Montgomery Lawrence (28 June 1806 – 4 July 1857) was a British military officer, surveyor, administrator and statesman in British India. He is best known for leading a group of administrators in the Punjab affectionately known as Henry Lawrence's "Young Men", as the founder of the Lawrence Military Asylums and for his death at the Siege of Lucknow during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. Background Lawrence was born in June 1806 into an Ulster-Scots family at Matara in Ceylon. Both his parents were from Ulster, the northern province of Ireland. His mother Letitia was the daughter of the Rev. George Knox from County Donegal, while his father, Lieutenant-Colonel Alexander William Lawrence, was born the son of a mill owner from Coleraine, County Londonderry, entered the service of the British Army and achieved distinction at the 1799 Siege of Seringapatnam.James Wills, The Irish Nation: Its History and Its Biography, Volume 4, A. Fullarton, 1876, p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |