|
Pressure Of Speech
Pressure of speech or pressured speech is a tendency to speak rapidly and frenziedly. Pressured speech is motivated by an urgency that may not be apparent to the listener. The speech produced is difficult to interpret. Such speech may be too fast, erratic, irrelevant, or too tangential for the listener to understand. It is an example of cluttered speech, and is often associated with certain mental disorders, particularly mania and schizophrenia. It can be unrelenting, loud, and without pauses. Description Pressured speech is unrelenting, rapid, often loud talking without pauses. Those with pressured speech do not respond to verbal and nonverbal cues indicating that others wish to speak, turning from one listener to another or speaking even when no listeners remain. They are unable to listen to others, either talking nonstop until they run out of steam, or just standing there and looking at the other speaker before moving away. The speech can be either intelligible or unintelligib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions. See glossary of psychiatry. Initial psychiatric assessment of a person typically begins with a case history and mental status examination. Physical examinations and psychological tests may be conducted. On occasion, neuroimaging or other neurophysiological techniques are used. Mental disorders are often diagnosed in accordance with clinical concepts listed in diagnostic manuals such as the '' International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD), edited and used by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the widely used '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). The fifth edition of the DSM ( DSM-5) was published in May 2013 which re-organized the larger categories of various diseases and expanded up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachylalia
Tachylalia or tachylogia is extremely rapid speech. Tachylalia by itself is not considered a speech disorder. Tachylalia occurs in many clutterers and many people who have speech disorders. Tachylalia is a generic term for speaking fast, and does not need to coincide with other speech problems. Tachylalia may be exhibited as a single stream of rapid speech without prosody, and can be delivered quietly or mumbled. Tachylalia can be simulated by stimulating the brain electronically. Tachylalia can occur with Parkinson's disease Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms beco .... References Speech disorders {{speech-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
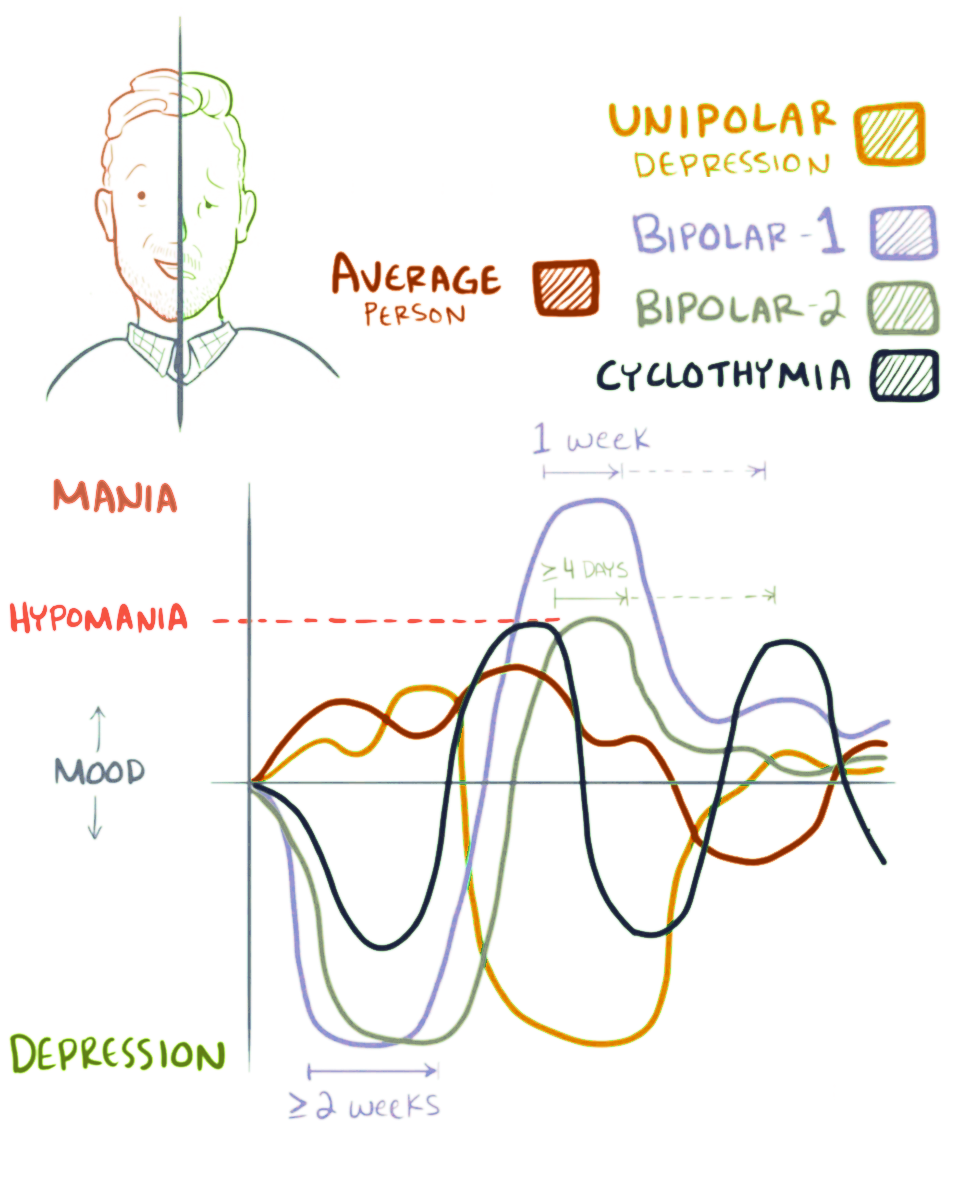
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logorrhea (psychology)
In psychology, logorrhea or logorrhoea (from Ancient Greek λόγος ''logos'' "word" and ῥέω ''rheo'' "to flow") is a communication disorder that causes excessive wordiness and repetitiveness, which can cause incoherency. Logorrhea is sometimes classified as a mental illness, though it is more commonly classified as a symptom of mental illness or brain injury. This ailment is often reported as a symptom of Wernicke's aphasia, where damage to the language processing center of the brain creates difficulty in self-centered speech. Characteristics Logorrhea is characterized by the constant need to talk. Occasionally, patients with logorrhea may produce speech with normal prosody and a slightly fast speech rate. Other related symptoms include the use of neologisms (new words without clear derivation, e.g. hipidomateous for hippopotamus), words that bear no apparent meaning, and, in some extreme cases, the creation of new words and morphosyntactic constructions. From the " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory Processing Disorder
Auditory processing disorder (APD), rarely known as King-Kopetzky syndrome or auditory disability with normal hearing (ADN), is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting the way the brain processes auditory information. Individuals with APD usually have normal structure and function of the outer, middle, and inner ear (peripheral hearing). However, they cannot process the information they hear in the same way as others do, which leads to difficulties in recognizing and interpreting sounds, especially the sounds composing speech. It is thought that these difficulties arise from dysfunction in the central nervous system. It is highly prevalent in individuals with other neurodevelopmental disorders, such as Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Autism Spectrum Disorders, Dyslexia, and Sensory Processing Disorder. The American Academy of Audiology notes that APD is diagnosed by difficulties in one or more auditory processes known to reflect the function of the central auditory ner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphasia
Aphasia is an inability to comprehend or formulate language because of damage to specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in the Global North. Aphasia can also be the result of brain tumors, brain infections, or neurodegenerative diseases (such as dementias). To be diagnosed with aphasia, a person's speech or language must be significantly impaired in one (or more) of the four aspects of communication following acquired brain injury. Alternatively, in the case of progressive aphasia, it must have significantly declined over a short period of time. The four aspects of communication are auditory comprehension, verbal expression, reading and writing, and functional communication. The difficulties of people with aphasia can range from occasional trouble finding words, to losing the ability to speak, read, or write; intelligence, however, is unaffected. Expressive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stuttering
Stuttering, also known as stammering, is a speech disorder in which the flow of speech is disrupted by involuntary repetitions and prolongations of sounds, syllables, words, or phrases as well as involuntary silent pauses or blocks in which the person who stutters is unable to produce sounds. The term ''stuttering'' is most commonly associated with involuntary sound repetition, but it also encompasses the abnormal hesitation or pausing before speech, referred to by people who stutter as ''blocks'', and the prolongation of certain sounds, usually vowels or semivowels. According to Watkins et al., stuttering is a disorder of "selection, initiation, and execution of motor sequences necessary for fluent speech production".[Carlson, N. (2013). Human Communication. In Physiology of behavior (11th ed., pp. 497–500). Boston: Allyn and Bacon.] For many people who stutter, repetition is the main concern. The term "stuttering" covers a wide range of severity, from barely perceptible impedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Disorder
A communication disorder is any disorder that affects an individual's ability to comprehend, detect, or apply language and speech to engage in dialogue effectively with others. The delays and disorders can range from simple sound substitution to the inability to understand or use one's native language. Diagnosis Disorders and tendencies included and excluded under the category of communication disorders may vary by source. For example, the definitions offered by the American Speech–Language–Hearing Association differ from those of the Diagnostic Statistical Manual 4th edition (DSM-IV). Gleanson (2001) defines a communication disorder as a speech and language disorder which refers to problems in communication and in related areas such as oral motor function. The delays and disorders can range from simple sound substitution to the inability to understand or use one's native language. In general, communication disorders commonly refer to problems in speech (comprehension and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumstantial Speech
Circumstantial speech, also referred to as circumstantiality, is the result of a so-called "non-linear thought pattern" and occurs when the focus of a conversation drifts, but often comes back to the point.''Problem-Based Psychiatry'' by Ben Green 2009 page 15 In circumstantiality, apparently unnecessary details and seemingly irrelevant remarks cause a delay in getting to the point. If someone exhibits circumstantial speech during a conversation, they will often seem to "talk the long way around" to their point, which may be an attempt by the speaker to include pertinent details, that may contrast with the speech which is more direct, succinct, and to the point (the gist) even at the expense of more precise, accurate communication. Circumstantial speech is more direct than tangential speech in which the speaker wanders and drifts and usually never returns to the original topic, and is far less severe than logorrhea. Signs and symptoms A person with circumstantiality has slowed thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |