|
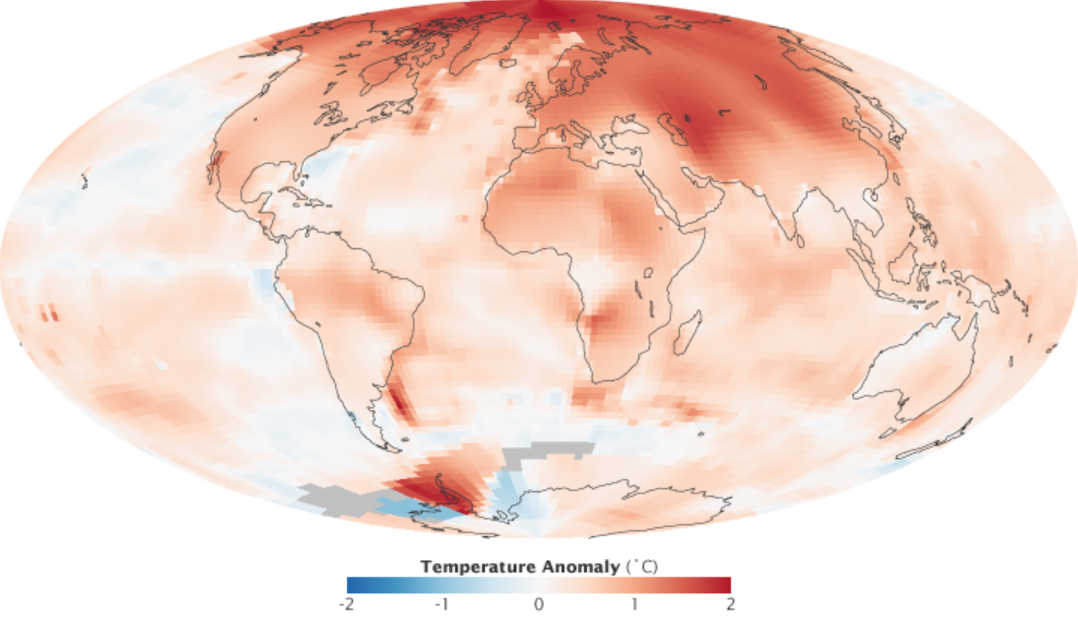
Polar Amplification
Polar amplification is the phenomenon that any change in the net radiation balance (for example greenhouse intensification) tends to produce a larger change in temperature near the poles than in the planetary average. This is commonly referred to as the ratio of polar warming to tropical warming. On a planet with an atmosphere that can restrict emission of longwave radiation to space (a greenhouse effect), surface temperatures will be warmer than a simple planetary equilibrium temperature calculation would predict. Where the atmosphere or an extensive ocean is able to transport heat polewards, the poles will be warmer and equatorial regions cooler than their local net radiation balances would predict. The poles will experience the most cooling when the global-mean temperature is lower relative to a reference climate; alternatively, the poles will experience the greatest warming when the global-mean temperature is higher. In the extreme, the planet Venus is thought to have experien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GISS Temperature 2000-09
The Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) is a laboratory in the Earth Sciences Division of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center affiliated with the Columbia University Earth Institute. The institute is located at Columbia University in New York City. It was named after Robert H. Goddard, American engineer, professor, physicist and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first liquid-fueled rocket. Research at the GISS emphasizes a broad study of global change, the natural and anthropogenic changes in our environment that affect the habitability of our planet. These effects may occur on greatly differing time scales, from one-time forcings such as volcanic explosions, to seasonal/annual effects such as El Niño, and on up to the millennia of ice ages. The institute's research combines analysis of comprehensive global datasets (derived from surface stations combined with satellite data for sea surface temperatures) with global models of atmospheri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Feedback
Climate Feedback (CF) is a web-based content annotation tool that allows qualified scientists to comment on stories online, adding context and noting inaccuracies. It is one of three websites under the Science Feedback parent organization that fact-checks media coverage. Science Feedback is a non-profit organization registered in France. The CF website asks climate scientists in relevant fields to assess the credibility and accuracy of media stories related to climate change. The website published its first review in 2015. The website was founded by Emmanuel Vincent, who has a PhD in Oceanography & Climate from Université Pierre et Marie Curie. Vincent partnered with the non-profit Hypothes.is, who created a free Internet browser plug-in that allows users to make sentence-level comments on web pages, to create an evaluation of content. Climate Feedback, an application of the Hypothes.is platform to climate science communication, allows active climate scientists to add comme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
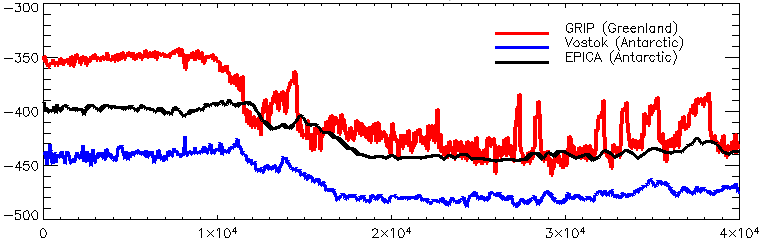
Polar See-saw
The polar see-saw (also: bipolar seesaw) is the phenomenon that temperature changes in the northern and southern hemispheres may be out of phase. The hypothesis states that large changes, for example when the glaciers are intensely growing or depleting, in the formation of ocean bottom water in both poles take a long time to exert their effect in the other hemisphere. Estimates of the period of delay vary; one typical estimate is 1,500 years. This is usually studied in the context of ice cores taken from Antarctica and Greenland. See also * Polar amplification *Climate of the Arctic *Climate of Antarctica The climate of Antarctica is the coldest on Earth. The continent is also extremely dry (it is a desert), averaging of precipitation per year. Snow rarely melts on most parts of the continent, and, after being compressed, becomes the glacier ic ... References * * * Meteorological phenomena Environment of Antarctica Climate and weather statistics {{Climate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milankovitch Cycles
Milankovitch cycles describe the collective effects of changes in the Earth's movements on its climate over thousands of years. The term was coined and named after Serbian geophysicist and astronomer Milutin Milanković. In the 1920s, he hypothesized that variations in eccentricity, axial tilt, and precession combined to result in cyclical variations in the intra-annual and latitudinal distribution of solar radiation at the Earth's surface, and that this orbital forcing strongly influenced the Earth's climatic patterns. Earth's movements The Earth's rotation around its axis, and revolution around the Sun, evolve over time due to gravitational interactions with other bodies in the Solar System. The variations are complex, but a few cycles are dominant. The Earth's orbit varies between nearly circular and mildly elliptical (its eccentricity varies). When the orbit is more elongated, there is more variation in the distance between the Earth and the Sun, and in the amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Air Temperature
Temperature measurement (also known as thermometry) describes the process of measuring a current local temperature for immediate or later evaluation. Datasets consisting of repeated standardized measurements can be used to assess temperature trends. History Attempts at standardized temperature measurement prior to the 17th century were crude at best. For instance in 170 AD, physician Claudius Galenus mixed equal portions of ice and boiling water to create a "neutral" temperature standard. The modern scientific field has its origins in the works by Florentine scientists in the 1600s including Galileo constructing devices able to measure relative change in temperature, but subject also to confounding with atmospheric pressure changes. These early devices were called thermoscopes. The first sealed thermometer was constructed in 1654 by the Grand Duke of Toscani, Ferdinand II. The development of today's thermometers and temperature scales began in the early 18th century, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature Anomaly
A temperature anomaly is the departure, positive or negative, of a temperature from a base temperature that is normally chosen as an average of temperatures over a certain reference period, often called a base period. Commonly, the average temperature is calculated over a period of at least 30 years over a homogeneous geographic region, or globally over the entire planet. Temperatures are obtained from surface and offshore weather stations or inferred from meteorological satellite data. Anomalies can be calculated based on datasets of surface and upper-air atmospheric temperatures or sea surface temperatures. Description Temperature anomalies are a measure of temperature compared to a reference temperature, which is often calculated as an average of temperatures over a reference period, often called a base period. Publication datePrecursor webpagewas archived as early as December 2013. Records of global average surface temperature are usually presented as anomalies rather than a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossby Wave
Rossby waves, also known as planetary waves, are a type of inertial wave naturally occurring in rotating fluids. They were first identified by Sweden-born American meteorologist Carl-Gustaf Arvid Rossby. They are observed in the atmospheres and oceans of planets owing to the rotation of the planet. Atmospheric Rossby waves on Earth are giant meanders in high-altitude winds that have a major influence on weather. These waves are associated with pressure systems and the jet stream (especially around the polar vortices). Oceanic Rossby waves move along the thermocline: the boundary between the warm upper layer and the cold deeper part of the ocean. Rossby wave types Atmospheric waves Atmospheric Rossby waves result from the conservation of potential vorticity and are influenced by the Coriolis force and pressure gradient. The rotation causes fluids to turn to the right as they move in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. For example, a fluid th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of sea water generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents are primarily horizontal water movements. An ocean current flows for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth’s regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temperature of the area by warming the sea breezes that blow over them. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate for its high latitude compared to other area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nutrient-rich upwelled water stimulates the growth and reproduction of primary producers such as phytoplankton. The biomass of phytoplankton and the presence of cool water in those regions allow upwelling zones to be identified by cool sea surface temperatures (SST) and high concentrations of chlorophyll-a. The increased availability of nutrients in upwelling regions results in high levels of primary production and thus fishery production. Approximately 25% of the total global marine fish catches come from five upwellings, which occupy only 5% of the total ocean area.Jennings, S., Kaiser, M.J., Reynolds, J.D. (2001) "Marine Fisheries Ecology." Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd. Upwellings that are driven by coastal currents or diverging ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Circumpolar Current
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is an ocean current that flows clockwise (as seen from the South Pole) from west to east around Antarctica. An alternative name for the ACC is the West Wind Drift. The ACC is the dominant circulation feature of the Southern Ocean and has a mean transport estimated at 100–150 Sverdrups (Sv, million m3/s), or possibly even higher, making it the largest ocean current. The current is circumpolar due to the lack of any landmass connecting with Antarctica and this keeps warm ocean waters away from Antarctica, enabling that continent to maintain its huge ice sheet. Associated with the Circumpolar Current is the Antarctic Convergence, where the cold Antarctic waters meet the warmer waters of the subantarctic, creating a zone of upwelling nutrients. These nurture high levels of phytoplankton with associated copepods and krill, and resultant foodchains supporting fish, whales, seals, penguins, albatrosses, and a wealth of other species. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |