|
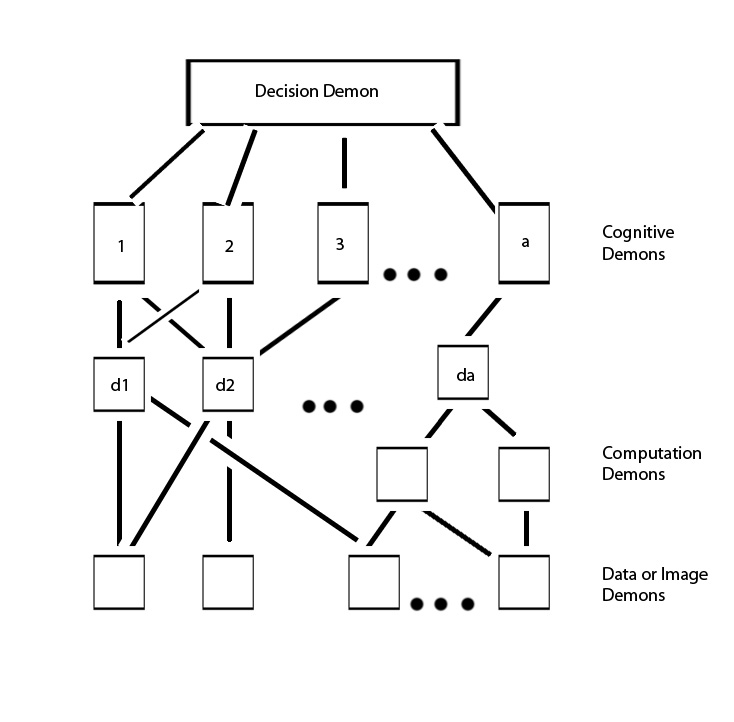
Pandemonium Architecture
Pandemonium architecture is a theory in cognitive science that describes how visual images are processed by the brain. It has applications in artificial intelligence and pattern recognition. The theory was developed by the artificial intelligence pioneer Oliver Selfridge in 1959. It describes the process of object recognition as a hierarchical system of detection and association by a metaphorical set of "demons" sending signals to each other. This model is now recognized as the basis of visual perception in cognitive science. Pandemonium architecture arose in response to the inability of template matching theories to offer a biologically plausible explanation of the image constancy phenomenon. Contemporary researchers praise this architecture for its elegancy and creativity; that the idea of having multiple independent systems (e.g., feature detectors) working in parallel to address the image constancy phenomena of pattern recognition is powerful yet simple. The basic idea of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Original Pande2
Originality is the aspect of created or invented works that distinguish them from reproductions, clones, forgeries, or substantially derivative works. The modern idea of originality is according to some scholars tied to Romanticism, by a notion that is often called romantic originality.Smith (1924)Waterhouse (1926)Macfarlane (2007) The validity of "originality" as an operational concept has been questioned. For example, there is no clear boundary between "derivative" and "inspired by" or "in the tradition of." The concept of originality is both culturally and historically contingent. For example, unattributed reiteration of a published text in one culture might be considered plagiarism but in another culture might be regarded as a convention of veneration. At the time of Shakespeare, it was more common to appreciate the similarity with an admired classical work, and Shakespeare himself avoided "unnecessary invention". Royal Shakespeare Company (2007) ''The RSC Shakespeare - W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock dating suggests their split from other amphibians may extend further back to the Permian, 265 million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest. Frogs account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from taxonomy or evolutionary history. An adult frog has a stout body, protruding eyes, anteriorly-attached tongue, limbs folded underneath, and no tail (the tail of tailed frogs is an ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feature Integration Theory
Feature integration theory is a theory of attention developed in 1980 by Anne Treisman and Garry Gelade that suggests that when perceiving a stimulus, features are "registered early, automatically, and in parallel, while objects are identified separately" and at a later stage in processing. The theory has been one of the most influential cognitive model, psychological models of human visual attention. Stages According to Treisman, the first stage of the feature integration theory is the preattentive stage. During this stage, different parts of the brain automatically gather information about basic features (colors, shape, movement) that are found in the visual field. The idea that features are automatically separated appears counterintuitive. However, we are not aware of this process because it occurs early in perceptual processing, before we become conscious of the object. The second stage of feature integration theory is the focused attention stage, where a subject combines indiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-organizing Map
A self-organizing map (SOM) or self-organizing feature map (SOFM) is an unsupervised machine learning technique used to produce a low-dimensional (typically two-dimensional) representation of a higher dimensional data set while preserving the topological structure of the data. For example, a data set with p variables measured in n observations could be represented as clusters of observations with similar values for the variables. These clusters then could be visualized as a two-dimensional "map" such that observations in proximal clusters have more similar values than observations in distal clusters. This can make high-dimensional data easier to visualize and analyze. An SOM is a type of artificial neural network but is trained using competitive learning rather than the error-correction learning (e.g., backpropagation with gradient descent) used by other artificial neural networks. The SOM was introduced by the Finnish professor Teuvo Kohonen in the 1980s and therefore is someti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensemble Learning
In statistics and machine learning, ensemble methods use multiple learning algorithms to obtain better predictive performance than could be obtained from any of the constituent learning algorithms alone. Unlike a statistical ensemble in statistical mechanics, which is usually infinite, a machine learning ensemble consists of only a concrete finite set of alternative models, but typically allows for much more flexible structure to exist among those alternatives. Overview Supervised learning algorithms perform the task of searching through a hypothesis space to find a suitable hypothesis that will make good predictions with a particular problem. Even if the hypothesis space contains hypotheses that are very well-suited for a particular problem, it may be very difficult to find a good one. Ensembles combine multiple hypotheses to form a (hopefully) better hypothesis. The term ''ensemble'' is usually reserved for methods that generate multiple hypotheses using the same base learn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competitive Learning
Competitive learning is a form of unsupervised learning in artificial neural networks, in which nodes compete for the right to respond to a subset of the input data. A variant of Hebbian learning, competitive learning works by increasing the specialization of each node in the network. It is well suited to finding clusters within data. Models and algorithms based on the principle of competitive learning include vector quantization and self-organizing maps (Kohonen maps). Principles There are three basic elements to a competitive learning rule: * A set of neurons that are all the same except for some randomly distributed synaptic weights, and which therefore respond differently to a given set of input patterns * A limit imposed on the "strength" of each neuron * A mechanism that permits the neurons to compete for the right to respond to a given subset of inputs, such that only one output neuron (or only one neuron per group), is active (i.e. "on") at a time. The neuron that wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebbian Theory
Hebbian theory is a neuroscientific theory claiming that an increase in synaptic efficacy arises from a presynaptic cell's repeated and persistent stimulation of a postsynaptic cell. It is an attempt to explain synaptic plasticity, the adaptation of brain neurons during the learning process. It was introduced by Donald Hebb in his 1949 book '' The Organization of Behavior.'' The theory is also called Hebb's rule, Hebb's postulate, and cell assembly theory. Hebb states it as follows: Let us assume that the persistence or repetition of a reverberatory activity (or "trace") tends to induce lasting cellular changes that add to its stability. ... When an axon of cell ''A'' is near enough to excite a cell ''B'' and repeatedly or persistently takes part in firing it, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells such that ''A''’s efficiency, as one of the cells firing ''B'', is increased. The theory is often summarized as "Cells that fire together wire toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consciousness
Consciousness, at its simplest, is sentience and awareness of internal and external existence. However, the lack of definitions has led to millennia of analyses, explanations and debates by philosophers, theologians, linguisticians, and scientists. Opinions differ about what exactly needs to be studied or even considered consciousness. In some explanations, it is synonymous with the mind, and at other times, an aspect of mind. In the past, it was one's "inner life", the world of introspection, of private thought, imagination and volition. Today, it often includes any kind of cognition, experience, feeling or perception. It may be awareness, awareness of awareness, or self-awareness either continuously changing or not. The disparate range of research, notions and speculations raises a curiosity about whether the right questions are being asked. Examples of the range of descriptions, definitions or explanations are: simple wakefulness, one's sense of selfhood or sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morse Code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of the inventors of the telegraph. International Morse code encodes the 26 basic Latin letters through , one accented Latin letter (), the Arabic numerals, and a small set of punctuation and procedural signals ( prosigns). There is no distinction between upper and lower case letters. Each Morse code symbol is formed by a sequence of ''dits'' and ''dahs''. The ''dit'' duration is the basic unit of time measurement in Morse code transmission. The duration of a ''dah'' is three times the duration of a ''dit''. Each ''dit'' or ''dah'' within an encoded character is followed by a period of signal absence, called a ''space'', equal to the ''dit'' duration. The letters of a word are separated by a space of duration equal to three ''dits' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
More A's
More or Mores may refer to: Computing * MORE (application), outline software for Mac OS * more (command), a shell command * MORE protocol, a routing protocol * Missouri Research and Education Network Music Albums * ''More!'' (album), by Booka Shade, 2010 * ''More'' (soundtrack), by Pink Floyd with music from the 1969 film * ''More...'' (Trace Adkins album), or the title song, 1999 * ''More'' (Mary Alessi album), 2005 * ''More'' (Beyoncé EP), 2014 * ''More'' (Michael Bublé EP), 2005 * ''More'' (Clarke-Boland Big Band album), 1968 * ''More'' (Double Dagger album), 2009 * ''More...'' (Montell Jordan album), 1996 * ''More'' (Crystal Lewis album), 2001 * ''More'' (Giuseppi Logan album), 1966 * ''More'' (No Trend album), 2001 * ''More'' (Jeremy Riddle album), or the title song, 2017 * ''More'' (Symphony Number One album), 2016 * ''More'' (Tamia album), or the title song, 2004 * ''More'' (Vitamin C album), 2001 * ''More'', by Mylon LeFevre, 1983 * ''More'', by Resin D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pareidolia
Pareidolia (; ) is the tendency for perception to impose a meaningful interpretation on a nebulous stimulus, usually visual, so that one sees an object, pattern, or meaning where there is none. Common examples are perceived images of animals, faces, or objects in cloud formations, seeing faces in inanimate objects, or lunar pareidolia like the Man in the Moon or the Moon rabbit. The concept of pareidolia may extend to include hidden messages in recorded music played in reverse or at higher- or lower-than-normal speeds, and hearing voices (mainly indistinct) or music in random noise, such as that produced by air conditioners or fans. Scientists have taught computers to use visual clues to "see" faces and other images. Etymology The word derives from the Greek words ''pará'' (, "beside, alongside, instead f) and the noun ''eídōlon'' (, "image, form, shape"). The German word was used in articles by Karl Ludwig Kahlbaum—for example in his 1866 paper "" ("On Delusion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Alphabet
The Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. Largely unaltered with the exception of extensions (such as diacritics), it used to write English and the other modern European languages. With modifications, it is also used for other alphabets, such as the Vietnamese alphabet. Its modern repertoire is standardised as the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Etymology The term ''Latin alphabet'' may refer to either the alphabet used to write Latin (as described in this article) or other alphabets based on the Latin script, which is the basic set of letters common to the various alphabets descended from the classical Latin alphabet, such as the English alphabet. These Latin-script alphabets may discard letters, like the Rotokas alphabet, or add new letters, like the Danish and Norwegian alphabets. Letter shapes have evolved over the centuries, including the development in Medieval Latin of lower-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Ranomafana.jpg)





.jpg)
