|
PRKAA2
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKAA2'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a catalytic subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha catalytic subunit, and non-catalytic beta and gamma subunits. AMPK is an important energy-sensing enzyme that monitors cellular energy status. In response to cellular metabolic stresses, AMPK is activated, and thus phosphorylates and inactivates acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and beta-hydroxy beta-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase ( HMGCR), key enzymes involved in regulating de novo biosynthesis of fatty acid and cholesterol. Studies of the mouse counterpart suggest that this catalytic subunit may control whole-body insulin sensitivity and is necessary for maintaining myocardial energy homeostasis during ischemia Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMP-activated Protein Kinase
5' AMP-activated protein kinase or AMPK or 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase is an enzyme (EC 2.7.11.31) that plays a role in cellular energy homeostasis, largely to activate glucose and fatty acid uptake and oxidation when cellular energy is low. It belongs to a highly conserved eukaryotic protein family and its orthologues are SNF1 in yeast, and SnRK1 in plants. It consists of three proteins ( subunits) that together make a functional enzyme, conserved from yeast to humans. It is expressed in a number of tissues, including the liver, brain, and skeletal muscle. In response to binding AMP and ADP, the net effect of AMPK activation is stimulation of hepatic fatty acid oxidation, ketogenesis, stimulation of skeletal muscle fatty acid oxidation and glucose uptake, inhibition of cholesterol synthesis, lipogenesis, and triglyceride synthesis, inhibition of adipocyte lipogenesis, inhibition of adipocyte lipolysis, and modulation of insulin secretion by pancreatic β ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP : ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
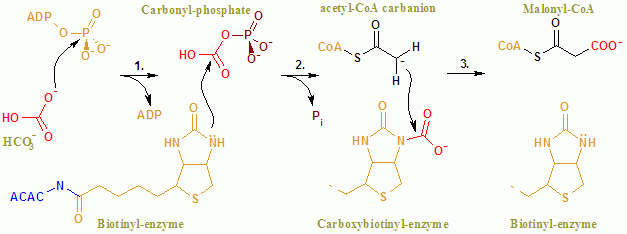
Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a biotin-dependent enzyme () that catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to produce malonyl-CoA through its two catalytic activities, biotin carboxylase (BC) and carboxyltransferase (CT). ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in most prokaryotes and in the chloroplasts of most plants and algae, whereas it is a large, multi-domain enzyme in the cytoplasm of most eukaryotes. The most important function of ACC is to provide the malonyl-CoA substrate for the biosynthesis of fatty acids. The activity of ACC can be controlled at the transcriptional level as well as by small molecule modulators and covalent modification. The human genome contains the genes for two different ACCs—'' ACACA'' and ''ACACB''. Structure Prokaryotes and plants have multi-subunit ACCs composed of several polypeptides. Biotin carboxylase (BC) activity, biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP), and carboxyl transferase (CT) activity are each contained on a different s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMG-CoA Reductase
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, official symbol HMGCR) is the rate-controlling enzyme (NADH-dependent, ; NADPH-dependent, ) of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia. HMG-CoA reductase is anchored in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, and was long regarded as having seven transmembrane domains, with the active site located in a long carboxyl terminal domain in the cytosol. More recent evidence shows it to contain eight transmembrane domains. In humans, the gene for HMG-CoA reductase (NADPH) is located on the long arm of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides. Biosynthesis is usually synonymous with anabolism. The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oily acid"). Types of fatty acids Fatty acids are classified in many ways: by length, by saturation vs unsaturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as '' Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine". Etymology The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek ''chole-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into liver, fat and skeletal muscle cells. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen via glycogenesis or fats (triglycerides) via lipogenesis, or, in the case of the liver, into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver is strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large molecules inside the cells. Low insulin levels in the blood have the opposite effect by promoting widespread catabolism, especially o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue i.e. hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. It also implies local hypoxia in a part of a body resulting from constriction (such as vasoconstriction, thrombosis, or embolism). Ischemia causes not only insufficiency of oxygen, but also reduced availability of nutrients and inadequate removal of metabolic wastes. Ischemia can be partial (poor perfusion) or total blockage. The inadequate delivery of oxygenated blood to the organs must be resolved either by treating the cause of the inadequate delivery or reducing the oxygen demand of the system that needs it. For example, patients with myocardial ischemia have a decreased blood flow to the heart and are prescribed with medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |