|
Pythagorean Mathematics
Pythagoreanism originated in the 6th century BC, based on and around the teachings and beliefs held by Pythagoras and his followers, the Pythagoreans. Pythagoras established the first Pythagorean community in the ancient Greek colony of Kroton, in modern Calabria (Italy) circa 530 BC. Early Pythagorean communities spread throughout Magna Graecia. Already during Pythagoras' life it is likely that the distinction between the ''akousmatikoi'' ("those who listen"), who is conventionally regarded as more concerned with religious, and ritual elements, and associated with the oral tradition, and the ''mathematikoi'' ("those who learn") existed. The ancient biographers of Pythagoras, Iamblichus () and his master Porphyry ( ) seem to make the distinction of the two as that of 'beginner' and 'advanced'. As the Pythagorean cenobites practiced an esoteric path, like the mystery schools of antiquity, the adherents, ''akousmatikoi'', following initiation became ''mathematikoi''. It is wrong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cropped Image Of Pythagoras From Raphael's School Of Athens
Cropping is the removal of unwanted outer areas from a photographic or illustrated image. The process usually consists of the removal of some of the peripheral areas of an image to remove extraneous visual data from the picture, improve its framing, change the aspect ratio, or accentuate or isolate the subject matter from its background. Depending on the application, this can be performed on a physical photograph, artwork, or film footage, or it can be achieved digitally by using image editing software. The process of cropping is common to the photographic, film processing, broadcasting, graphic design, and printing businesses. In photography, print, and design In the printing, graphic design and photography industries, cropping is the removal of unwanted areas from the periphery of a photographic or illustrated image. Cropping is one of the most basic photo manipulation processes, and it is carried out to remove an unwanted object or irrelevant noise from the periphery o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Persian Invasion Of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC) occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasion of Greece (492–490 BC) at the Battle of Marathon, which ended Darius I's attempts to subjugate Greece. After Darius's death, his son Xerxes spent several years planning for the second invasion, mustering an enormous army and navy. The Athenians and Spartans led the Greek resistance. About a tenth of the Greek city-states joined the 'Allied' effort; most remained neutral or submitted to Xerxes. The invasion began in spring 480 BC, when the Persian army crossed the Hellespont and marched through Thrace and Macedon to Thessaly. The Persian advance was blocked at the pass of Thermopylae by a small Allied force under King Leonidas I of Sparta; simultaneously, the Persian fleet was blocked by an Allied fleet at the straits of Artemisium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
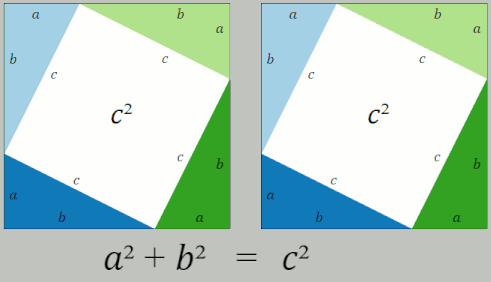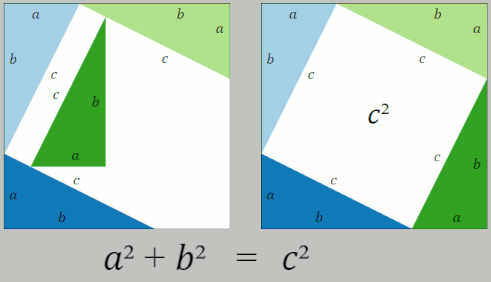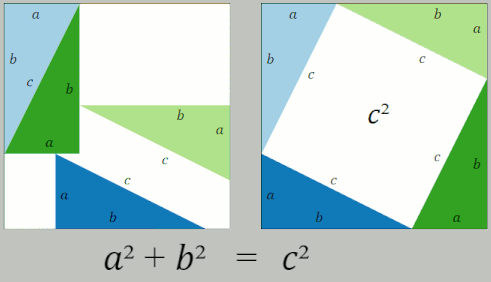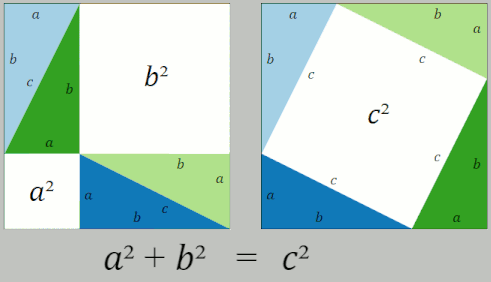
Pythagorean Theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. The theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides , and the hypotenuse , sometimes called the Pythagorean equation: :a^2 + b^2 = c^2 . The theorem is named for the Ancient Greece, Greek philosopher Pythagoras, born around 570 BC. The theorem has been Mathematical proof, proved numerous times by many different methods – possibly the most for any mathematical theorem. The proofs are diverse, including both Geometry, geometric proofs and Algebra, algebraic proofs, with some dating back thousands of years. When Euclidean space is represented by a Cartesian coordinate system in analytic geometry, Euclidean distance satisfies th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Theorem - Ani
Pythagorean, meaning of or pertaining to the ancient Ionian mathematician, philosopher, and music theorist Pythagoras, may refer to: Philosophy * Pythagoreanism, the esoteric and metaphysical beliefs purported to have been held by Pythagoras * Neopythagoreanism, a school of philosophy reviving Pythagorean doctrines that became prominent in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD * Pythagorean diet, the name for vegetarianism before the nineteenth century Mathematics * Pythagorean theorem * Pythagorean triple * Pythagorean prime * Pythagorean trigonometric identity * Table of Pythagoras, another name for the multiplication table Music * Pythagorean comma * Pythagorean hammers * Pythagorean tuning Other uses * Pythagorean cup * Pythagorean expectation, a baseball statistical term * Pythagorean letter See also * List of things named after Pythagoras {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plimpton 322
Plimpton 322 is a Babylonian clay tablet, believed to have been written around 1800 BC, that contains a mathematical table written in cuneiform script. Each row of the table relates to a Pythagorean triple, that is, a triple of integers (s,\ell,d) that satisfies the Pythagorean theorem, s^2+\ell^2=d^2, the rule that equates the sum of the squares of the legs of a right triangle to the square of the hypotenuse. The era in which Plimpton 322 was written was roughly 13 to 15 centuries prior to the era in which the major Greek discoveries in geometry were made. At the time that Otto Neugebauer and Abraham Sachs first realized the mathematical significance of the tablet in the 1940s, a few Old Babylonian tablets making use of the Pythagorean rule were already known. In addition to providing further evidence that Mesopotamian scribes knew and used the rule, Plimpton 322 strongly suggested that they had a systematic method for generating Pythagorean triples as some of the tripl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orphism (religion)
Orphism is the name given to a set of religious beliefs and practices originating in the ancient Greek and Hellenistic world, associated with literature ascribed to the mythical poet Orpheus, who descended into the Greek underworld and returned. Orphism has been described as a reform of the earlier Dionysian religion, involving a re-interpretation or re-reading of the myth of Dionysus and a re-ordering of Hesiod's ''Theogony'', based in part on pre-Socratic philosophy. The suffering and death of the god Dionysus at the hands of the Titans has been considered the central myth of Orphism. According to this myth, the infant Dionysus is killed, torn apart, and consumed by the Titans. In retribution, Zeus strikes the Titans with a thunderbolt, turning them to ash. From these ashes, humanity is born. In Orphic belief, this myth describes humanity as having a dual nature: body (), inherited from the Titans, and a divine spark or soul (), inherited from Dionysus. In order to achieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacchic
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; ) is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also known as Bacchus ( or ; ) by the Greeks (a name later adopted by the Romans) for a frenzy he is said to induce called ''baccheia''. His wine, music, and ecstatic dance were considered to free his followers from self-conscious fear and care, and subvert the oppressive restraints of the powerful. His ''thyrsus'', a fennel-stem sceptre, sometimes wound with ivy and dripping with honey, is both a beneficent wand and a weapon used to destroy those who oppose his cult and the freedoms he represents. Those who partake of his mysteries are believed to become possessed and empowered by the god himself. His origins are uncertain, and his cults took many forms; some are described by ancient sources as Thracian, others as Greek. In Orphism, he was variously a son of Zeus and Persephone; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intentional Community
An intentional community is a voluntary residential community designed to foster a high degree of group cohesiveness, social cohesion and teamwork. Such communities typically promote shared values or beliefs, or pursue a common vision, which may be political, religious, Utopia, utopian or Spirituality, spiritual, or are simply focused on the practical benefits of cooperation and mutual support. While some groups emphasise shared Ideology, ideologies, others are centred on enhancing social connections, sharing resources, and creating meaningful relationships. Although intentional communities are sometimes described as alternative lifestyles or social experiments, some see them as a natural response to the isolation and fragmentation of modern housing, offering a return to the social bonds and collaborative spirit found in traditional village life. List of intentional communities, The multitude of intentional communities includes collective households, cohousing communities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neopythagoreanism
Neopythagoreanism (or neo-Pythagoreanism) was a school of Hellenistic and Roman philosophy which revived Pythagorean doctrines. Neopythagoreanism was influenced by middle Platonism and in turn influenced Neoplatonism. It originated in the 1st century BC and flourished during the 1st and 2nd centuries AD. The ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Eleventh Edition describes Neopythagoreanism as "a link in the chain between the old and the new" within Hellenistic philosophy. Central to Neopythagorean thought was the concept of a soul and its inherent desire for a ''unio mystica'' with the divine. The word ''Neopythagoreanism'' is a modern (19th century) term, coined as a parallel of "Neoplatonism". History In the 1st century BC Cicero's friend Nigidius Figulus made an attempt to revive Pythagorean doctrines, but the most important members of the school were Apollonius of Tyana and Moderatus of Gades in the 1st century AD. Other important Neopythagoreans include the mathematician Nicoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripatetic School
The Peripatetic school ( ) was a philosophical school founded in 335 BC by Aristotle in the Lyceum in ancient Athens. It was an informal institution whose members conducted philosophical and scientific inquiries. The school fell into decline after the middle of the 3rd century BC, but had a revival in the Roman Empire. History The term ''peripatetic'' is a transliteration of the Ancient Greek word , meaning 'of walking' or 'given to walking about'. The Peripatetic school, founded by Aristotle, was actually known simply as the Peripatos. Aristotle's school came to be so named because of the ('walkways', some covered or with colonnades) of the Lyceum where the members met. The legend that the name came from Aristotle's alleged habit of walking while lecturing may have started with Hermippus of Smyrna. Unlike Plato (born BC, died 348 BC), Aristotle was not a citizen of Athens, and could not own property; he and his colleagues therefore used the grounds of the Lyceum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, and the arts. As the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy in the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum in Athens, he began the wider Aristotelianism, Aristotelian tradition that followed, which set the groundwork for the development of modern science. Little is known about Aristotle's life. He was born in the city of Stagira (ancient city), Stagira in northern Greece during the Classical Greece, Classical period. His father, Nicomachus (father of Aristotle), Nicomachus, died when Aristotle was a child, and he was brought up by a guardian. At around eighteen years old, he joined Plato's Platonic Academy, Academy in Athens and remained there until the age of thirty seven (). Shortly after Plato died, Aristotle left Athens and, at the request ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |