|
Protein Dynamics
In molecular biology, proteins are generally thought to adopt unique structures determined by their amino acid sequences. However, proteins are not strictly static objects, but rather populate ensembles of (sometimes similar) conformations. Transitions between these states occur on a variety of length scales (tenths of angstroms to nm) and time scales (ns to s), and have been linked to functionally relevant phenomena such as allosteric signaling and enzyme catalysis. The study of protein dynamics is most directly concerned with the transitions between these states, but can also involve the nature and equilibrium populations of the states themselves. These two perspectives— kinetics and thermodynamics, respectively—can be conceptually synthesized in an " energy landscape" paradigm: highly populated states and the kinetics of transitions between them can be described by the depths of energy wells and the heights of energy barriers, respectively. Local flexibility: atoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. Though cells and other microscopic structures had been observed in living organisms as early as the 18th century, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms and interactions governing their behavior did not emerge until the 20th century, when technologies used in physics and chemistry had advanced sufficiently to permit their application in the biological sciences. The term 'molecular biology' was first used in 1945 by the English physicist William Astbury, who described it as an approach focused on discerning the underpinnings of biological phenomena—i.e. uncovering the physical and chemical structures and properties of biological molecules, as well as their interactions with other molecules and how these interactions explain observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the structure and dynamics of proteins, and also nucleic acids, and their complexes. The field was pioneered by Richard R. Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich at the ETH, and by Ad Bax, Marius Clore, Angela Gronenborn at the National Institutes of Health, NIH, and Gerhard Wagner (physicist), Gerhard Wagner at Harvard University, among others. Structure determination by NMR spectroscopy usually consists of several phases, each using a separate set of highly specialized techniques. The sample is prepared, measurements are made, interpretive approaches are applied, and a structure is calculated and validated. NMR involves the quantum-mechanical properties of the central core ("Atomic nucleus, nucleus") of the atom. These properties depend on the local molecular environment, and their measurement provides a map of how t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Sheet
The beta sheet (β-sheet, also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a generally twisted, pleated sheet. A β-strand is a stretch of polypeptide chain typically 3 to 10 amino acids long with backbone in an extended conformation. The supramolecular association of β-sheets has been implicated in the formation of the fibrils and protein aggregates observed in amyloidosis, Alzheimer's disease and other proteinopathies. History The first β-sheet structure was proposed by William Astbury in the 1930s. He proposed the idea of hydrogen bonding between the peptide bonds of parallel or antiparallel extended β-strands. However, Astbury did not have the necessary data on the bond geometry of the amino acids in order to build accurate models, especially since he did not then know that the peptide bond was planar. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Helix
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix). The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the Protein secondary structure, secondary structure of proteins. It is also the most extreme type of local structure, and it is the local structure that is most easily predicted from a sequence of amino acids. The alpha helix has a right-handed helix conformation in which every backbone amino, N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone carbonyl, C=O group of the amino acid that is four residue (biochemistry), residues earlier in the protein sequence. Other names The alpha helix is also commonly called a: * Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix (from the names of three scientists who described its structure) * 3.613-helix because there are 3.6 amino acids in one ring, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond (starting with amidic hydrogen and ending with carbonyl oxygen) Discovery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Der Waals Force
In molecular physics and chemistry, the van der Waals force (sometimes van der Waals' force) is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and therefore more susceptible to disturbance. The van der Waals force quickly vanishes at longer distances between interacting molecules. Named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, the van der Waals force plays a fundamental role in fields as diverse as supramolecular chemistry, structural biology, polymer science, nanotechnology, surface science, and condensed matter physics. It also underlies many properties of organic compounds and molecular solids, including their solubility in polar and non-polar media. If no other force is present, the distance between atoms at which the force becomes repulsive rather than attractive as the atoms approach one another is called the van der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Bond
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons a ...ing that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply different electronegativities, and is the primary interaction occurring in ionic compounds. It is one of the main types of bonding, along with covalent bonding and metallic bonding. Ions are atoms (or groups of atoms) with an electrostatic charge. Atoms that gain electrons make negatively charged ions (called anions). Atoms that lose electrons make positively charged ions (called cations). This transfer of electrons is known as electrovalence in contrast to covalent bond, covalence. In the simplest case, the cation is a metal atom and the anion is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently bonded to a more Electronegativity, electronegative donor atom or group (Dn), interacts with another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Unlike simple Dipole–dipole attraction, dipole–dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding arises from charge transfer (nB → σ*AH), Atomic orbital, orbital interactions, and quantum mechanical Delocalized electron, delocalization, making it a resonance-assisted interaction rather than a mere electrostatic attraction. The general notation for hydrogen bonding is Dn−H···Ac, where the solid line represents a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are nitrogen (N), oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
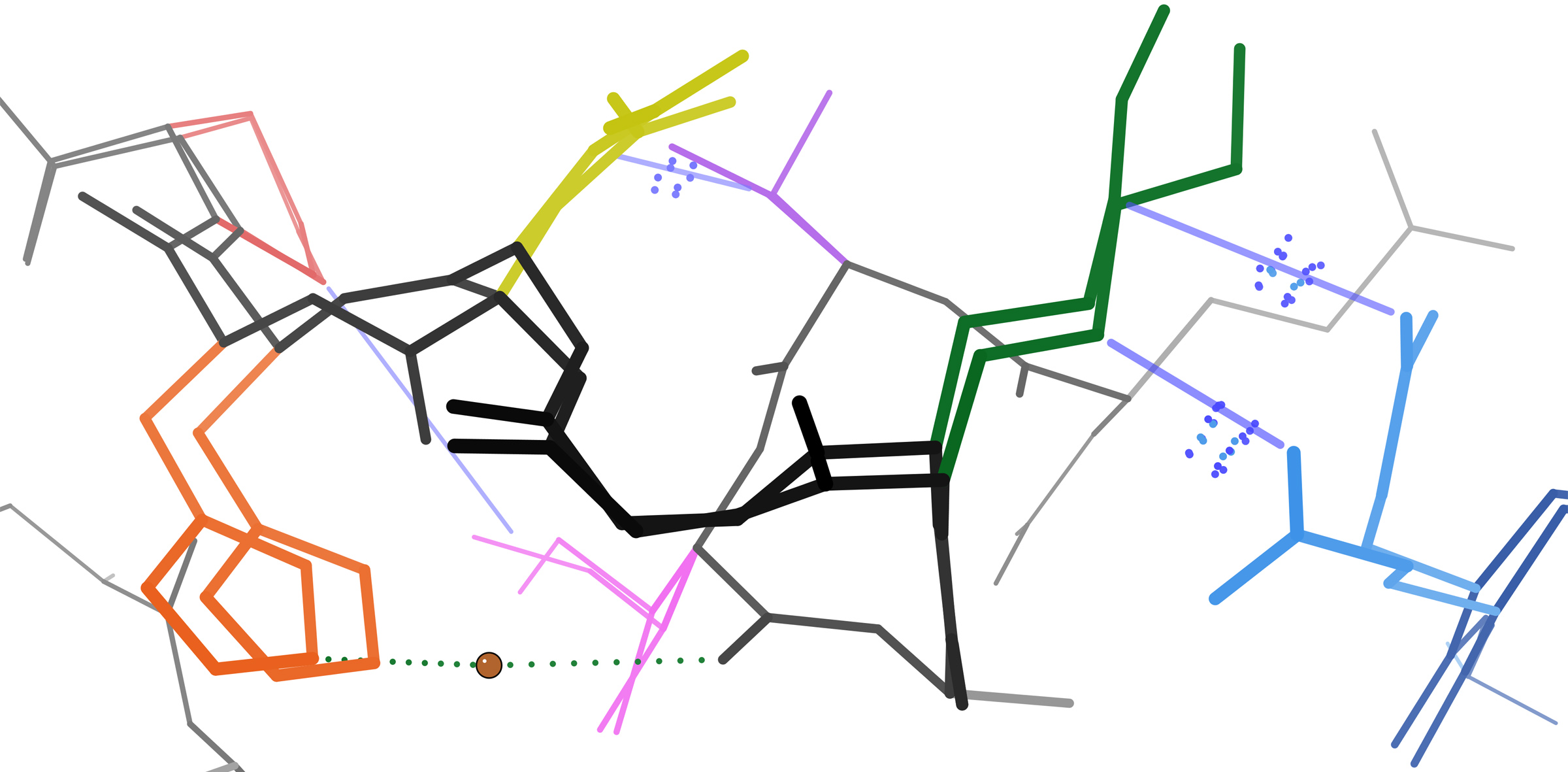
Catalase Diverse Alternate Conformation Network
Catalase is a common enzyme found in nearly all living organisms exposed to oxygen (such as bacteria, plants, and animals) which catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen. It is a very important enzyme in protecting the cell from oxidative damage by reactive oxygen species (ROS). Catalase has one of the highest turnover numbers of all enzymes; one catalase molecule can convert millions of hydrogen peroxide molecules to water and oxygen each second. Catalase is a tetramer of four polypeptide chains, each over 500 amino acids long. It contains four iron-containing heme groups that allow the enzyme to react with hydrogen peroxide. The optimum pH for human catalase is approximately 7, and has a fairly broad maximum: the rate of reaction does not change appreciably between pH 6.8 and 7.5. The pH optimum for other catalases varies between 4 and 11 depending on the species. The optimum temperature also varies by species. Structure Human catalase forms a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscoelasticity
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist both shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials strain when stretched and immediately return to their original state once the stress is removed. Viscoelastic materials have elements of both of these properties and, as such, exhibit time-dependent strain. Whereas elasticity is usually the result of bond stretching along crystallographic planes in an ordered solid, viscosity is the result of the diffusion of atoms or molecules inside an amorphous material.Meyers and Chawla (1999): "Mechanical Behavior of Materials", 98-103. Background In the nineteenth century, physicists such as James Clerk Maxwell, Ludwig Boltzmann, and Lord Kelvin researched and experimented with creep and recovery of glasses, metals, and rubbers. Viscoel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisotropic Terahertz Microspectroscopy
Anisotropic terahertz microspectroscopy (ATM) is a spectroscopic technique in which molecular vibrations in an Anisotropy, anisotropic material are probed with short pulses of terahertz radiation whose electric field is linearly Polarization (waves)#Wave propagation and polarization, polarized parallel to the surface of the material. The technique has been demonstrated in studies involving single crystal sucrose, fructose, oxalic acid, and molecular Protein crystallization, protein crystals in which the spatial orientation of molecular vibrations are of interest. Explanation When the electric field of a propagating beam of light oscillates in a direction perpendicular to its direction of propagation, it is said to be a Polarization_(waves), polarized transverse wave. Light with an electric field constrained to a particular angle in the transverse plane is said to be linearly polarized. When linearly polarized light is transmitted through an isotropy, isotropic material — a mater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerr Effect
The Kerr effect, also called the quadratic electro-optic (QEO) effect, is a change in the refractive index of a material in response to an applied electric field. The Kerr effect is distinct from the Pockels effect in that the induced index change for the Kerr effect is directly proportional to the ''square'' of the electric field instead of varying linearly with it. All materials show a Kerr effect, but certain liquids display it more strongly than others. The Kerr effect was discovered in 1875 by Scottish physicist John Kerr. Two special cases of the Kerr effect are normally considered, these being the Kerr electro-optic effect, or DC Kerr effect, and the optical Kerr effect, or AC Kerr effect. Kerr electro-optic effect The Kerr electro-optic effect, or DC Kerr effect, is the special case in which a slowly varying external electric field is applied by, for instance, a voltage on electrodes across the sample material. Under this influence, the sample becomes birefringent, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after physicist C. V. Raman) is a Spectroscopy, spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible spectrum, visible, near infrared, or ultraviolet, near ultraviolet range is used, although X-ray Raman scattering, X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Time-resolved spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |