|
Proportional–integral–derivative Controller
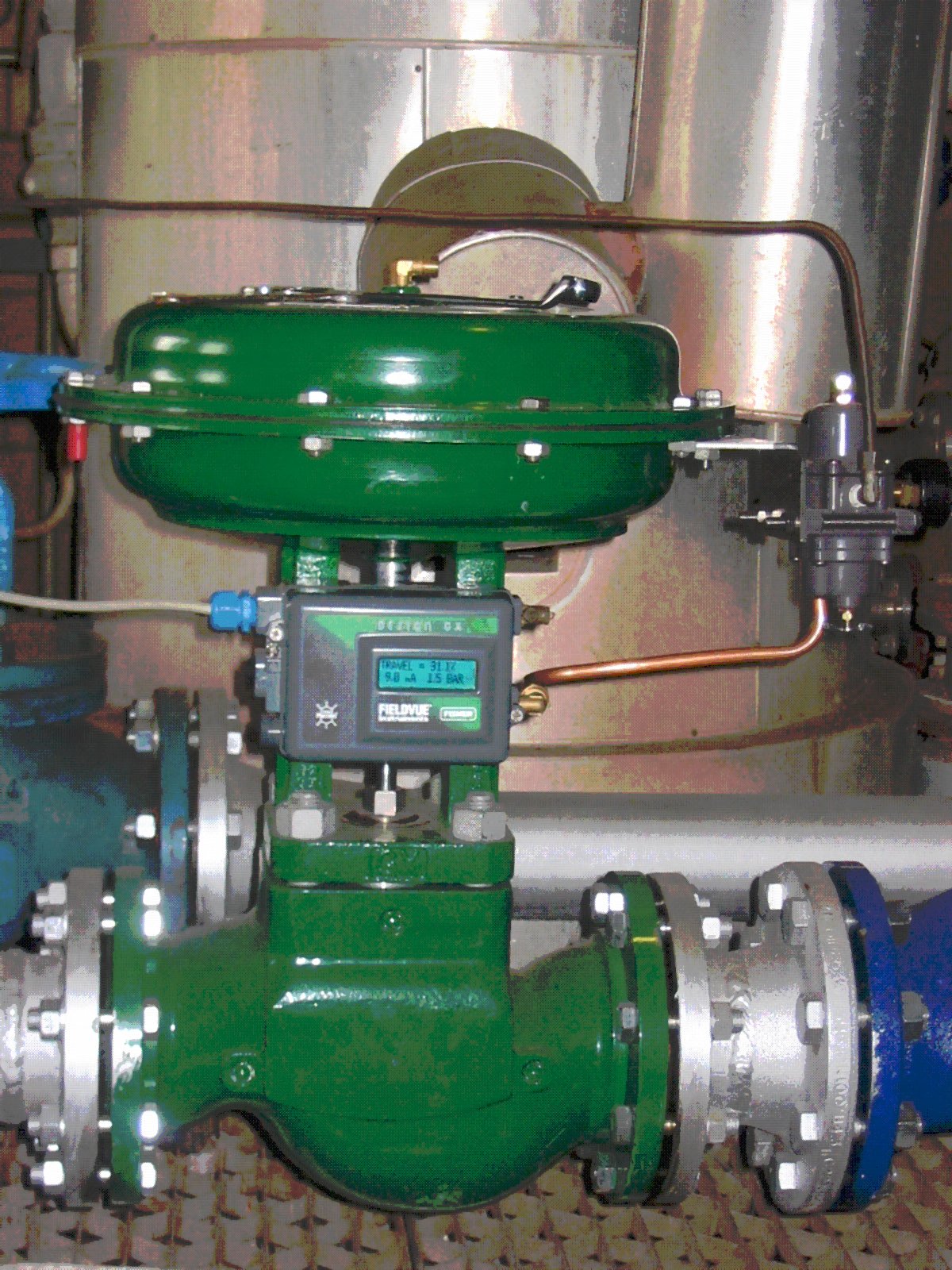
A proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID controller or three-term controller) is a feedback-based control loop mechanism commonly used to manage machines and processes that require continuous control and automatic adjustment. It is typically used in industrial control systems and various other applications where constant control through modulation is necessary without human intervention. The PID controller automatically compares the desired target value (Setpoint (control system), setpoint or SP) with the actual value of the system (process variable or PV). The difference between these two values is called the ''error value'', denoted as e(t). It then applies corrective actions automatically to bring the PV to the same value as the SP using three methods: The proportional () component responds to the current error value by producing an Output (computing), output that is directly proportional to the magnitude of the error. This provides immediate correction based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
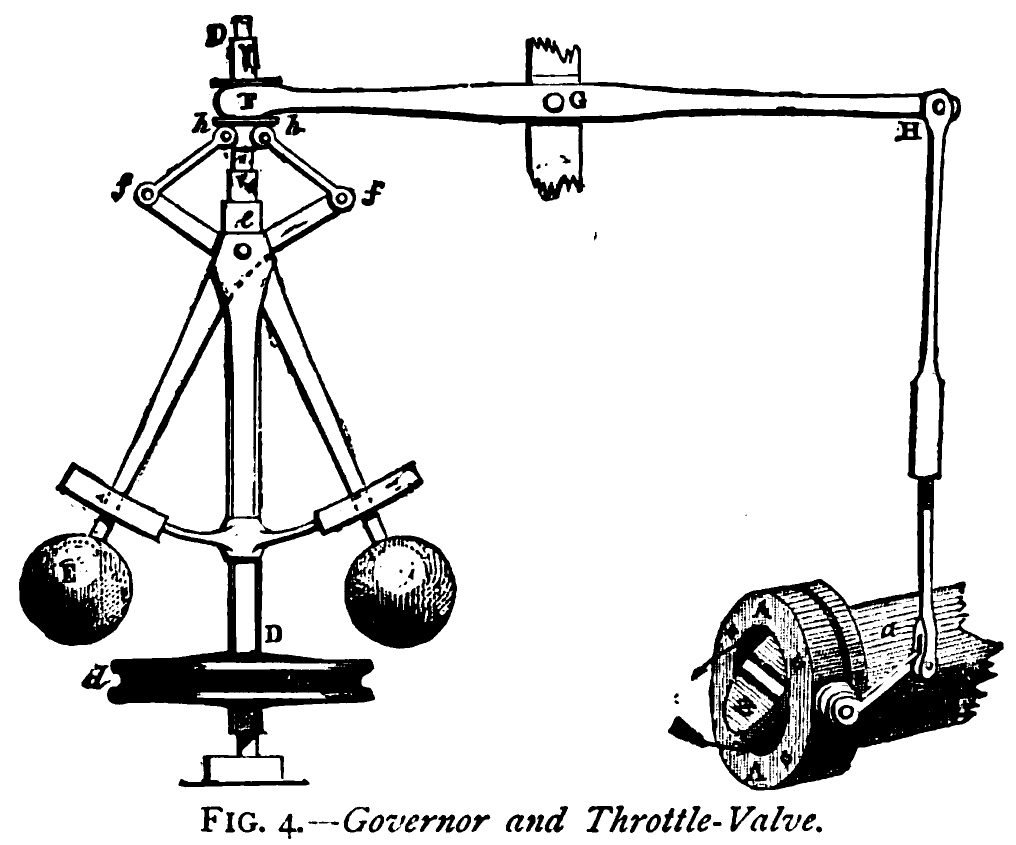
Feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause and effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled carefully when applied to feedback systems: History Self-regulating mechanisms have existed since antiquity, and the idea of feedback started to enter economic theory in Britain by the 18th century, but it was not at that time recognized as a universal abstraction and so did not have a name. The first ever known artificial feedback device was a float valve, for maintaining water at a constant level, invented in 270 BC in Alexandria, Egypt. This device illustrated the principle of feedback: a low water level opens the valve, the rising water then provides feedback into the system, closing the valve when the required level is reached. This then reoccurs in a circular fashion as the water level fluctuates. Centrifugal governors were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportional Control
Proportional control, in engineering and process control, is a type of linear feedback control system in which a correction is applied to the controlled variable, and the size of the correction is proportional to the difference between the desired value ( setpoint, SP) and the measured value ( process variable, PV). Two classic mechanical examples are the toilet bowl float proportioning valve and the fly-ball governor. The proportional control concept is more complex than an on–off control system such as a bi-metallic domestic thermostat, but simpler than a proportional–integral–derivative (PID) control system used in something like an automobile cruise control. On–off control will work where the overall system has a relatively long response time, but can result in instability if the system being controlled has a rapid response time. Proportional control overcomes this by modulating the output to the controlling device, such as a control valve at a level which avoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms. Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator–prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy. The term ''vibration'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation. Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, may be an undesirable phenomenon in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
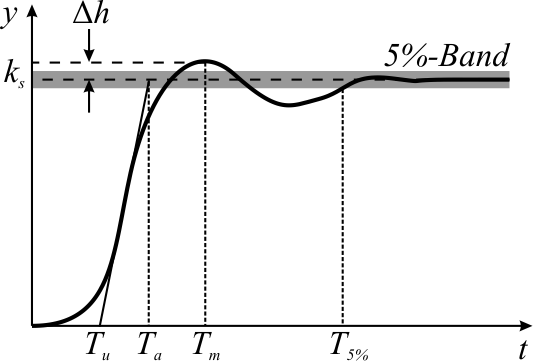
Overshoot (signal)
In signal processing, control theory, electronics, and mathematics, overshoot is the occurrence of a signal or function exceeding its target. Undershoot is the same phenomenon in the opposite direction. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filters. It is often followed by ringing (signal), ringing, and at times conflated with the latter. Definition Maximum overshoot is defined in Katsuhiko Ogata's ''Discrete-time control systems'' as "the maximum peak value of the response curve measured from the desired response of the system." Control theory In control theory, overshoot refers to an output exceeding its final, steady-state value. For a step response, step input, the ''percentage overshoot'' (PO) is the maximum value minus the step value divided by the step value. In the case of the unit step, the ''overshoot'' is just the maximum value of the step response minus one. Also see the definition of ''overshoot'' in an #Electronics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead–lag Compensator
A lead–lag compensator is a component in a control system that improves an undesirable frequency response in a feedback and control system. It is a fundamental building block in classical control theory. Applications Lead–lag compensators influence disciplines as varied as robotics, satellite control, automobile diagnostics, LCDs and laser frequency stabilisation. They are an important building block in analog control systems, and can also be used in digital control. Given the control plant, desired specifications can be achieved using compensators. I, P, PI, PD, and PID, are optimizing controllers which are used to improve system parameters (such as reducing steady state error, reducing resonant peak, improving system response by reducing rise time). All these operations can be done by compensators as well, used in cascade compensation technique. Theory Both lead compensators and lag compensators introduce a pole–zero pair into the open loop transfer function. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyquist Stability Criterion
In control theory and stability theory, the Nyquist stability criterion or Strecker–Nyquist stability criterion, independently discovered by the German electrical engineer at Siemens in 1930 and the Swedish-American electrical engineer Harry Nyquist at Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1932, is a graphical technique for determining the stability criterion, stability of a linear dynamical system. Because it only looks at the Nyquist plot of the Open-loop controller, open loop systems, it can be applied without explicitly computing the poles and zeros of either the closed-loop or open-loop system (although the number of each type of right-half-plane Singularity (mathematics), singularities must be known). As a result, it can be applied to systems defined by non-rational functions, such as systems with delays. In contrast to Bode plots, it can handle transfer functions with right half-plane singularities. In addition, there is a natural generalization to more complex systems with M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optimal Control
Optimal control theory is a branch of control theory that deals with finding a control for a dynamical system over a period of time such that an objective function is optimized. It has numerous applications in science, engineering and operations research. For example, the dynamical system might be a spacecraft with controls corresponding to rocket thrusters, and the objective might be to reach the Moon with minimum fuel expenditure. Or the dynamical system could be a nation's economy, with the objective to minimize unemployment; the controls in this case could be fiscal and monetary policy. A dynamical system may also be introduced to embed operations research problems within the framework of optimal control theory. Optimal control is an extension of the calculus of variations, and is a mathematical optimization method for deriving control policies. The method is largely due to the work of Lev Pontryagin and Richard Bellman in the 1950s, after contributions to calculus of v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fail-safe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that, in the event of a failure causes, failure of the design feature, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent safety to a particular hazard, a system being "fail-safe" does not mean that failure is naturally inconsequential, but rather that the system's design prevents or mitigates unsafe consequences of the system's failure. If and when a "fail-safe" system fails, it remains at least as safe as it was before the failure. Since many types of failure are possible, failure mode and effects analysis is used to examine failure situations and recommend safety design and procedures. Some systems can never be made fail-safe, as continuous availability is needed. Redundancy (engineering), Redundancy, fault tolerance, or contingency plans are used for these situations (e.g. multiple independently controlled and fuel-fed engines). Examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loop Tuning
Loop or LOOP may refer to: Brands and enterprises * Loop (mobile), a Bulgarian virtual network operator and co-founder of Loop Live * Loop, clothing, a company founded by Carlos Vasquez in the 1990s and worn by Digable Planets * Loop Mobile, an Indian mobile phone operator * Loop Internet, an internet service provider in Pennsylvania, United States * Loop, a reusable container program announced in 2019 by TerraCycle Geography * Loop, Germany, a municipality in Schleswig-Holstein * Loop (Texarkana), a roadway loop around Texarkana, Arkansas, United States * Loop, Blair County, Pennsylvania, United States * Loop, Indiana County, Pennsylvania, United States * Loop, West Virginia, United States * Loop 101, a semi-beltway of the Phoenix Metropolitan Area * Loop 202, a semi-beltway of the Phoenix Metropolitan Area * Loop 303, a semi-beltway of the Phoenix Metropolitan Area * Chicago Loop, the downtown neighborhood of Chicago bounded by the elevated railway The Loop ** Loo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weighted Sum
A weight function is a mathematical device used when performing a sum, integral, or average to give some elements more "weight" or influence on the result than other elements in the same set. The result of this application of a weight function is a weighted sum or weighted average. Weight functions occur frequently in statistics and analysis, and are closely related to the concept of a measure. Weight functions can be employed in both discrete and continuous settings. They can be used to construct systems of calculus called "weighted calculus" and "meta-calculus".Jane Grossma''Meta-Calculus: Differential and Integral'' , 1981. Discrete weights General definition In the discrete setting, a weight function w \colon A \to \R^+ is a positive function defined on a discrete set A, which is typically finite or countable. The weight function w(a) := 1 corresponds to the ''unweighted'' situation in which all elements have equal weight. One can then apply this weight to various conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |