|
Property Tax In The United States
Most local governments in the United States impose a property tax, also known as a millage rate, as a principal source of revenue. This tax may be imposed on real estate or personal property. The tax is nearly always computed as the fair market value of the property times an assessment ratio times a tax rate, and is generally an obligation of the owner of the property. Values are determined by local officials, and may be disputed by property owners. For the taxing authority, one advantage of the property tax over the sales tax or income tax is that the revenue always equals the tax levy, unlike the other taxes. The property tax typically produces the required revenue for municipalities' tax levies. A disadvantage to the taxpayer is that the tax liability is fixed, while the taxpayer's income is not. The tax is administered at the local government level. Many states impose limits on how local jurisdictions may tax property. Because many properties are subject to tax by mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
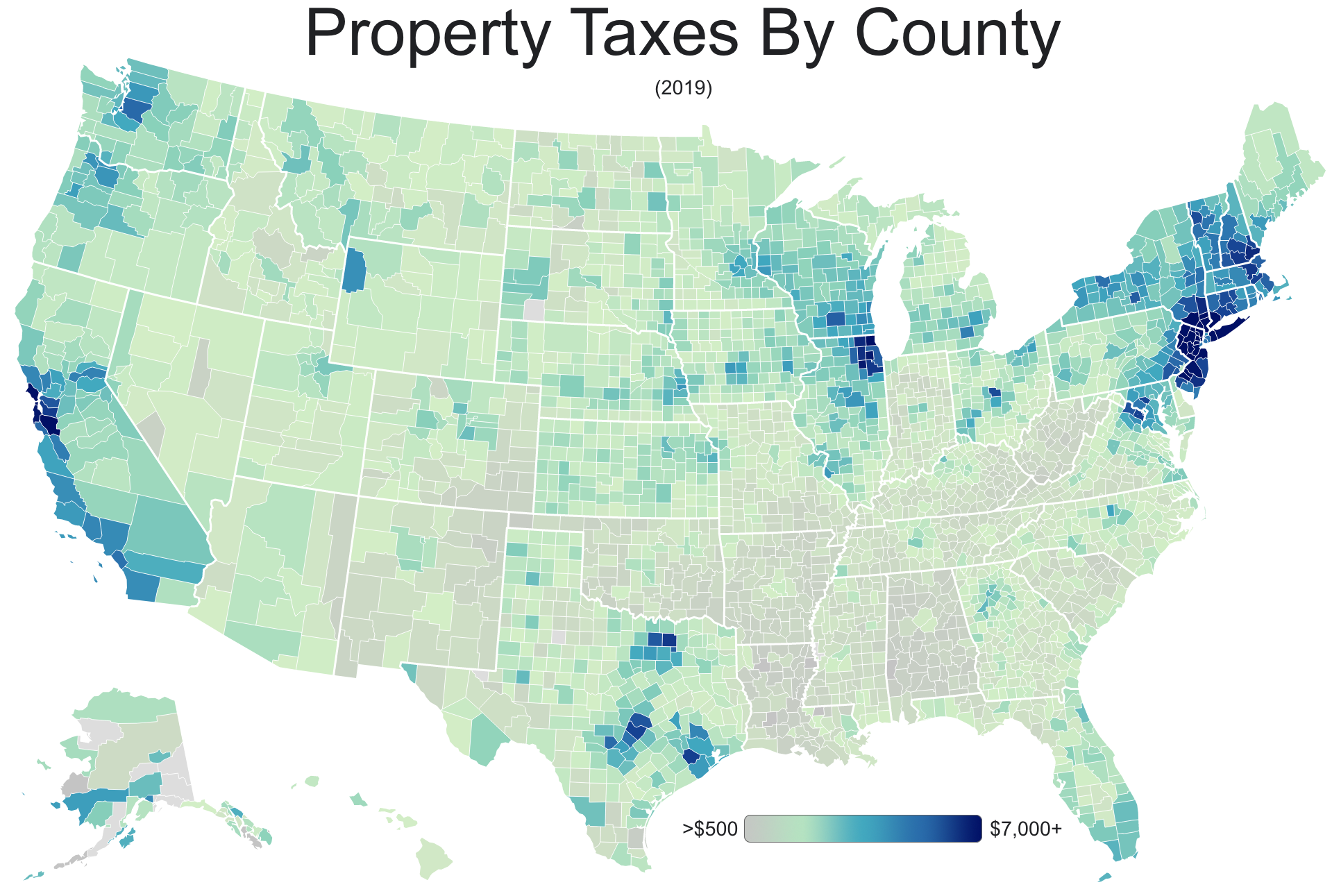
Property Taxes By County
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, redefine, rent, mortgage, pawn, sell, exchange, transfer, give away or destroy it, or to exclude others from doing these things, as well as to perhaps abandon it; whereas regardless of the nature of the property, the owner thereof has the right to properly use it under the granted property rights. In economics and political economy, there are three broad forms of property: private property, public property, and collective property (also called cooperative property). Property that jointly belongs to more than one party may be possessed or controlled thereby in very similar or very distinct ways, whether simply or complexly, whether equally or unequally. However, there is an expectation that each party's will (rather discretion) with rega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than city, cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world. Origin and use The word "town" shares an origin with the German language, German word , the Dutch language, Dutch word , and the Old Norse . The original Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic word, *''tūnan'', is thought to be an early borrowing from Proto-Celtic language, Proto-Celtic *''dūnom'' (cf. Old Irish , Welsh language, Welsh ). The original sense of the word in both Germanic and Celtic was that of a fortress or an enclosure. Cognates of ''town'' in many modern Germanic languages designate a fence or a hedge. In English and Dutch, the meaning of the word took on the sense of the space which these fences enclosed, and through which a track must run. In England, a town was a small community that could not afford or was not allowed to build walls or other larger fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tax Sale
A tax sale is the forced sale of property (usually real estate) by a governmental entity for unpaid taxes by the property's owner. The sale, depending on the jurisdiction, may be a tax deed sale (whereby the actual property is sold) or a tax lien sale (whereby a lien on the property is sold) Under the tax lien sale process, depending on the jurisdiction, after a specified period of time if the lien is not redeemed, the lienholder may seek legal action which will result in the lienholder either automatically obtaining the property, or forcing a future tax deed sale of the property and possibly obtaining the property as a result. General The governmental entity can be any level of government that can assess and collect property taxes or other governmental debt, such as counties (parishes, in the case of Louisiana), cities, townships (in New England and other jurisdictions), and school districts (in places where they are independent of other governmental jurisdictions, such as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homestead Exemption
The homestead exemption is a legal regime to protect the value of the homes of residents from property taxes, creditors, and circumstances that arise from the death of the homeowner's spouse. Such laws are found in the statutes or the constitution of many of the states in the United States. The homestead exemption in some states of the South has its legal origins in the exemption laws of the Spanish Empire. In other states, they were enacted in response to the effects of 19th-century economy. Description Homestead exemption laws typically have four primary features: # Preventing the forced sale of a home to meet the demands of creditors, usually except mortgages, mechanics liens, or sales to pay property taxes # Providing the surviving spouse with shelter # Providing an exemption from property taxes on a home # Allowing a tax-exempt homeowner to vote on property tax increases to homeowners over the threshold, by bond or millage requests For the purposes of statutes, a ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proposition 13
Proposition 13 (officially named the People's Initiative to Limit Property Taxation) is an amendment of the Constitution of California enacted during 1978, by means of the initiative process. The initiative was approved by California voters on June 6, 1978. It was upheld as constitutional by the United States Supreme Court in the case of ''Nordlinger v. Hahn'', . Proposition 13 is embodied in Article XIII A of the Constitution of the State of California. The most significant portion of the act is the first paragraph, which limits the tax rate for real estate: The proposition decreased property taxes by assessing values at their 1976 value and restricted annual increases of assessed value to an inflation factor, not to exceed 2% per year. It prohibits reassessment of a new base year value except in cases of (a) change in ownership, or (b) completion of new construction. These rules apply equally to all real estate, residential and commercial—whether owned by individuals or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
.jpg)
.jpg)
