|
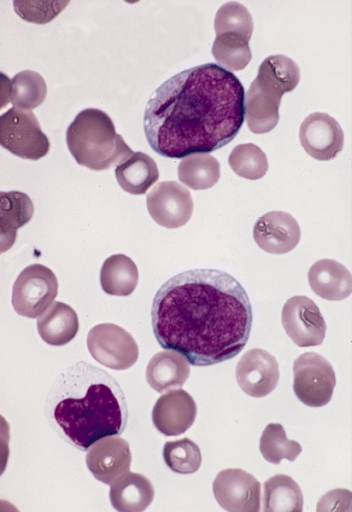
Promegakaryocyte
A promegakaryocyte is a precursor cell for a megakaryocyte, the development of which proceeds as follows: : CFU-Meg (hematopoietic stem cell/hemocytoblast) → megakaryoblast → promegakaryocyte → megakaryocyte Promegakaryocytes and other precursor cells to megakaryocytes arise from pluripotential hematopoietic progenitors, also known as hemocytoblasts. The megakaryoblast is then produced, followed by the promegakaryocyte, the granular megakaryocyte, and then the mature megakaryocyte. When it is in its promegakaryocyte stage, it is considered an undifferentiated cell. When the megakaryoblast matures into the promegakaryocyte, it undergoes endoreduplication and forms a promegakaryocyte which has multiple nuclei, azurophilic granules, and a basophilic cytoplasm. The promegakaryocyte has rotary motion, but no forward migration. Megakaryocyte pieces will eventually break off and begin circulating the body as platelets. Platelets are very important because of their role in bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megakaryoblast
A megakaryoblast () is a precursor cell to a promegakaryocyte. During thrombopoiesis, the promegakaryocyte matures into the form of a megakaryocyte. From the megakaryocyte, platelets are formed. The megakaryoblast is the beginning of the thrombocytic series or platelet forming series. Megakaryoblasts typically have a large oval-shaped nucleus or a nucleus that is lobed with many nuclei. The megakaryoblast resembles the myeloblast or lymphoblast morphologically; however the megakaryoblast varies in phenotype and the structure viewed with electron microscopy. Increased amounts of megakaryoblasts in the bone marrow may indicate a disease state. An example of this is acute megakaryoblastic leukemia, which occurs when the level of megakaryoblasts in the bone marrow exceeds 20%. Development The megakaryocyte develops through the following lineage: : CFU-Meg (hematopoietic stem cell/hemocytoblast) → megakaryoblast → promegakaryocyte → megakaryocyte The megakaryoblast is deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematopoiesis
Haematopoiesis (; ; also hematopoiesis in American English, sometimes h(a)emopoiesis) is the formation of blood cellular components. All cellular blood components are derived from haematopoietic stem cells. In a healthy adult human, roughly ten billion () to a hundred billion () new blood cells are produced per day, in order to maintain steady state levels in the peripheral circulation.Semester 4 medical lectures at Uppsala University 2008 by Leif Jansson Process Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) Haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) reside in the medulla of the bone ( bone marrow) and have the unique ability to give rise to all of the different mature blood cell types and tissues. HSCs are self-renewing cells: when they differentiate, at least some of their daughter cells remain as HSCs so the pool of stem cells is not depleted. This phenomenon is called asymmetric division. The other daughters of HSCs ( myeloid and lymphoid progenitor cells) can follow any of the other diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precursor Cell
In cell biology, precursor cells—also called blast cells—are partially differentiated, or intermediate, and are sometimes referred to as progenitor cells. A precursor cell is a stem cell with the capacity to differentiate into only one cell type, meaning they are unipotent stem cells. In embryology, precursor cells are a group of cells that later differentiate into one organ. However, progenitor cells are considered multipotent. Due to their contribution to the development of various organs and cancers, precursor and progenitor cells have many potential uses in medicine. There is ongoing research on using these cells to build heart valves, blood vessels, and other tissues by using blood and muscle precursor cells. Cytological types * Oligodendrocyte precursor cell * Myeloblast * Thymocyte * Meiocyte * Megakaryoblast * Promegakaryocyte * Melanoblast * Lymphoblast * Bone marrow precursor cells * Normoblast * Angioblast ( endothelial precursor cells) * Myeloid precursor cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basophilic
Basophilic is a technical term used by pathologists. It describes the appearance of cells, tissues and cellular structures as seen through the microscope after a histological section has been stained with a basic dye. The most common such dye is haematoxylin. The name basophilic refers to the characteristic of these structures to be stained very well by basic dyes. This can be explained by their charges. Basic dyes are cationic, i.e. contain positive charges, and thus they stain anionic structures (i.e. structures containing negative charges), such as the phosphate backbone of DNA in the cell nucleus and ribosomes. "Basophils" are cells that "love" (from greek "-phil") basic dyes, for example haematoxylin, azure and methylene blue. Specifically, this term refers to: * basophil granulocytes * anterior pituitary basophils An abnormal increase in basophil granulocytes is therefore also described as basophilia."Basophilia" ''Collins Online Dictionary'' 2024 https://www.colli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Vessel
Blood vessels are the tubular structures of a circulatory system that transport blood throughout many Animal, animals’ bodies. Blood vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to most of the Tissue (biology), tissues of a Body (biology), body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from the tissues. Some tissues such as cartilage, epithelium, and the lens (anatomy), lens and cornea of the eye are not supplied with blood vessels and are termed ''avascular''. There are five types of blood vessels: the arteries, which carry the blood away from the heart; the arterioles; the capillaries, where the exchange of water and chemicals between the blood and the tissues occurs; the venules; and the veins, which carry blood from the capillaries back towards the heart. The word ''vascular'', is derived from the Latin ''vas'', meaning ''vessel'', and is mostly used in relation to blood vessels. Etymology * artery – late Middle English; from Latin ''arteria'', from Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and splitting, but processes such as coalescent angiogenesis, vessel elongation and vessel cooption also play a role. Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors, and from neovascularization, although discussions are not always precise (especially in older texts). The first vessels in the developing embryo form through vasculogenesis, after which angiogenesis is responsible for most, if not all, blood vessel growth during development and in disease. Angiogenesis is a normal and vital process in growth and development, as well as in wound healing and in the formation of granulation tissue. However, it is also a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellular bacteria, protozoa, Parasitic worm, helminths, and Fungus, fungi which could cause serious problems to the health of the host organism if not cleared from the body. In addition, there are other forms of immune response. For example, harmless exogenous factors (such as pollen and food components) can trigger allergy; latex and metals are also known allergens. A transplanted tissue (for example, blood) or organ can cause graft-versus-host disease. A type of immune reactivity known as Rh disease can be observed in pregnant women. These special forms of immune response are classified as hypersensitivity. Another special form of immune response is CD4+ T cells and antitumor immunity, antitumor immunity. In general, there are two branches of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Clotting
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a thrombus, blood clot. It results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The process of coagulation involves Platelet-activating factor, activation, Cell adhesion, adhesion and aggregation of platelets, as well as deposition and maturation of fibrin. Coagulation begins almost instantly after an injury to the endothelium that lines a blood vessel. Exposure of blood to the subendothelial space initiates two processes: changes in platelets, and the exposure of subendothelial Tissue factor, platelet tissue factor to coagulation factor VII, which ultimately leads to cross-linked fibrin formation. Platelets immediately form a plug at the site of injury; this is called ''primary hemostasis. Secondary hemostasis'' occurs simultaneously: additional coagulation factors beyond factor VII (#Coagulation factors, listed below) respond in a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or Lung, lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact agranulocyte, mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion (medicine), adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multinucleate
Multinucleate cells (also known as multinucleated cells or polynuclear cells) are eukaryotic cells that have more than one nucleus, i.e., multiple nuclei share one common cytoplasm. Mitosis in multinucleate cells can occur either in a coordinated, synchronous manner where all nuclei divide simultaneously or asynchronously where individual nuclei divide independently in time and space. Certain organisms may have a multinuclear stage of their life cycle. For example, slime molds have a vegetative, multinucleate life stage called a plasmodium. Multinucleate cells, depending on the mechanism by which they are formed, can be divided into "syncytia" (formed by cell fusion) or " coenocytes" (formed by nuclear division not being followed by cytokinesis). Some bacteria, such as '' Mycoplasma pneumoniae'', a pathogen of the respiratory tract, may display multinuclear filaments as a result of a delay between genome replication and cellular division. Terminology Some biologists use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azurophilic Granule
An azurophilic granule is a cellular object readily stainable with a Romanowsky stain. In white blood cells and hyperchromatin, staining imparts a burgundy or merlot coloration. Neutrophils in particular are known for containing azurophils loaded with a wide variety of anti-microbial defensins that fuse with phagocytic vacuoles. Azurophils may contain myeloperoxidase, phospholipase A2, acid hydrolases, elastase, defensins, neutral serine proteases, bactericidal permeability-increasing protein, lysozyme, cathepsin G, proteinase 3, and proteoglycans. Azurophil granules are also known as "primary granules". Furthermore, the term "azurophils" may refer to a unique type of cells, identified only in reptiles. These cells are similar in size to so-called heterophils with abundant cytoplasm that is finely to coarsely granular and may sometimes contain vacuoles. Granules may impart a purplish hue to the cytoplasm, particularly to the outer region. Occasionally, azurophils are o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |