|
Projection Screen
A projection screen is an installation consisting of a surface and a support structure used for displaying a projected image for the view of an audience. Projection screens may be permanently installed on a wall, as in a movie theater, mounted to or placed in a ceiling using a rollable projection surface that retracts into a casing (these can be motorized or manually operated), painted on a wall, or portable with tripod or floor rising models as in a office, conference room or other non-dedicated viewing space. Another popular type of portable screens are inflatable screens for outdoor movie screening (Outdoor cinema, open-air cinema). Uniformly white or grey screens are used almost exclusively as to avoid any discoloration to the image, while the most desired brightness of the screen depends on a number of variables, such as the low-key lighting, ambient light level and the luminous power of the image source. Flat or curved screens may be used depending on the optics used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sala De Cine
Sala or SALA may refer to: Places Europe * Sala, the historical name of the river IJssel and home of the Salii Franks * Sala (Estonian island), one of the Uhtju islands * Sala Baganza, a municipality in Emilia-Romagna, Italy * Sala Bolognese, a municipality in Emilia-Romagna, Italy * Sala Consilina, a municipality in Campania, Italy * Sala Municipality, Latvia, a municipality in Latvia * Sala, Sala Parish, a village in Latvia, an administrative centre of Sala municipality * Šaľa, Slovakia, a city in Slovakia * Sala Municipality, Sweden, a municipality in Sweden * Sala, Sweden, a city in Sweden, seat of Sala Municipality * Sala Parish (other), parishes (''socken'') in Sweden Africa * Salé (), Morocco * Chellah, Sala, an ancient city at Rabat#Ancient Sala, Rabat, Morocco * Sala, Houet, a village in Satiri Department, Houet Province, Burkina Faso * Sala, Ziro, a village in Ziro Province, Burkina Faso * Sala Colonia, a Phoenician and Roman colony whose ruins are located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slide Projector
A slide projector is an optical device for projecting enlarged images of photographic slides onto a screen. Many projectors have mechanical arrangements to show a series of slides loaded into a special tray sequentially. 35 mm slide projectors, direct descendants of the larger-format magic lantern, first came into widespread use during the 1950s for slide shows as home entertainment, and for use by educational and other institutes. Reversal film created a small positive projectable image rather than the negatives used since the early days of photography; photography now produced 35mm directly viewable small colour slides, rather than large monochrome negatives. The slide images were too small for unaided viewing, and required enlargement by a projector or enlarging viewer. Photographic film slides and projectors have been replaced by image files on digital storage media shown on a projection screen by using a video projector, or displayed on a large-screen video ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast Sensitivity
Contrast is the difference in luminance or color that makes an object (or its representation in an image or display) visible against a background of different luminance or color. The human visual system is more sensitive to contrast than to absolute luminance; thus, we can perceive the world similarly despite significant changes in illumination throughout the day or across different locations. The maximum contrast of an image is termed the contrast ratio or dynamic range. In images where the contrast ratio approaches the maximum possible for the medium, there is a ''conservation of contrast''. In such cases, increasing contrast in certain parts of the image will necessarily result in a decrease in contrast elsewhere. Brightening an image increases contrast in darker areas but decreases it in brighter areas; conversely, darkening the image will have the opposite effect. Bleach bypass reduces contrast in the darkest and brightest parts of an image while enhancing luminance contras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
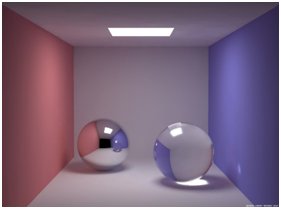
Specular Reflection
Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection (physics), reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface. The law of reflection states that a reflected ray (optics), ray of light emerges from the reflecting surface at the same angle to the surface normal as the incident ray, but on the opposing side of the surface normal in the plane formed by the incident and reflected rays. The earliest known description of this behavior was recorded by Hero of Alexandria (Anno Domini, AD c. 10–70). Later, Ibn al-Haytham, Alhazen gave a complete statement of the law of reflection. He was first to state that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in a same plane perpendicular to reflecting plane. Specular reflection may be contrasted with diffuse reflection, in which light is scattered away from the surface in a range of directions. Law of reflection When light encounters a boundary of a material, it is affected by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror
A mirror, also known as a looking glass, is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror forms an image of whatever is in front of it, which is then focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the direction of light at an angle equal to its incidence. This allows the viewer to see themselves or objects behind them, or even objects that are at an angle from them but out of their field of view, such as around a corner. Natural mirrors have existed since Prehistory, prehistoric times, such as the surface of water, but people have been manufacturing mirrors out of a variety of materials for thousands of years, like stone, metals, and glass. In modern mirrors, metals like silver or aluminium are often used due to their high reflectivity, applied as a thin coating on glass because of its naturally smooth and very Hardness (materials science), hard surface. A mirror is a Wave (physics), wave reflector. Light consists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloss (material Appearance)
Gloss is an optical property which indicates how well a surface reflects light in a specular (mirror-like) direction. It is one of the important parameters that are used to describe the visual appearance of an object. Other categories of visual appearance related to the perception of regular or diffuse reflection and transmission of light have been organized under the concept of '' cesia'' in an order system with three variables, including gloss among the involved aspects. The factors that affect gloss are the refractive index of the material, the angle of incident light and the surface texture. Apparent gloss depends on the amount of ''specular'' reflection – light reflected from the surface in an equal amount and the symmetrical angle to the one of incoming light – in comparison with ''diffuse'' reflection – the amount of light scattered into other directions. Theory When light illuminates an object, it interacts with it in a number of ways: * Absorbed within it (l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barium Sulfate
Barium sulfate (or sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba SO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is odorless and insoluble in water. It occurs in nature as the mineral barite, which is the main commercial source of barium and materials prepared from it. Its opaque white appearance and its high density are exploited in its main applications.Holleman, A. F. and Wiberg, E. (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', San Diego, CA. Academic Press, . Uses Drilling fluids About 80% of the world's barium sulfate production, mostly purified mineral, is consumed as a component of oil well drilling fluid. It increases the density of the fluid, increasing the hydrostatic pressure in the well and reducing the chance of a blowout. Radiocontrast agent Barium sulfate in suspension is often used medically as a radiocontrast agent for X-ray imaging and other diagnostic procedures. It is most often used in imaging of the GI tract during what is colloquially known as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index International, CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble in water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structures of rutile and anatase are tetragonal in symmetry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
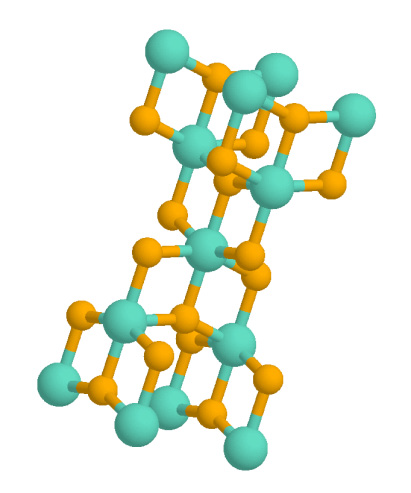
Magnesium Carbonate
Magnesium carbonate, (archaic name magnesia alba), is an inorganic salt that is a colourless or white solid. Several hydrated and Base (chemistry), basic forms of magnesium carbonate also exist as minerals. Forms The most common magnesium carbonate forms are the anhydrous salt called magnesite (), and the di, tri, and pentahydrates known as barringtonite (), nesquehonite (), and lansfordite (), respectively. Some basic forms such as artinite (), hydromagnesite (), and dypingite () also occur as minerals. All of those minerals are colourless or white. Magnesite consists of colourless or white trigonal crystals. The anhydrous salt is practically insoluble in water, acetone, and ammonia. All forms of magnesium carbonate react with acids. Magnesite crystallizes in the calcite structure wherein magnesium, is Coordination geometry#Crystallography usage, surrounded by six oxygen atoms. The dihydrate has a triclinic structure, while the trihydrate has a monoclinic structure. Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gain (projection Screens)
Gain is a property of a projection screen and is one of the specifications quoted by projection screen manufacturers. Interpretation The measured number is called the peak gain at zero degrees viewing axis. It represents the gain value for a viewer seated along a line perpendicular to the screen's viewing surface. The gain value represents the screen's brightness ratio relative to a set standard (in this case, a sheet of magnesium carbonate Magnesium carbonate, (archaic name magnesia alba), is an inorganic salt that is a colourless or white solid. Several hydrated and Base (chemistry), basic forms of magnesium carbonate also exist as minerals. Forms The most common magnesium car ...). Screens with a higher brightness than this standard are rated with a gain higher than 1.0, while screens with lower brightness are rated from 0.0 to 1.0. Since a projection screen is designed to scatter the impinging light back to the viewers, the scattering can be highly diffuse or highly con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflatable Movie Screen
An inflatable movie screen is an inflatable framework with an attached projection screen. Inflatable screens are used for outdoor movies, film festivals, drive-in theaters, sports, social, fundraising and other events requiring outdoor projection. Design The projection frame is made from PVC-coated fabric layers joined by high-frequency welding or mechanical sewing. The projection surface can be made of PVC or spandex, with the latter providing for rear projection capabilities. The projection surface can be detachable for ease of care. The frame is inflated with a high-pressure air blower. Larger frames may require a three-phase blower. For bigger screens, the blower typically continues to operate, ensuring the screen remains fully inflated. With some brands, screen sizes up to 7m or 24ft width do not require a constantly operating air blower. Screens can be held upright with help of a supporting structure (A-frame or inflatable legs) or with the system of straps and counte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |