|
Principes Fondamentaux Reconnus Par Les Lois De La République
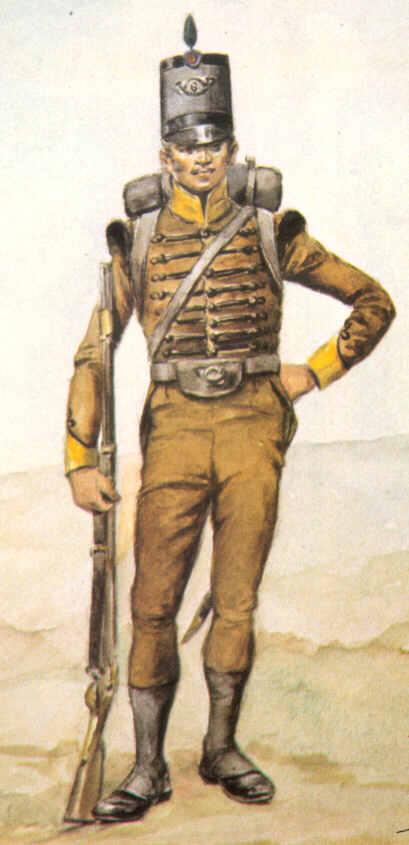
''Principes'' (Singular: ''princeps'') were spearmen, and later swordsmen, in the armies of the early Roman Republic. They were men in the prime of their lives who were fairly wealthy, and could afford decent equipment. They were the heavier infantry of the legion who carried large shields and wore good quality armor. Their usual position was the second battle line. They fought in a quincunx formation, supported by light troops. They were eventually disbanded after the Marian reforms of 107 BC. History and deployment According to Pat Southern, ''principes'' appear to have been born from remnants of the old second class of the army under the Etruscan kings when it was reformed by Marcus Furius Camillus. The second class stood in some of the first few ranks of a very large phalanx and were equipped in a similar manner to ''principes''. They would support the heavier first class in the front ranks. It is probable that engagements with the Samnites and a crushing defeat at the hand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spearmen
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastened to the shaft, such as bone, flint, obsidian, iron, steel, or bronze. The most common design for hunting or combat spears since ancient times has incorporated a metal spearhead shaped like a triangle, lozenge, or leaf. The heads of fishing spears usually feature barbs or serrated edges. The word ''spear'' comes from the Old English '' spere'', from the Proto-Germanic ''speri'', from a Proto-Indo-European root ''*sper-'' "spear, pole". Spears can be divided into two broad categories: those designed for thrusting as a melee weapon and those designed for throwing as a ranged weapon (usually referred to as javelins or darts). The spear has been used throughout human history both as a hunting and fishing tool and as a weapon. Along wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scutum (shield)
The ''scutum'' (; plural ''scuta'') was a type of shield used among Italic peoples in antiquity, most notably by the army of ancient Rome starting about the fourth century BC. The Romans adopted it when they switched from the military formation of the hoplite phalanx of the Greeks to the formation with maniples ( la, manipuli). In the former, the soldiers carried a round shield, which the Romans called a '' clipeus''. In the latter, they used the ''scutum'', which was larger. Originally it was oblong and convex, but by the first century BC it had developed into the rectangular, semi-cylindrical shield that is popularly associated with the ''scutum'' in modern times. This was not the only kind the Romans used; Roman shields were of varying types depending on the role of the soldier who carried it. Oval, circular and rectangular shapes were used throughout Roman history. History The first depictions of the scutum are by the Este culture in the 8th century bc, and subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gladius
''Gladius'' () is a Latin word meaning "sword" (of any type), but in its narrow sense it refers to the sword of ancient Roman foot soldiers. Early ancient Roman swords were similar to those of the Greeks, called '' xiphe'' (plural; singular ''xiphos''). From the 3rd century BC, however, the soldiers of the Roman Republic adopted a sword based on the celtic sword used by the Celtiberians in Hispania late into the Punic Wars, known in Latin as the ''gladius hispaniensis'', meaning "Hispanic-type sword". New variants of the gladius, such as the "Mainz gladius" and the "Pompeii gladius", were used from the first century AD and during the early centuries of the Roman Empire; in the third century AD the gladius was replaced by the " spatha". A fully equipped Roman legionary after the reforms of Gaius Marius was armed with a shield ('' scutum''), one or two javelins ('' pila''), a sword (''gladius''), often a dagger ('' pugio''), and, perhaps in the later empire period, darts (''plumba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of wars between 264 and 146BC fought between Rome and Carthage. Three conflicts between these states took place on both land and sea across the western Mediterranean region and involved a total of forty-three years of warfare. The Punic Wars are also considered to include the four-year-long revolt against Carthage which started in 241BC. Each war involved immense materiel and human losses on both sides. The First Punic War broke out on the Mediterranean island of Sicily in 264BC as a result of Rome's expansionary attitude combined with Carthage's proprietary approach to the island. At the start of the war Carthage was the dominant power of the western Mediterranean, with an extensive maritime empire, while Rome was a rapidly expanding power in Italy, with a strong army but no navy. The fighting took place primarily on Sicily and its surrounding waters, as well as in North Africa, Corsica and Sardinia. It lasted 23 years, until 241BC, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accensi
The term ''accensi'' (Singular: ''accensus'') is applied to two different groups. Originally, the ''accensi'' were light infantry in the armies of the early Roman Republic. They were the poorest men in the legion, and could not afford much equipment. They did not wear armour or carry shields, and their usual position was part of the third battle line. They fought in a loose formation, supporting the heavier troops. They were eventually phased out by the time of Second Punic War. In the later Roman Republic the term was used for civil servants who assisted the elected magistrates, particularly in the courts, where they acted as ushers and clerks. Infantry History and deployment ''Accensi'' appear to have evolved from the old fifth class of the army under the Etruscan kings when it was reformed by Marcus Furius Camillus. The fifth class was made up of the poorest soldiers in the legion who were equipped with slings and perhaps a small shield. They acted as skirmishers, scree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rorarii
''Rorarii'' were soldiers who formed the final lines, or else provided a reserve thereby, in the ancient pre-Marian Roman army. They may have been used with the ''triarii'' in battle near the final stages of fighting, since they are recorded as being located at the rear of the main battle formation. They may have been similar in role to the '' accensi'', acting as supernumeraries and filling the places of fallen soldiers as a battle or campaign wore on. Alternatively, they may have been skirmishers akin to ''velites'' as stated by Livy in Book VIII.8. Unfortunately, the evidence is so limited that it is difficult to understand what direct role the ''rorarii'' may have had, if any, in fighting. It seems most likely that they were not part of the line in the same way as ''triarii'', ''principes'' and ''hastati'' were. They may also have been the light equivalent of the ''triarii'', just like the ''accensi'' would have been the light equivalent of the ''principes'', both ''rorarii'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equites
The ''equites'' (; literally "horse-" or "cavalrymen", though sometimes referred to as "knights" in English) constituted the second of the property-based classes of ancient Rome, ranking below the senatorial class. A member of the equestrian order was known as an ''eques'' (). Description During the Roman kingdom and the first century of the Roman Republic, legionary cavalry was recruited exclusively from the ranks of the patricians, who were expected to provide six '' centuriae'' of cavalry (300 horses for each consular legion). Around 400BC, 12 more ''centuriae'' of cavalry were established and these included non-patricians (plebeians). Around 300 BC the Samnite Wars obliged Rome to double the normal annual military levy from two to four legions, doubling the cavalry levy from 600 to 1,200 horses. Legionary cavalry started to recruit wealthier citizens from outside the 18 ''centuriae''. These new recruits came from the first class of commoners in the Centuriate Assembly or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Infantry
Light infantry refers to certain types of lightly equipped infantry throughout history. They have a more mobile or fluid function than other types of infantry, such as heavy infantry or line infantry. Historically, light infantry often fought as scouts, raiders, and skirmishers. These are loose formations that fight ahead of the main army to harass, delay, disrupt supply lines, engage the enemy’s own skirmishing forces, and generally "soften up" an enemy before the main battle. Light infantrymen were also often responsible for screening the main body of a military formation. Post-World War II, the term "light infantry" evolved to include rapid-deployment units (including commandos and airborne units) that emphasize speed and mobility over armor and firepower. Some units or battalions that historically held a skirmishing role have kept their designation "light infantry" for the sake of tradition. History Ancient history The concept of a skirmishing screen is a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leves
''Leves'' (Singular: ''Levis'') were javelin-armed skirmishers in the army of the early Roman Republic. They were typically some of the youngest and poorest men in the legion, and could not afford much equipment. They were usually outfitted with just a number of light javelins and no other equipment. There were 300 leves in a legion, and unlike other infantry types they did not form their own units, but were assigned to units of ''hastati'' – heavier sword-armed troops. Their primary purpose on the battlefield was to harass the enemy with javelin fire and support the heavy infantry who fought in hand-to-hand combat. ''Accensi'' and ''rorarii'' were also light missile troops and had similar roles. History and deployment ''Leves'' appear to have evolved from the old poor classes of the army under the Etruscan kings when it was reformed by Marcus Furius Camillus ca. 386 BC. These soldiers stood at the rear of a very large phalanx and were equipped in a similar manner to ''lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
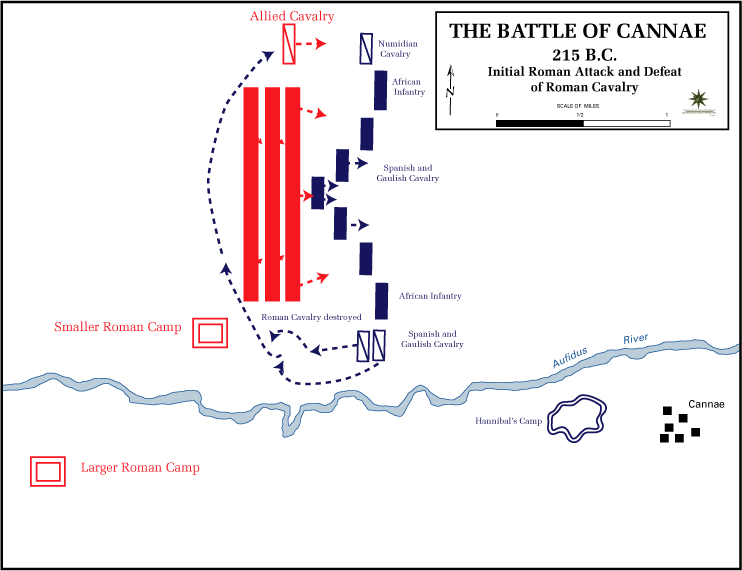
Pitched Battle
A pitched battle or set-piece battle is a battle in which opposing forces each anticipate the setting of the battle, and each chooses to commit to it. Either side may have the option to disengage before the battle starts or shortly thereafter. A pitched battle is not a chance encounter such as a meeting engagement, or where one side is forced to fight at a time not of its choosing such as happens in a siege or an ambush. Pitched battles are usually carefully planned, to maximize one's strengths against an opponent's weaknesses, and use a full range of deceptions, feints, and other manoeuvres. They are also planned to take advantage of terrain favourable to one's force. Forces strong in cavalry for example will not select swamp, forest, or mountain terrain for the planned struggle. For example, Ancient Carthage, Carthaginian general Hannibal selected relatively flat ground near the village of Cannae for his great confrontation with the Romans, not the rocky terrain of the high Apen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hastati
''Hastati'' (singular: ''hastatus'') were a class of infantry employed in the armies of the early Roman Republic, who originally fought as spearmen and later as swordsmen. These soldiers were the staple unit after Rome threw off Etruscan rule. They were originally some of the poorest men in the legion, and could afford only modest equipment—light chainmail and other miscellaneous equipment. The Senate supplied their soldiers with only a short stabbing sword, the gladius, and their distinctive squared shield, the scutum. The ''hastatus'' was typically equipped with these, and one or two soft iron tipped throwing spears called pila. This doubled their effectiveness, not only as a strong leading edge to their maniple, but also as a stand-alone missile troop. Later, the ''hastati'' contained the younger men rather than just the poorer, though most men of their age were relatively poor. Their usual position was the first battle line. They fought in a quincunx formation, suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


-Segunda_Edad_del_Hierro.jpg)