|
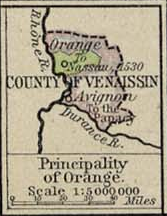
Principality Of Orange
The Principality of Orange (French language, French: Principauté d'Orange) was, from 1163 to 1713, a feudal state in Provence, in the south of modern-day France, on the east bank of the river Rhone, north of the city of Avignon, and surrounded by the independent papal state of Comtat Venaissin. It was constituted in 1163, when Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick I elevated the Kingdom of Burgundy, Burgundian County of Orange (consisting of the Orange, Vaucluse, city of Orange and the land surrounding it) to a imperial immediacy, sovereign principality within the Empire. The principality became part of the scattered holdings of the house of Orange-Nassau from the time that William the Silent inherited the title of Prince of Orange from René of Châlon, his cousin in 1544, until it was finally ceded to France in 1713 under the Treaty of Utrecht (1713), Treaty of Utrecht. Although permanently lost by the Nassaus then, this fief gave its name to the exta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vassal State
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to the era of the Egyptian, Hittite, and Mitanni conflict, as well as in ancient China. The relationships between vassal rulers and empires were dependent on the policies and agreements of each empire. While the payment of tribute and military service was common amongst vassal states, the degree of independence and benefits given to vassal states varied. Today, more common terms are puppet state, protectorate, client state, associated state, or satellite state. Historical examples Ancient Egypt The reign of Thutmose III (1479 BC – 1425 BC) laid the foundations for the systems that functioned during the Amarna period of Egypt. Vassal states in the Levant became fully integrated in Egypt's economy with the construction of harbours � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Principality
A principality (or sometimes princedom) is a type of monarchy, monarchical state or feudalism, feudal territory ruled by a prince or princess. It can be either a sovereign state or a constituent part of a larger political entity. The term "principality" is often used to describe small monarchies, particularly those in Europe, where the ruler holds the title of prince or an equivalent. Historically, principalities emerged during the Middle Ages as part of the feudal system, where local princes gained significant power within a king's domain. This led to political fragmentation and the creation of mini-states. Over time, many of these principalities consolidated into larger Monarchy, kingdoms and empires, while others retained their independence and prospered. Sovereign principalities which exist today include Liechtenstein, Monaco, and the co-principality of Andorra. Additionally, some royal primogenitures, such as Asturias in Spain, are styled as principalities. The term is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mary Of Baux-Orange
Mary of Baux-Orange (died 1417) was ''suo jure'' Princess of Orange. She was the last holder of this title from the House of Baux. Life Marie was the only child and therefore the sole heiress of Raymond V of Baux and Joan of Geneva. On 11 April 1386, she married John III, the son of Louis I, Lord of Chalon-Arlay and Margaret of Vienne. They had: * Louis II, nicknamed ''Louis the Good'' (1390-1463) Mary died in 1417 in Orange and was buried in ''L'église des Cordeliers'' at Lons-le-Saunier. Her husband died in 1418. Louis II inherited Chalon-Arlay from his father and Baux-Orange, including the Principality of Orange, from his mother. He claimed to have also inherited the County of Geneva via his grandmother, but lost a lengthy legal battle over this claim against the House of Savoy The House of Savoy (, ) is a royal house (formally a dynasty) of Franco-Italian origin that was established in 1003 in the historical region of Savoy, which was originally part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
King Of Arles
The following is a list of the kings of the two kingdoms of Burgundy, and a number of related political entities devolving from Carolingian machinations over family relations. Kings of the Burgundians * Gebicca (late 4th century – c. 407) *Gundomar I (c. 407 – 411), son of Gebicca * Giselher (c. 407 – 411), son of Gebicca *Gunther (c. 407 – 436), son of Gebicca ''Flavius Aëtius moves the Burgundians into Sapaudia ( Upper Rhône Basin)''. * Gunderic/Gundioc (436–473) opposed by **Chilperic I, brother of Gundioc (443–c. 480) *division of the kingdom among the four sons of Gundioc: **Gundobad (473–516 in Lyon, king of all of Burgundy from 480), **Chilperic II (473–493 in Valence) ** Godomar I (473–486 in Vienne) **Godegisel (473–500, in Vienne and Geneva) *Sigismund, son of Gundobad (516–523) *Godomar or Gundomar, son of Gundobad (523–534) Frankish kings in Burgundy ''Gradually conquered by the Franki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arles
Arles ( , , ; ; Classical ) is a coastal city and Communes of France, commune in the South of France, a Subprefectures in France, subprefecture in the Bouches-du-Rhône Departments of France, department of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region, in the former Provinces of France, province of Provence. A large part of the Camargue, the largest wetlands in France, is located within the territory of the commune, which is the List of French communes by surface area, largest in Metropolitan France in terms of geographic territory. In non-metropolitan France, Maripasoula in French Guiana is the largest French commune in general. The commune's land area is roughly similar to that of Singapore. The city has a long history, and was of considerable importance in the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis. The Arles, Roman and Romanesque Monuments, Roman and Romanesque Monuments of Arles were listed as UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 1981 for their testimony to the his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles IV (; ; ; 14 May 1316 – 29 November 1378''Karl IV''. In: (1960): ''Geschichte in Gestalten'' (''History in figures''), vol. 2: ''F–K''. 38, Frankfurt 1963, p. 294), also known as Charles of Luxembourg, born Wenceslaus (, ), was Holy Roman Emperor from 1355 until his death in 1378. He was elected King of Germany (King of the Romans) in 1346 and became King of Bohemia (as Charles I) that same year. He was a member of the House of Luxembourg from his father's side and the Bohemian House of Přemyslid from his mother's side; he emphasized the latter due to his lifelong affinity for the Bohemian side of his inheritance, and also because his direct ancestors in the Přemyslid line included two saints. He was the eldest son and heir of John of Bohemia, King of Bohemia and Count of Luxembourg, who died at the Battle of Crécy on 26 August 1346. His mother, Elizabeth of Bohemia (1292–1330), Elizabeth, Queen of Bohemia, was the sister of Wenceslaus III of Bohemia, W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal allegiance, services or payments. The fees were often lands, land revenue or revenue-producing real property like a watermill, held in feudal land tenure: these are typically known as fiefs or fiefdoms. However, not only land but anything of value could be held in fee, including governmental office, rights of exploitation such as hunting, fishing or felling trees, monopolies in trade, money rents and tax farms. There never existed a standard feudal system, nor did there exist only one type of fief. Over the ages, depending on the region, there was a broad variety of customs using the same basic legal principles in many variations. Terminology In ancient Rome, a " benefice" (from the Latin noun , meaning "benefit") was a gift of land () f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kingdom Of Burgundy-Arles
The Kingdom of Burgundy, known from the 12th century as the Kingdom of Arles, was a realm established in 933 by the merger of the kingdoms of Upper and Lower Burgundy under King Rudolf II. It was incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire in 1033 and from then on was one of the empire's three constituent realms, together with the Kingdom of Germany and the Kingdom of Italy. By the mid-13th century at the latest, however, it had lost its concrete political relevance. Its territory stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the High Rhine River in the north, roughly corresponding to the present-day French regions of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, Rhône-Alpes and Franche-Comté, as well as western Switzerland. Until 1032 it was ruled by independent kings of the Elder House of Welf.''The New Columbia Encyclopedia'' 1975, 150 Carolingian Burgundy Since the conquest of the Ancient Kingdom of Burgundy by the Franks in 534, its territory had been ruled within the Merovingian state, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lords Of Baux
This is a list of the Lords, Barons and Marquisses of Baux. List of rulers of Baux Lords of Baux of the House of Baux * Pons the Younger (born , ) * Hugh I (born after 1059), son of the above * or "Guilhem Uc" (after 10301105), son of the above * Raymond I (before 10951150), son of the above * Hugh II (reigned 11501167; retired to Sardinia where he died in 1179), son of the above * Bertrand I (1167–1181), brother of Hugh II and son of Raymond I * Hugh III (1181–1240), lord of Baux, viscount of Marseille, eldest son of Bertrand I * Barral of Baux (Barral I, 1240–1268), son of Hugh III * Bertrand III (1268–1305), son of the above * Raymond II (1305–1322), son of the above * Hugh IV (1322–1351), son of the above *Robert (1351–1353), son of the above * Raymond III (1353–1372), brother of Robert and son of Hugh IV *John I (1372–1375), son of Raymond III * Alice I (1372–1426), sister of John and daughter of Raymond III This branch of the House of Baux was decla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
States And Territories Disestablished In 1713
State most commonly refers to: * State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory **Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country **Nation state, a state where the majority identify with a single nation (with shared culture or ethnic group) ** Constituent state, a political subdivision of a state ** Federated state, constituent states part of a federation *** U.S. state * State of nature, a concept within philosophy that describes the way humans acted before forming societies or civilizations State may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Literature * '' State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State * ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States * '' Our State'', a monthly magazine published in North Carolina and formerly called ''The State'' * The State (Larry Niven), a fictional future gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
House Of Orange
The House of Orange-Nassau (, ), also known as the House of Orange because of the prestige of the princely title of Orange, also referred to as the Fourth House of Orange in comparison with the other noble houses that held the Principality of Orange, is the current reigning house of the Netherlands. A branch of the European House of Nassau, the house has played a central role in the politics and government of the Netherlands and elsewhere in Europe, particularly since William the Silent organised the Dutch Revolt against Spanish rule, which after the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) led to an independent Dutch state. William III of Orange led the resistance of the Netherlands and Europe to Louis XIV of France and orchestrated the Glorious Revolution in England that established parliamentary rule. Similarly, Queen Wilhelmina of the Netherlands was instrumental in the Dutch resistance during World War II. Several members of the house served during the Eighty Years war and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |