|
Pressure Vessel
A pressure vessel is a container designed to hold gases or liquids at a pressure substantially different from the ambient pressure. Construction methods and materials may be chosen to suit the pressure application, and will depend on the size of the vessel, the contents, working pressure, mass constraints, and the number of items required. Pressure vessels can be dangerous, and fatal accidents have occurred in the history of their development and operation. Consequently, pressure vessel design, manufacture, and operation are regulated by engineering authorities backed by legislation. For these reasons, the definition of a pressure vessel varies from country to country. The design involves parameters such as maximum safe operating pressure and temperature, safety factor, corrosion allowance and minimum design temperature (for brittle fracture). Construction is tested using nondestructive testing, such as ultrasonic testing, radiography, and pressure tests. Hydrostatic pressure t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modified Hanson Steelwatertank
Modified may refer to: *Modified (album), ''Modified'' (album), the second full-length album by Save Ferris *Modified racing, or "Modifieds", an American automobile racing genre See also * Modification (other) * Modifier (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquefied Gas
Liquefied gas (sometimes referred to as liquid gas) is a gas that has been turned into a liquid by cooling or compressing it. Examples of liquefied gases include liquid air, liquefied natural gas, and liquefied petroleum gas. Liquid air At the Lister Institute of Preventive Medicine, liquid air has been brought into use as an agent in biological research. An inquiry into the intracellular constituents of the typhoid bacillus, initiated under the direction of Doctor Allan Macfadyen, necessitated the separation of the cell-plasma of the organism. The method at first adopted for the disintegration of the bacteria was to mix them with silver-sand and churn the whole up in a closed vessel in which a series of horizontal vanes revolved at a high speed. But certain disadvantages attached to this procedure, and accordingly some means was sought to do away with the sand and triturate the bacilli per se. This was found in liquid air, which, as had long before been shown at the Royal Insti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial processes, industrial process Factory, plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refining, refined into products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, Bitumen, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liquefied petroleum gas and petroleum naphtha. Petrochemical feedstock like ethylene and propene, propylene can also be produced directly by Cracking (chemistry), cracking crude oil without the need of using refined products of crude oil such as naphtha. The crude oil feedstock has typically been processed by an oil production plant. There is usually an oil depot at or near an oil refinery for the storage of incoming crude oil feedstock as well as bulk liquid products. In 2020, the total capacity of global refineries for crude oil was about 101.2 million barrels per day. Oil refineries are typically large, sprawling industrial complexes with extensive piping running throughout, carrying streams of fluids b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasibly created Chemical synthesis, artificially in a laboratory or factory. Ores recovered by mining include Metal#Extraction, metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk mining, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. The ore must be a rock or mineral that contains valuable constituent, can be extracted or mined and sold for profit. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even fossil water, water. Modern mining processes involve prospecting for ore bodies, analysis of the profit potential of a proposed mine, extraction of the desired materials, and final mine reclamation, reclamation or restoration of the land after the mine is closed. Mining ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
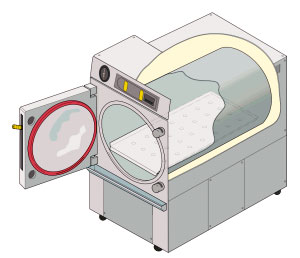
Autoclave
An autoclave is a machine used to carry out industrial and scientific processes requiring elevated temperature and pressure in relation to ambient pressure and/or temperature. Autoclaves are used before surgical procedures to perform sterilization and in the chemical industry to cure coatings and vulcanize rubber and for hydrothermal synthesis. Industrial autoclaves are used in industrial applications, especially in the manufacturing of composites. Many autoclaves are used to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to pressurized saturated steam at for 30–60 minutes at a gauge pressure of 103 kPa depending on the size of the load and the contents. The autoclave was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the steam digester was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek ''auto-'', ultimately meaning self, and Latin ''clavis'' meaning key, thus a self-locking device. Uses Sterilization autoclaves are widely us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Reactor
A pressure reactor, sometimes referred to as a pressure tube, or a sealed tube, is a chemical reaction vessel which can conduct a reaction under pressure. A pressure reactor is a special application of a pressure vessel. The pressure can be caused by the reaction itself or created by an external source, like hydrogen in catalytic transfer hydrogenation. Advantages A pressure reactor can offer several advantages over the conventional round-bottom flask. Firstly, it can conduct a reaction above the boiling point of a solvent. Secondly, the pressure can reduce the reaction volume, including the liquid phase, and in turn increase concentration and collision frequency, and accelerate a reaction. Increase in temperature can speed up the desired reaction, but also speed up the decomposition of reagents and starting materials. However, pressure can speed up the desired reaction and only impacts decomposition when it involves the release of a gas or a reaction with a gas in the vessel. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to fractionate. Generally the component parts have boiling points that differ by less than 25 °C (45 °F) from each other under a pressure of one atmosphere. If the difference in boiling points is greater than 25 °C, a simple distillation is typically used. A crude oil distillation unit uses fractional distillation in the process of refining crude oil. History The fractional distillation of organic substances played an important role in the 9th-century works attributed to the Islamic alchemist Jabir ibn Hayyan, as for example in the ('The Book of Seventy'), translated into Latin by Gerard of Cremona (c. 1114–1187) under the title . The Jabirian experiments with fractional distillation of animal and vegetable subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recompression Chamber
A diving chamber is a vessel for human occupation, which may have an entrance that can be sealed to hold an internal pressure significantly higher than ambient pressure, a pressurised gas system to control the internal pressure, and a supply of breathing gas for the occupants. There are two main functions for diving chambers: * as a simple form of submersible vessel to transport divers underwater and to provide a temporary base and retrieval system in the depths; * as a land, ship or offshore platform-based hyperbaric chamber or system, to artificially reproduce the hyperbaric conditions under the sea. Internal pressures above normal atmospheric pressure are provided for diving-related applications such as saturation diving and diver decompression, and non-diving medical applications such as hyperbaric medicine. Also known as a Pressure vessel for human occupancy, or PVHO. The engineering safety design code is ASME PVHO-1. Basic types of diving chambers There are two bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diving Cylinder
A diving cylinder or diving gas cylinder is a gas cylinder used to store and transport high pressure gas used in diving operations. This may be breathing gas used with a scuba set, in which case the cylinder may also be referred to as a scuba cylinder, scuba tank or diving tank. When used for an emergency gas supply for surface supplied diving or scuba, it may be referred to as a bailout cylinder or bailout bottle. It may also be used for surface-supplied diving or as decompression gas . A diving cylinder may also be used to supply inflation gas for a dry suit or buoyancy compensator. Cylinders provide gas to the diver through the demand valve of a diving regulator or the breathing loop of a diving re-breather. Diving cylinders are usually manufactured from aluminum or steel alloys, and when used on a scuba set are normally fitted with one of two common types of cylinder valve for filling and connection to the regulator. Other accessories such as manifolds, cylinder ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
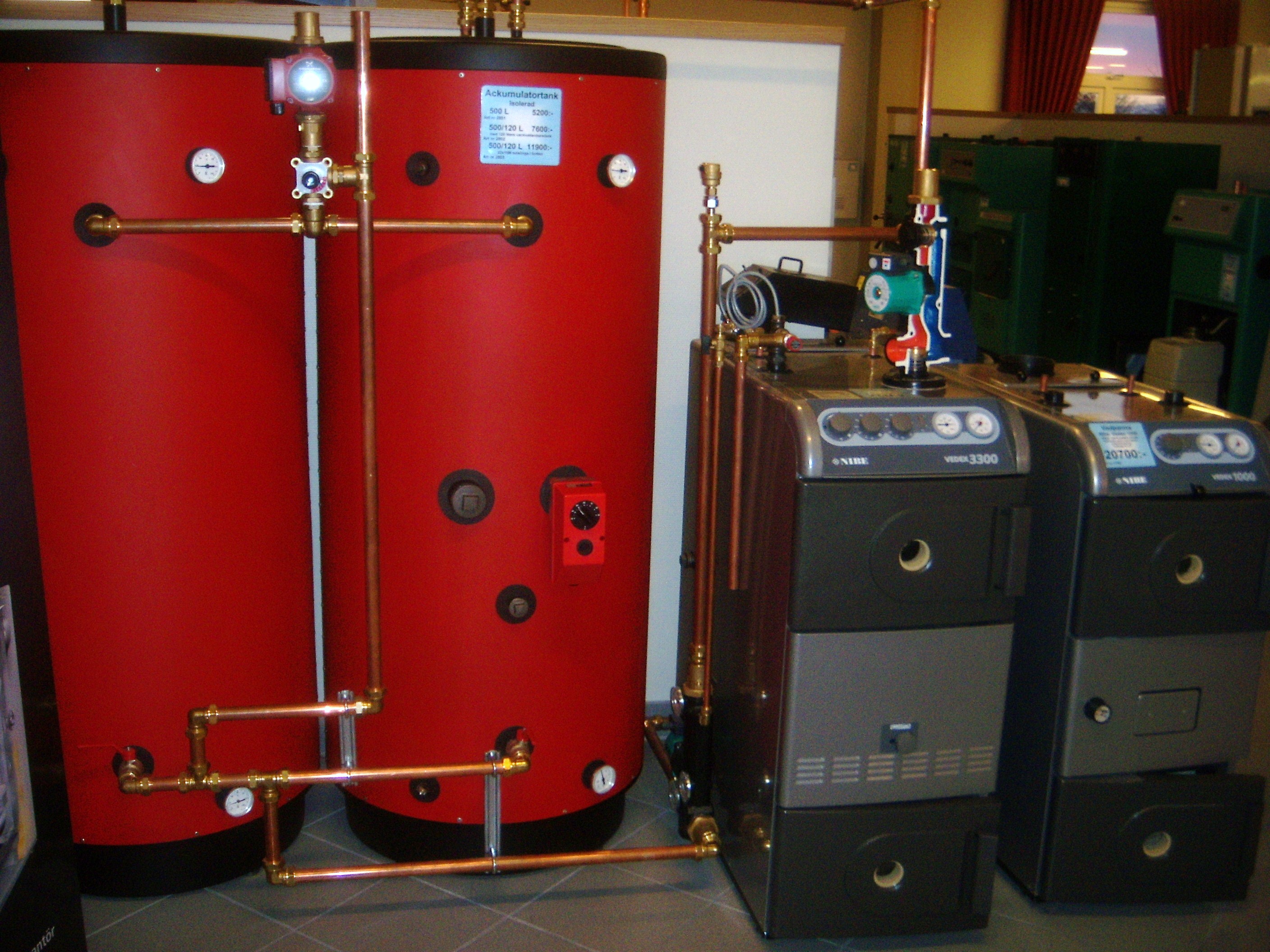
Domestic Hot Water Storage Tank
A hot water storage tank (also called a hot water tank, thermal storage tank, hot water thermal storage unit, heat storage tank, hot water cylinder, and geyser) is a water tank used for storing hot water for space heating or domestic use. Water is a convenient heat storage medium because it has a high specific heat capacity. This means, compared to other substances, it can store more heat per unit of weight. Water is non-toxic and low cost. An efficiently insulated tank can retain stored heat for days, reducing fuel costs. Hot water tanks may have a built-in gas or oil burner system, electric immersion heaters. Some types use an external heat exchanger such as a Central heating, central heating system, or heated water from another energy source. The most typical, in the domestic context, is a fossil-fuel burner, electric immersion elements, or a district heating scheme. Water heaters for washing, bathing, or laundry have thermostat controls to regulate the temperature, in the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation. Heat sources In a fossil fuel power plant using a steam cycle for power generation, the primary heat source will be combustion of coal, oil, or natural gas. In some cases byproduct fuel such as the carbon monoxide rich offgasses of a coke battery can be burned to heat a boiler; biofuels such as bagasse, where economically available, can also be used. In a nuclear power plant, boilers called steam generators are heated by the heat produced by nuclear fission. Where a large volume of hot gas is available from some process, a heat recovery steam generator or recovery boiler can use the heat to produce steam, with little or no extra fuel consumed; such a configuration is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressed Air
Compressed air is air kept under a pressure that is greater than atmospheric pressure. Compressed air in vehicle tires and shock absorbers are commonly used for improved traction and reduced vibration. Compressed air is an important medium for the transfer of energy in industrial processes and is used for power tools such as air hammer (fabrication), air hammers, Jackhammer, drills, power wrench, wrenches, and others, as well as to atomize paint, to operate air cylinders for automation, and can also be used to propel vehicles. Brakes applied by compressed air made large railway trains safer and more efficient to operate. Compressed air brakes are also found on large highway vehicles. Compressed air is used as a breathing gas by underwater diving, underwater divers. The diver may carry it in a high-pressure diving cylinder, or surface supplied diving, supplied from the surface at lower pressure through an air line or diver's umbilical. Similar arrangements are used in breathing ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |