|
Pre-exposure Prophylaxis For HIV Prevention
Pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention, commonly known as PrEP, is the use of antiviral drugs as a strategy for the prevention of HIV/AIDS by people that do not have HIV/AIDS. PrEP is one of a number of HIV prevention strategies for people who are HIV-negative but who have a higher risk of acquiring HIV, including sexually-active adults who are at increased risk of contracting HIV, people who engage in intravenous drug use (see drug injection), and serodiscordant sexually-active couples. The first form of PrEP for HIV prevention—Emtricitabine/tenofovir, emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil (FTC/TDF; ''Truvada'')—was approved in 2012. In October 2019, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the combination of emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide (FTC/TAF; ''Descovy'') to be used as PrEP in addition to Truvada, which provides similar levels of protection. ''Descovy'', however, is currently approved only for cisgender males and transgender women as the ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Truvada
Emtricitabine/tenofovir, sold under the brand name Truvada among others, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication used to treat and prevent HIV/AIDS. It contains the antiretroviral medications emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil. For treatment, it must be used in combination with other antiretroviral medications. For prevention before exposure, in those who are at high risk, it is recommended along with safer sex practices. It does not cure HIV/AIDS. Emtricitabine/tenofovir is taken by mouth. Common side effects include headache, tiredness, trouble sleeping, abdominal pain, weight loss, and rash. Serious side effects may include high blood lactate levels and enlargement of the liver. Use of this medication during pregnancy does not appear to harm the fetus, but this has not been well studied. Emtricitabine/tenofovir was approved for medical use in the United States in 2004. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Centers For Disease Control And Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The CDC's current nominee for director is Susan Monarez. She became acting director on January 23, 2025, but stepped down on March 24, 2025 when nominated for the director position. On May 14, 2025, Robert F. Kennedy Jr. stated that lawyer Matthew Buzzelli is acting CDC director. However, the CDC web site does not state the acting director's name. The agency's main goal is the protection of public health and safety through the control and prevention of disease, injury, and disability in the US and worldwide. The CDC focuses national attention on developing and applying disease control and prevention. It e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Steatosis
Steatosis, also called fatty change, is abnormal retention of fat (lipids) within a cell or organ. Steatosis most often affects the liver – the primary organ of lipid metabolism – where the condition is commonly referred to as fatty liver disease. Steatosis can also occur in other organs, including the kidneys, heart, and muscle. When the term is not further specified (as, for example, in 'cardiac steatosis'), it is assumed to refer to the liver. Risk factors associated with steatosis are varied, and may include diabetes mellitus, protein malnutrition, hypertension, cell toxins, obesity, anoxia, and sleep apnea. Steatosis reflects an impairment of the normal processes of synthesis and elimination of triglyceride fat. Excess lipid accumulates in vesicles that displace the cytoplasm. When the vesicles are large enough to distort the nucleus, the condition is known as macrovesicular steatosis; otherwise, the condition is known as microvesicular steatosis. While not particula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly is enlargement of the liver. It is a non-specific sign (medicine), medical sign, having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into infection, hepatic tumours, and metabolic disorder. Often, hepatomegaly presents as an abdominal mass. Depending on the cause, it may sometimes present along with jaundice. Signs and symptoms The patient may experience many symptoms, including weight loss, poor appetite, and lethargy; jaundice and bruising may also be present. Causes Among the causes of hepatomegaly are the following: Infective Mechanism The mechanism of hepatomegaly consists of Blood vessel, vascular swelling, inflammation (infectious in origin), and deposition of (1) non-hepatic cells or (2) increased cell contents (such as that due to iron in hemochromatosis or hemosiderosis and fat in fatty liver disease). Diagnosis Suspicion of hepatomegaly indicates a thorough medical history and Abdominal examination, physical examination, wherein the latter typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lactic Acidosis
Lactic acidosis refers to the process leading to the production of lactate by anaerobic metabolism. It increases hydrogen ion concentration tending to the state of acidemia or low pH. The result can be detected with high levels of lactate and low levels of bicarbonate. This is usually considered the result of illness but also results from strenuous exercise. The effect on pH is moderated by the presence of respiratory compensation. Lactic acidosis is usually the result of tissue hypoxia which is not the same as arterial hypoxia. Adequate circulation of blood and perfusion of metabolizing tissue to meet demand is necessary to prevent tissue hypoxia. Lactic acidosis can also be the result of illnesses, medications, poisonings or inborn errors of metabolism that interfere directly with oxygen utilization by cells. The symptoms are generally attributable to the underlying cause, but may include nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, and generalised weakness. The diagnosis is made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection. Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. For others, symptoms may appear 30 to 180 days after becoming infected and can include a rapid onset of sickness with nausea, vomiting, yellowish skin, fatigue, yellow urine, and abdominal pain. Symptoms during acute infection typically last for a few weeks, though some people may feel sick for up to six months. Deaths resulting from acute stage HBV infections are rare. An HBV infection lasting longer than six months is usually considered chronic. The likelihood of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for those who are infected with HBV at a younger age. About 90% of those infected during or shortly after birth develop chronic hepatitis B, while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five develop chronic cases. Most of those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Osteopenia
Osteopenia, known as "low bone mass" or "low bone density", is a condition in which bone mineral density is low. Because their bones are weaker, people with osteopenia may have a higher risk of fractures, and some people may go on to develop osteoporosis. In 2010, 43 million older adults in the US had osteopenia. Unlike osteoporosis, osteopenia does not usually cause symptoms, and losing bone density in itself does not cause pain. There is no single cause for osteopenia, although there are several risk factors, including modifiable (behavioral, including dietary and use of certain drugs) and non-modifiable (for instance, loss of bone mass with age). For people with risk factors, screening via a DXA scanner may help to detect the development and progression of low bone density. Prevention of low bone density may begin early in life and includes a healthy diet and weight-bearing exercise, as well as avoidance of tobacco and alcohol. The treatment of osteopenia is controversial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Los Angeles Times
The ''Los Angeles Times'' is an American Newspaper#Daily, daily newspaper that began publishing in Los Angeles, California, in 1881. Based in the Greater Los Angeles city of El Segundo, California, El Segundo since 2018, it is the List of newspapers in the United States, sixth-largest newspaper in the U.S. and the largest in the Western United States with a print circulation of 118,760. It has 500,000 online subscribers, the fifth-largest among U.S. newspapers. Owned by Patrick Soon-Shiong and published by California Times, the paper has won over 40 Pulitzer Prizes since its founding. In the 19th century, the paper developed a reputation for civic boosterism and opposition to Trade union, labor unions, the latter of which led to the Los Angeles Times bombing, bombing of its headquarters in 1910. The paper's profile grew substantially in the 1960s under publisher Otis Chandler, who adopted a more national focus. As with other regional newspapers in California and the United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AIDS Healthcare Foundation
AIDS Healthcare Foundation (AHF) is a Los Angeles-based 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization that provides HIV/AIDS prevention, treatment, and advocacy services. As of 2024, AHF operates about 400 clinics, 69 outpatient healthcare centers, 62 pharmacies, and 22 Out of the Closet thrift stores across 16 U.S. states, Washington, D.C., Puerto Rico, and 47 countries, with over 5,000 employees, and provides care to more than 2.1 million patients. The organization's aim is to end the AIDS epidemic by ensuring access to quality healthcare, including HIV and STD testing, prescription of medications like Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP), and referrals to specialty pharmacies. AHF is the largest provider of Pre-exposure prophylaxis for HIV prevention, PrEP in the United States, though its founder Michael Weinstein has received criticism for his past opposition to the drug. Since 2012, AHF has become highly active in sponsoring and exclusively financing multiple high-profile ballot initiatives i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
DailyMed
DailyMed is a website operated by the United States National Library of Medicine, U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM) to publish up-to-date and accurate drug labels (also called a "package insert") to health care providers and the general public. The contents of DailyMed is provided and updated daily by the Food and Drug Administration (United States), U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The FDA in turn collects this information from the pharmaceutical industry. The documents published use the HL7 version 3 Structured Product Labeling (SPL) standard, which is an XML format that combines the human readable text of the product label with structured data elements that describe the composition, form, packaging, and other properties of the drug products in detail according to the HL7 Reference Information Model (RIM). , it contained information about 140,232 drug listings. It includes an RSS feed for updated drug information. History In 2006 the FDA revised the drug label an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Contraindication
In medicine, a contraindication is a condition (a situation or factor) that serves as a reason not to take a certain medical treatment due to the harm that it would cause the patient. Contraindication is the opposite of indication, which is a reason to use a certain treatment. Absolute contraindications are contraindications for which there are no reasonable circumstances for undertaking a course of action (that is, overriding the prohibition). For example: * Children and teenagers with viral infections should not be given aspirin because of the risk of Reye syndrome. * A person with an anaphylactic food allergy should never eat the food to which they are allergic. * A person with hemochromatosis should not be administered iron preparations. * Some medications are so teratogenic that they are absolutely contraindicated in pregnancy; examples include thalidomide and isotretinoin. Relative contraindications are contraindications for circumstances in which the patient is at hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
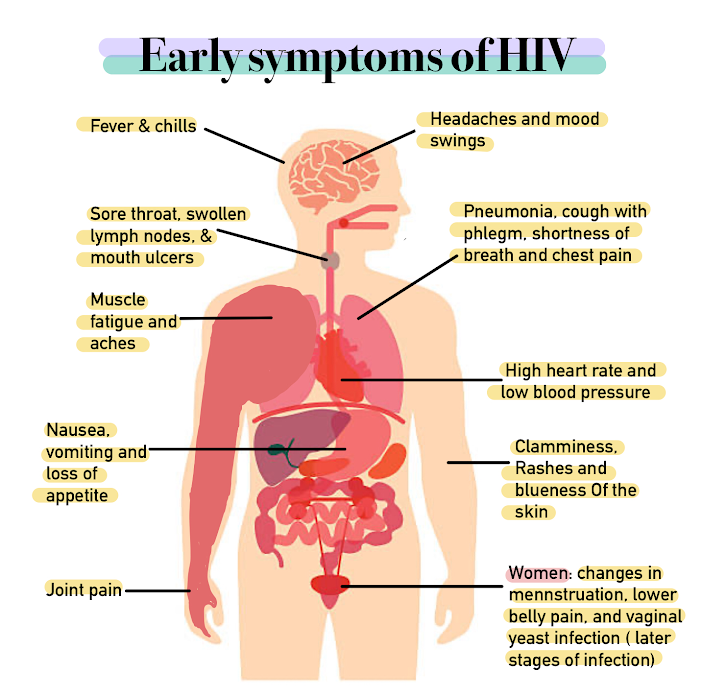
Signs And Symptoms Of HIV/AIDS
The stages of HIV infection are Acute (medicine), acute infection (also known as primary infection), latency, and HIV/AIDS, AIDS. Acute infection lasts for several weeks and may include symptoms such as fever, lymphadenopathy, swollen lymph nodes, pharyngitis, inflammation of the throat, rash, myalgia, muscle pain, malaise, and mouth and esophageal sores. The latency stage involves few or no symptoms and can last anywhere from two weeks to twenty years or more, depending on the individual. AIDS, the final stage of HIV infection, is defined by low CD4+ T cell counts (fewer than 200 per Litre, μL), various opportunistic infections, cancers, and other conditions. Acute infection Acute HIV infection, primary HIV infection or acute seroconversion syndrome is the first stage of HIV infection. It occurs after the incubation stage, before the latency stage, and the potential AIDS succeeding the latency stage. During this period (usually days to weeks post-exposure) fifty to ninety perc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |