|
Pompey's Eastern Settlement
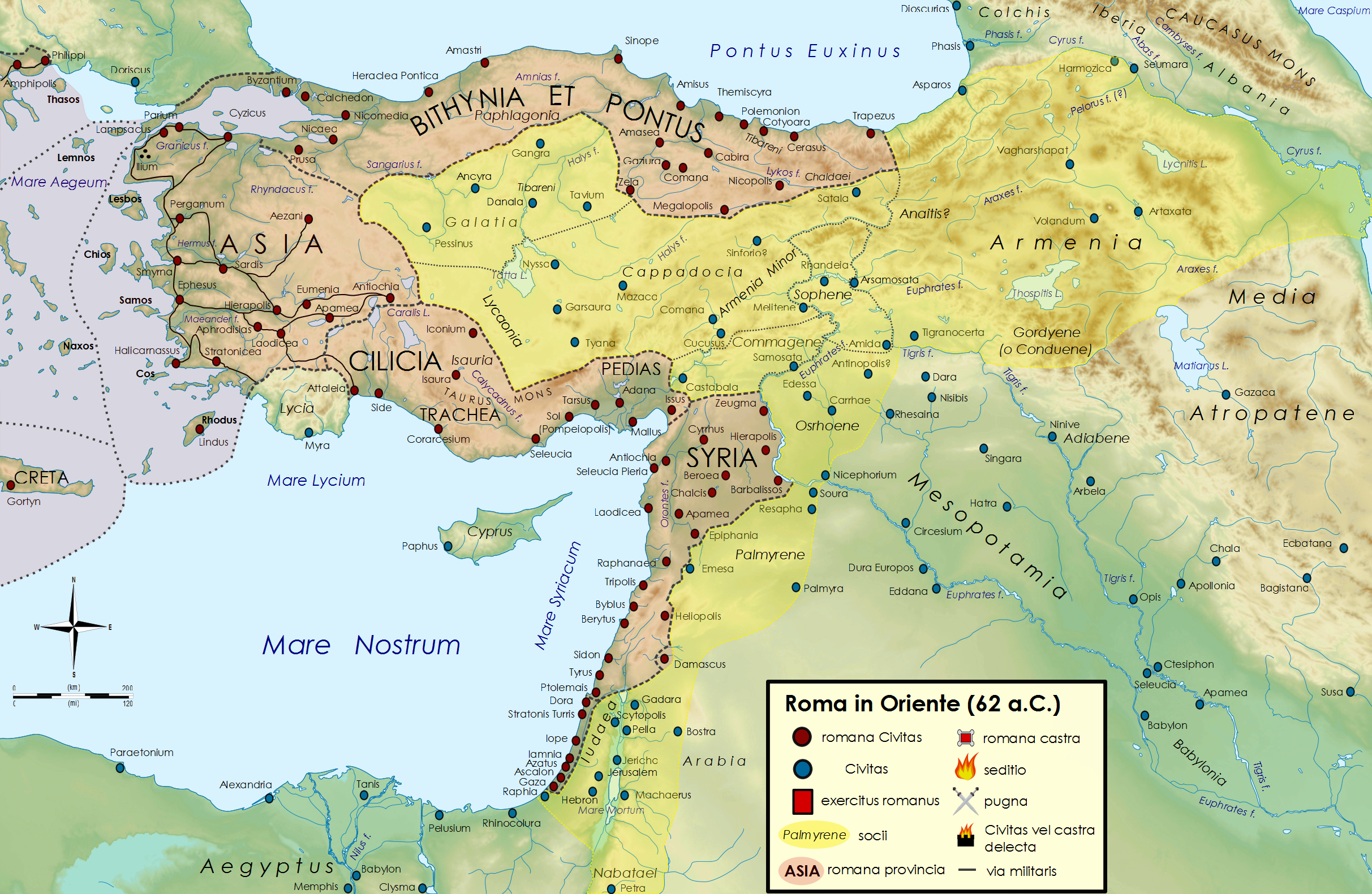
Pompey's eastern settlement was the reorganization of Asia Minor and the Levant carried out by the Roman general Pompey in the 60s BC, in the aftermath of his suppression of piracy, his victory in the Third Mithridatic War and the dissolution of the Seleucid Empire, which brought the entire Near East under Roman control. It involved the establishment of new Roman provinces: alongside an enlarged Asia, Bithynia and Pontus in the north and Cilicia in the south, while the Seleucid realm was annexed as the province of Syria. In the interior, a network of native client kingdoms was established as a buffer to the Parthian Empire. Pompey also carried out reforms to the provincial administrative and taxation systems in the Roman East, and founded new cities. Although generally acknowledged as humane and sound, the Eastern Settlement was carried out without the advice or consent of the Roman Senate, and the reorganization was not ratified for several years due to senatorial opposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roma In Oriente 62aC
Roma or ROMA may refer to: People, characters, figures, names * Roma or Romani people, an ethnic group living mostly in Europe and the Americas. * Roma called Roy, ancient Egyptian High Priest of Amun * Roma (footballer, born 1979), born ''Paulo Marcel Pereira Merabet'', Brazilian football forward * Roma (footballer, born 1985), born ''Juliano Laurentino dos Santos'', Brazilian football winger * Sister Roma or Michael Williams (born 1962), American drag performer and director * Roma (personification), goddess in ancient Rome Names * Roma (given name), a female given name * Roma (surname), a surname (and list of people with the name) * Roman (given name), or Roma, a male given name * Roman (surname), a surname (and list of people with the name) Places * 472 Roma, the asteroid "Roma", the 472nd asteroid registered, a main belt asteroid Australia * Roma, Queensland, a town ** Roma Airport ** Roma Courthouse ** Electoral district of Roma, defunct ** Town of Roma, defunct tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Client Kingdom
A client state in the context of international relations is a state that is economically, politically, and militarily subordinated to a more powerful controlling state. Alternative terms for a ''client state'' are satellite state, associated state, and dominion, condominium, self-governing colony, and neo-colony, protectorate, vassal state, puppet state, and tributary state. Controlling states in history Persia, Greece, Ancient China and Rome Ancient states such as Persia, Parthia, Greek city-states, Ancient China, and Ancient Rome sometimes created client states by making the leaders of that state subservient, having to provide tribute and soldiers. Classical Athens, for example, forced weaker states into the Delian League and in some cases imposed democratic governments on them. Later, Philip II of Macedon similarly imposed the League of Corinth. One of the most prolific users of client states was Republican Rome which, instead of conquering and then absorbing into an empire, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Syria
Roman Syria was an early Roman province annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC by Pompey in the Third Mithridatic War following the defeat of King of Armenia Tigranes the Great, who had become the protector of the Hellenistic kingdom of Syria. Following the partition of the Herodian Kingdom of Judea into a tetrarchy in 4 BC, it was gradually absorbed into Roman provinces, with Roman Syria annexing Iturea and Trachonitis. By the late 2nd century AD, the province was divided into Coele Syria and Syria Phoenice. Provincia Syria Syria was annexed to the Roman Republic in 64 BC, when Pompey the Great had the Seleucid king Antiochus XIII Asiaticus executed and deposed his successor Philip II Philoromaeus. Pompey appointed Marcus Aemilius Scaurus to the post of governor of Syria. Following the fall of the Roman Republic and its transformation into the Roman Empire, Syria became a Roman imperial province, governed by a Legate. During the early empire, the Roman army in Sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Anatolia
Classical Anatolia is Anatolia during classical antiquity. Early in that period, Anatolia was divided into several Iron Age Anatolia, Iron Age kingdoms, most notably Lydia in the west, Phrygia in the center and Urartu in the east. Anatolia fell under Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian rule c. 550 BC. In the aftermath of the Greco-Persian Wars, all of Anatolia remained under Persian control except for the Aegean coast, which was incorporated in the Delian League in the 470s BC. Alexander the Great finally wrested control of the whole region from Persia in the 330s BC. After Alexander's death, his conquests were split amongst several of his trusted generals, but were under constant threat of invasion from both the Gauls and other powerful rulers in Pergamon, Kingdom of Pontus, Pontus, and History of Ptolemaic Egypt, Egypt. The Seleucid Empire, the largest of Alexander's territories, and which included Anatolia, became involved in a disastrous war with Roman Republic, Rome culmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
60s BC
This article concerns the period 69 BC – 60 BC. Significant people * Pompey, Roman general, (lived 106 BC–48 BC) * Mithridates VI, King of Pontus, (lived 132 BC–63 BC) * Philip II Philoromaeus * Gaius Antonius Hybrida, elected praetor in 66 BC * Cleopatra VII is born (69 BC–30 BC __NOTOC__ Year 30 BC was either a common year starting on Wednesday, Thursday or Friday or a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar (the sources differ, see leap year error for further information) and a common year starting on W ...) and grows into a young girl passing age 9. Citations References * {{DEFAULTSORT:60s Bc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Consul
The consuls were the highest elected public officials of the Roman Republic ( to 27 BC). Romans considered the consulship the second-highest level of the ''cursus honorum''an ascending sequence of public offices to which politicians aspiredafter that of the Roman censor, censor, which was reserved for former consuls. Each year, the Centuriate Assembly elected two consuls to serve jointly for a one-year term. The consuls alternated each month holding ''fasces'' (taking turns leading) when both were in Rome. A consul's ''imperium'' (military power) extended over Rome and all its Roman provinces, provinces. Having two consuls created a check on the power of any one individual, in accordance with the republican belief that the powers of the former King of Rome, kings of Rome should be spread out into multiple offices. To that end, each consul could veto the actions of the other consul. After the establishment of the Roman Empire, Empire (27 BC), the consuls became mere symboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Triumvirate
The First Triumvirate was an informal political alliance among three prominent politicians in the late Roman Republic: Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, Marcus Licinius Crassus, and Gaius Julius Caesar. The republican constitution had many veto points. In order to bypass constitutional obstacles and force through the political goals of the three men, they forged an alliance in secret where they promised to use their respective influence to support each other. The "triumvirate" was not a formal magistracy, nor did it achieve a lasting domination over state affairs. It was formed among the three men due to their mutual need to overcome opposition in the senate against their proposals in the previous years. Initially secret, it emerged publicly during Caesar's first consulship in 59 BC to push through legislation for the three allies. Caesar secured passage of an agrarian law which helped resettle Pompey's veterans, a law ratifying Pompey's settlements after the Third Mithridatic War, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115–53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome". Wallechinsky, David & Wallace, Irving.Richest People in History Ancient Roman Crassus. Trivia-Library. '' The People's Almanac''. 1975–1981. Web. 23 December 2009."Often named as the richest man ever, a more accurate conversion of sesterce would put his modern figure between $200 million and $20 billion." Peter L. BernsteinThe 20 Richest People Of All Time/ref> Crassus began his public career as a military commander under Lucius Cornelius Sulla during his civil war. Following Sulla's assumption of the dictatorship, Crassus amassed an enormous fortune through property speculation. Crassus rose to political prominence following his victory over the slave revolt led by Spartacus, sharing the consulship with his rival Pompey the Great. A political and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patronage In Ancient Rome
Patronage (''clientela'') was the distinctive relationship in Social class in ancient Rome, ancient Roman society between the ''patronus'' ('patron') and their ''cliens'' ('client'). Apart from the patron-client relationship between individuals, there were also client kingdoms and tribes, whose rulers were in a subordinate relationship to the Roman state. The relationship was hierarchical, but obligations were mutual. The patron was the protector, sponsor, and benefactor of the client; the technical term for this protection was ''patrocinium''. Although typically the client was of inferior social class, a patron and client might even hold the same social rank, but the former would possess greater wealth, power, or prestige that enabled him to help or do favors for the client. From the emperor at the top to the commoner at the bottom, the bonds between these groups found formal expression in legal definition of patrons' responsibilities to clients. Patronage relationships were n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Senate of the Roman Kingdom, to the Senate of the Roman Republic and Senate of the Roman Empire and eventually the Byzantine Senate of the Eastern Roman Empire, existing well into the post-classical era and Middle Ages. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, the Senate was generally little more than an advisory council to the king. However, as Rome was an electoral monarchy, the Senate also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive Roman magistrates who appointed the senators for life (or until expulsion by Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |