|
Polya's Shire Theorem
Pólya's shire theorem, named after George Pólya, is a theorem in complex analysis that describes the asymptotic distribution of the zeros of successive derivatives of a meromorphic function on the complex plane. It has applications in Nevanlinna theory. Statement Let f be a meromorphic function on the complex plane with P \neq \emptyset as its set of poles. If E is the set of all zeros of all the successive derivatives f', f'', f^, \ldots, then the derived set E' (or the set of all limit points) is as follows: # if f has only one pole, then E' is empty. # if , P, \geq 2, then E' coincides with the edges of the Voronoi diagram determined by the set of poles P. In this case, if a \in P, the interior of each Voronoi cell consisting of the points closest to a than any other point in P is called the a-''shire''. The derived set is independent of the order of each pole. References {{reflist *Rikard Bögvad, Christian Hägg, A refinement of Pólya's method to construct Vorono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Pólya
George Pólya (; ; December 13, 1887 – September 7, 1985) was a Hungarian-American mathematician. He was a professor of mathematics from 1914 to 1940 at ETH Zürich and from 1940 to 1953 at Stanford University. He made fundamental contributions to combinatorics, number theory, numerical analysis and probability theory. He is also noted for his work in heuristics and mathematics education. He has been described as one of The Martians (scientists), The Martians, an informal category which included one of his most famous students at ETH Zurich, John von Neumann. Life and works Pólya was born in Budapest, Austria-Hungary, to Anna Deutsch and Jakab Pólya, History of the Jews in Hungary, Hungarian Jews who had converted to Christianity in 1886. Although his parents were religious and he was baptized into the Catholic Church upon birth, George eventually grew up to be an agnostic. He received a PhD under Lipót Fejér in 1912, at Eötvös Loránd University. He was a professor o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Analysis
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebraic geometry, number theory, analytic combinatorics, and applied mathematics, as well as in physics, including the branches of hydrodynamics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, and twistor theory. By extension, use of complex analysis also has applications in engineering fields such as nuclear, aerospace, mechanical and electrical engineering. As a differentiable function of a complex variable is equal to the sum function given by its Taylor series (that is, it is analytic), complex analysis is particularly concerned with analytic functions of a complex variable, that is, '' holomorphic functions''. The concept can be extended to functions of several complex variables. Complex analysis is contrasted with real analysis, which dea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
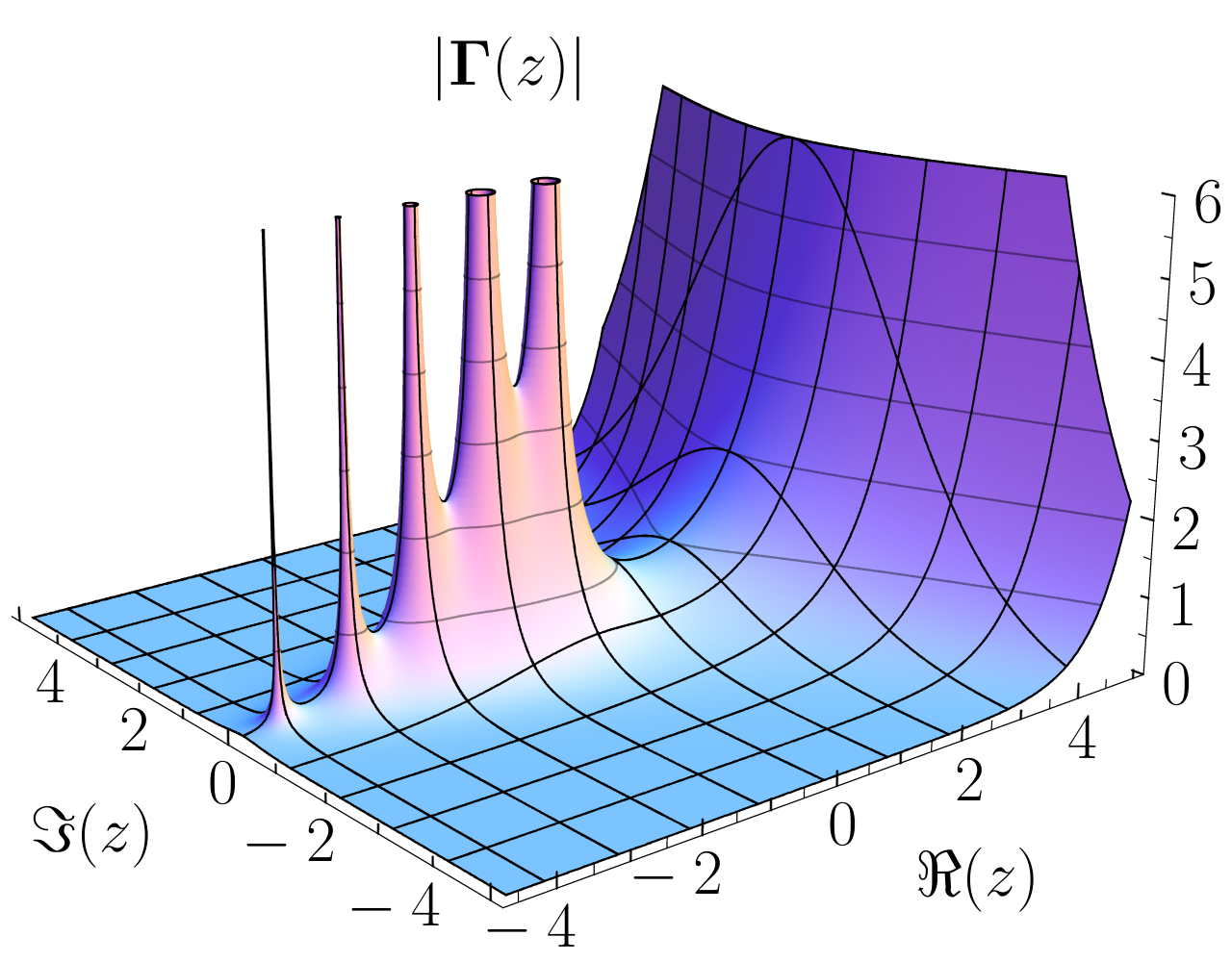
Meromorphic Function
In the mathematical field of complex analysis, a meromorphic function on an open subset ''D'' of the complex plane is a function that is holomorphic on all of ''D'' ''except'' for a set of isolated points, which are ''poles'' of the function. The term comes from the Greek ''meros'' ( μέρος), meaning "part". Every meromorphic function on ''D'' can be expressed as the ratio between two holomorphic functions (with the denominator not constant 0) defined on ''D'': any pole must coincide with a zero of the denominator. Heuristic description Intuitively, a meromorphic function is a ratio of two well-behaved (holomorphic) functions. Such a function will still be well-behaved, except possibly at the points where the denominator of the fraction is zero. If the denominator has a zero at ''z'' and the numerator does not, then the value of the function will approach infinity; if both parts have a zero at ''z'', then one must compare the multiplicity of these zeros. From an algeb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Math
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevanlinna Theory
In the mathematical field of complex analysis, Nevanlinna theory is part of the theory of meromorphic functions. It was devised in 1925, by Rolf Nevanlinna. Hermann Weyl called it "one of the few great mathematical events of (the twentieth) century." The theory describes the asymptotic distribution of solutions of the equation ''f''(''z'') = ''a'', as ''a'' varies. A fundamental tool is the Nevanlinna characteristic ''T''(''r'', ''f'') which measures the rate of growth of a meromorphic function. Other main contributors in the first half of the 20th century were Lars Ahlfors, André Bloch, Henri Cartan, Edward Collingwood, Otto Frostman, Frithiof Nevanlinna, Henrik Selberg, Tatsujiro Shimizu, Oswald Teichmüller, and Georges Valiron. In its original form, Nevanlinna theory deals with meromorphic functions of one complex variable defined in a disc , ''z'', ≤ ''R'' or in the whole complex plane (''R'' = ∞). Subsequent generalizations extended Nevanlinna theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derived Set (mathematics)
In mathematics, more specifically in point-set topology, the derived set of a subset S of a topological space is the set of all limit points of S. It is usually denoted by S'. The concept was first introduced by Georg Cantor in 1872 and he developed set theory in large part to study derived sets on the real line. Definition The derived set of a subset S of a topological space X, denoted by S', is the set of all points x \in X that are limit points of S, that is, points x such that every neighbourhood of x contains a point of S other than x itself. Examples If \Reals is endowed with its usual Euclidean topology then the derived set of the half-open interval , 1) is the closed interval [0, 1 Consider \Reals with the Topology (structure)">topology (open sets) consisting of the empty set and any subset of \Reals that contains 1. The derived set of A := \ is A' = \Reals \setminus \. Properties Let X denote a topological space in what follows. If A and B are subsets of X, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voronoi Diagram
In mathematics, a Voronoi diagram is a partition of a plane into regions close to each of a given set of objects. It can be classified also as a tessellation. In the simplest case, these objects are just finitely many points in the plane (called seeds, sites, or generators). For each seed there is a corresponding region, called a Voronoi cell, consisting of all points of the plane closer to that seed than to any other. The Voronoi diagram of a set of points is dual to that set's Delaunay triangulation. The Voronoi diagram is named after mathematician Georgy Voronoy, and is also called a Voronoi tessellation, a Voronoi decomposition, a Voronoi partition, or a Dirichlet tessellation (after Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet). Voronoi cells are also known as Thiessen polygons, after Alfred H. Thiessen. Voronoi diagrams have practical and theoretical applications in many fields, mainly in science and technology, but also in visual art. Simplest case In the simplest case, shown in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometriae Dedicata
''Geometriae Dedicata'' is a mathematical journal, founded in 1972, concentrating on geometry and its relationship to topology, group theory and the theory of dynamical systems. It was created on the initiative of Hans Freudenthal in Utrecht, the Netherlands.. It is published by Springer Netherlands. The Editor-in-Chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accoun ... is Richard Alan Wentworth. References External links Springer site Geometry journals Springer Science+Business Media academic journals Algebra journals Dynamical systems journals Topology journals {{math-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wisconsin-Madison
A university () is an institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. The first universities in Europe were established by Catholic monks. The University of Bologna (), Italy, which was founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *being a high degree-awarding institute. *using the word (which was coined at its foundation). *having independence from the ecclesiastic schools and issuing secular as well as non-secular degrees (with teaching conducted by both clergy and non-clergy): grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law and notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, , p. 55f.de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde''A History of the University in Europe: Volume 1, Universities in the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theorems In Complex Analysis
In mathematics and formal logic, a theorem is a statement that has been proven, or can be proven. The ''proof'' of a theorem is a logical argument that uses the inference rules of a deductive system to establish that the theorem is a logical consequence of the axioms and previously proved theorems. In mainstream mathematics, the axioms and the inference rules are commonly left implicit, and, in this case, they are almost always those of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory with the axiom of choice (ZFC), or of a less powerful theory, such as Peano arithmetic. Generally, an assertion that is explicitly called a theorem is a proved result that is not an immediate consequence of other known theorems. Moreover, many authors qualify as ''theorems'' only the most important results, and use the terms ''lemma'', ''proposition'' and ''corollary'' for less important theorems. In mathematical logic, the concepts of theorems and proofs have been formalized in order to allow mathematical reasonin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |