|
Poisson's Ratio
In materials science and solid mechanics, Poisson's ratio (symbol: ( nu)) is a measure of the Poisson effect, the deformation (expansion or contraction) of a material in directions perpendicular to the specific direction of loading. The value of Poisson's ratio is the negative of the ratio of transverse strain to axial strain. For small values of these changes, is the amount of transversal elongation divided by the amount of axial compression. Most materials have Poisson's ratio values ranging between 0.0 and 0.5. For soft materials, such as rubber, where the bulk modulus is much higher than the shear modulus, Poisson's ratio is near 0.5. For open-cell polymer foams, Poisson's ratio is near zero, since the cells tend to collapse in compression. Many typical solids have Poisson's ratios in the range of 0.2 to 0.3. The ratio is named after the French mathematician and physicist Siméon Poisson. Origin Poisson's ratio is a measure of the Poisson effect, the phenomenon in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poisson Ratio Compression Example
Poisson may refer to: People *Siméon Denis Poisson, French mathematician *Eric Poisson, Canadian physicist Places *Poissons, a commune of Haute-Marne, France *Poisson, Saône-et-Loire, a commune of Saône-et-Loire, France Other uses *Poisson (surname), a French surname *Poisson (crater), a lunar crater named after Siméon Denis Poisson *The French word for fish See also *Adolphe-Poisson Bay, a body of water located to the southwest of Gouin Reservoir, in La Tuque, Mauricie, Quebec *Poisson distribution, a discrete probability distribution named after Siméon Denis Poisson *Poisson's equation, a partial differential equation named after Siméon Denis Poisson *List of things named after Siméon Denis Poisson *Poison (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxetics
Auxetic metamaterials are a type of metamaterial with a negative Poisson's ratio, so that axial elongation causes transversal elongation (in contrast to an ordinary material, where stretching in one direction causes compression in the other direction). Auxetics can be single molecules, crystals, or a particular structure of macroscopic matter. Auxetic materials are used in protective equipment such as body armor, helmets, and knee pads, as they absorb energy more effectively than traditional materials. They are also used in devices such as medical stents or implants. Auxetic fabrics can be used to create comfortable and flexible clothing, as well as technical fabrics for applications such as aerospace and sports equipment. Auxetic materials can also be used to create acoustic metamaterials for controlling sound and vibration. History The term ''auxetic'' derives from the Greek word () which means 'that which tends to increase' and has its root in the word (), meaning 'incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpose
In linear algebra, the transpose of a Matrix (mathematics), matrix is an operator which flips a matrix over its diagonal; that is, it switches the row and column indices of the matrix by producing another matrix, often denoted by (among other notations). The transpose of a matrix was introduced in 1858 by the British mathematician Arthur Cayley. Transpose of a matrix Definition The transpose of a matrix , denoted by , , , A^, , , or , may be constructed by any one of the following methods: #Reflection (mathematics), Reflect over its main diagonal (which runs from top-left to bottom-right) to obtain #Write the rows of as the columns of #Write the columns of as the rows of Formally, the -th row, -th column element of is the -th row, -th column element of : :\left[\mathbf^\operatorname\right]_ = \left[\mathbf\right]_. If is an matrix, then is an matrix. In the case of square matrices, may also denote the th power of the matrix . For avoiding a possibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix (: matrices) is a rectangle, rectangular array or table of numbers, symbol (formal), symbols, or expression (mathematics), expressions, with elements or entries arranged in rows and columns, which is used to represent a mathematical object or property of such an object. For example, \begin1 & 9 & -13 \\20 & 5 & -6 \end is a matrix with two rows and three columns. This is often referred to as a "two-by-three matrix", a " matrix", or a matrix of dimension . Matrices are commonly used in linear algebra, where they represent linear maps. In geometry, matrices are widely used for specifying and representing geometric transformations (for example rotation (mathematics), rotations) and coordinate changes. In numerical analysis, many computational problems are solved by reducing them to a matrix computation, and this often involves computing with matrices of huge dimensions. Matrices are used in most areas of mathematics and scientific fields, either directly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthotropic Material
In material science and solid mechanics, orthotropic materials have material properties at a particular point which differ along three orthogonal axes, where each axis has twofold rotational symmetry. These directional differences in strength can be quantified with Hankinson's equation. They are a subset of anisotropic materials, because their properties change when measured from different directions. A familiar example of an orthotropic material is wood. In wood, one can define three mutually perpendicular directions at each point in which the properties are different. It is most stiff (and strong) along the grain (axial direction), because most cellulose fibrils are aligned that way. It is usually least stiff in the radial direction (between the growth rings), and is intermediate in the circumferential direction. This anisotropy was provided by evolution, as it best enables the tree to remain upright. Because the preferred coordinate system is cylindrical-polar, this type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einstein Notation
In mathematics, especially the usage of linear algebra in mathematical physics and differential geometry, Einstein notation (also known as the Einstein summation convention or Einstein summation notation) is a notational convention that implies summation over a set of indexed terms in a formula, thus achieving brevity. As part of mathematics it is a notational subset of Ricci calculus; however, it is often used in physics applications that do not distinguish between tangent and cotangent spaces. It was introduced to physics by Albert Einstein in 1916. Introduction Statement of convention According to this convention, when an index variable appears twice in a single term and is not otherwise defined (see Free and bound variables), it implies summation of that term over all the values of the index. So where the indices can range over the set , y = \sum_^3 x^i e_i = x^1 e_1 + x^2 e_2 + x^3 e_3 is simplified by the convention to: y = x^i e_i The upper indices are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kronecker Delta
In mathematics, the Kronecker delta (named after Leopold Kronecker) is a function of two variables, usually just non-negative integers. The function is 1 if the variables are equal, and 0 otherwise: \delta_ = \begin 0 &\text i \neq j, \\ 1 &\text i=j. \end or with use of Iverson brackets: \delta_ = =j, For example, \delta_ = 0 because 1 \ne 2, whereas \delta_ = 1 because 3 = 3. The Kronecker delta appears naturally in many areas of mathematics, physics, engineering and computer science, as a means of compactly expressing its definition above. Generalized versions of the Kronecker delta have found applications in differential geometry and modern tensor calculus, particularly in formulations of gauge theory and topological field models. In linear algebra, the n\times n identity matrix \mathbf has entries equal to the Kronecker delta: I_ = \delta_ where i and j take the values 1,2,\cdots,n, and the inner product of vectors can be written as \mathbf\cdot\mathbf = \sum_^n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Stress
Shear stress (often denoted by , Greek alphabet, Greek: tau) is the component of stress (physics), stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. ''Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress or force per unit area is: \tau = ,where is the force applied and is the cross-sectional area. The area involved corresponds to the material face (geometry), face parallel to the applied force vector, i.e., with surface normal vector perpendicular to the force. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as:\tau_w := \mu\left.\frac\_,where is the dynamic viscosity, is the flow velocity, and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress (physics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity that describes Force, forces present during Deformation (physics), deformation. For example, an object being pulled apart, such as a stretched elastic band, is subject to Tension (physics), ''tensile'' stress and may undergo Elongation (materials science), elongation. An object being pushed together, such as a crumpled sponge, is subject to Compression (physics), ''compressive'' stress and may undergo shortening. The greater the force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Stress has Dimension (physics), dimension of force per area, with SI Units, SI units of newtons per square meter (N/m2) or Pascal (unit), pascal (Pa). Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while Strain (mechanics), ''strain'' is the measure of the relative deformation (mechanics), deformation of the material. For example, when a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
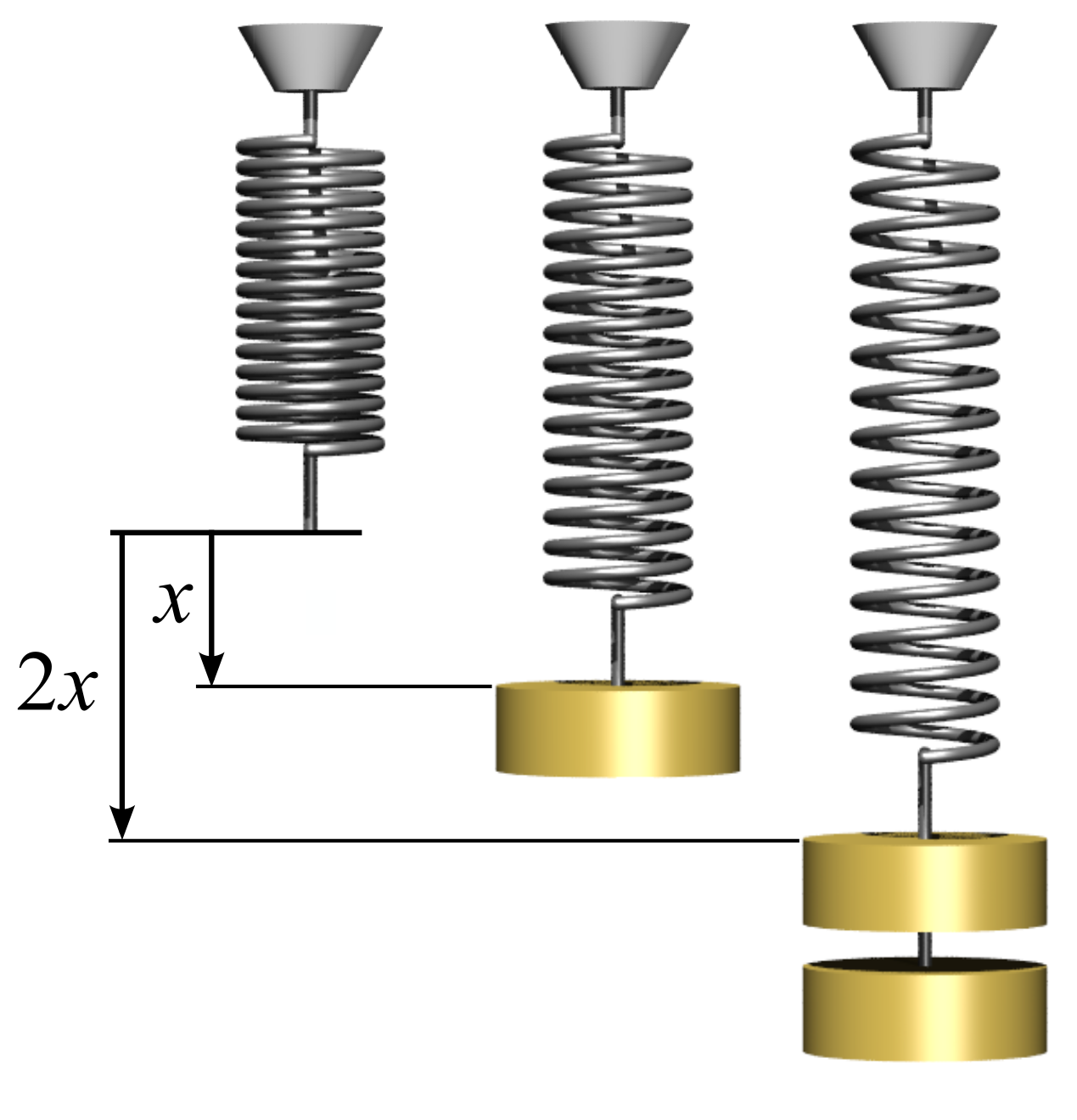
Hooke's Law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance () scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elastic body is deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string of a guitar. An elastic body or material for which this equation can be assumed is said to be linear-elastic or Hookean. Hooke's law is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rod Diameter Change Poisson
Rod, Ród, Rőd, Rød, Röd, ROD, or R.O.D. may refer to: Devices * Birch rod, made out of twigs from birch or other trees for corporal punishment * Ceremonial rod, used to indicate a position of authority * Connecting rod, main, coupling, or side rod, in a reciprocating engine * Control rod, used to control the rate of fission in a nuclear reactor * Divining rod, two rods believed by some to find water in a practice known as dowsing * Fishing rod, a tool used to catch fish, like a long pole with a hook on the end * Lightning rod, a conductor on top of a building to protect the building in the event of lightning by taking the charge harmlessly to earth * Measuring rod, a kind of ruler * Switch (corporal punishment), a piece of wood used as a staff or for corporal punishment, or a bundle of such switches * Truss rod, a steel part inside a guitar neck used for its tension adjustment Arts and entertainment * ''Read or Die'', a Japanese anime and manga ** ''Read or Die'' (OVA), an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamé Parameters
In continuum mechanics, Lamé parameters (also called the Lamé coefficients, Lamé constants or Lamé moduli) are two material-dependent quantities denoted by ''λ'' and ''μ'' that arise in strain- stress relationships. In general, ''λ'' and ''μ'' are individually referred to as ''Lamé's first parameter'' and ''Lamé's second parameter'', respectively. Other names are sometimes employed for one or both parameters, depending on context. For example, the parameter ''μ'' is referred to in fluid dynamics as the dynamic viscosity of a fluid (not expressed in the same units); whereas in the context of elasticity, ''μ'' is called the shear modulus, and is sometimes denoted by ''G'' instead of ''μ''. Typically the notation ''G'' is seen paired with the use of Young's modulus ''E'', and the notation ''μ'' is paired with the use of ''λ''. In homogeneous and isotropic materials, these define Hooke's law in 3D, \boldsymbol = 2\mu \boldsymbol + \lambda \; \operatorname(\boldsymbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |