|
Plural Form Of Words Ending In -us
In English, the plural form of words ending in ''-us'', especially those derived from Latin, often replaces ''-us'' with ''-i''. There are many exceptions, some because the word does not derive from Latin, and others due to custom (''e.g.'', ''campus'', plural ''campuses''). Conversely, some non-Latin words ending in ''-us'' and Latin words that did not have their Latin plurals with ''-i'' form their English plurals with ''-i'', ''e.g.'', ''octopi'' is sometimes used as a plural for octopus (the standard English plural is octopuses). Most Prescriptivists consider these forms incorrect, but descriptivists may simply describe them as a natural evolution of language; some prescriptivists do consider some such forms correct (e.g. ''octopi'' as the plural of ''octopus'' being analogous to ''polypi'' as the plural of ''polypus''). Some English words of Latin origin do not commonly take the Latin plural, but rather the regular English plurals in -(e)s: ''campus'', ''bonus'', and ''an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neo-Latin
Neo-LatinSidwell, Keith ''Classical Latin-Medieval Latin-Neo Latin'' in ; others, throughout. (also known as New Latin and Modern Latin) is the style of written Latin used in original literary, scholarly, and scientific works, first in Italy during the Italian Renaissance of the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, and then across northern Europe after about 1500, as a key feature of the humanist movement. Through comparison with Classical Latin, Latin of the Classical period, scholars from Petrarch onwards promoted a standard of Latin closer to that of the ancient Romans, especially in grammar, style, and spelling. The term ''Neo-Latin'' was however coined much later, probably in Germany in the late eighteenth century, as ''Neulatein'', spreading to French and other languages in the nineteenth century. Medieval Latin had diverged quite substantially from the classical standard and saw notable regional variation and influence from vernacular languages. Neo-Latin attempts to retur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first edition in 1884, traces the historical development of the English language, providing a comprehensive resource to scholars and academic researchers, and provides ongoing descriptions of English language usage in its variations around the world. In 1857, work first began on the dictionary, though the first edition was not published until 1884. It began to be published in unbound Serial (literature), fascicles as work continued on the project, under the name of ''A New English Dictionary on Historical Principles; Founded Mainly on the Materials Collected by The Philological Society''. In 1895, the title ''The Oxford English Dictionary'' was first used unofficially on the covers of the series, and in 1928 the full dictionary was republished in 10 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
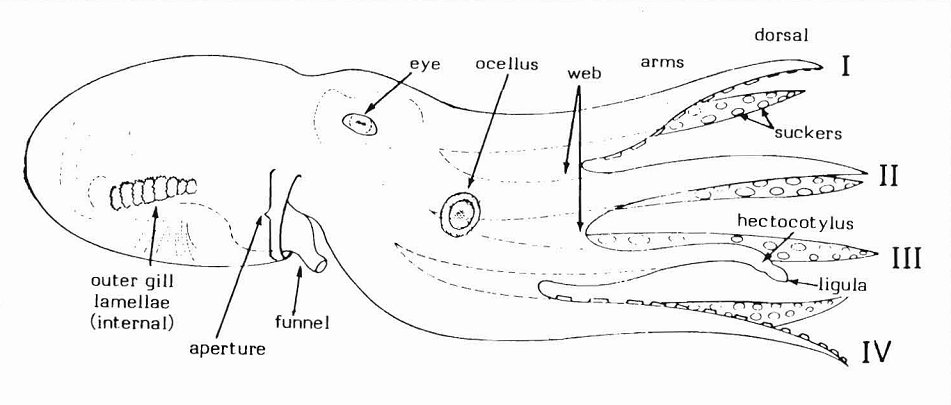
Octopodes
An octopus (: octopuses or octopodes) is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the centre point of the eight limbs. An octopus can radically deform its shape, enabling it to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used for respiration and locomotion (by water jet propulsion). Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various ocean habitats, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in the intertidal zone and others at abyssal depths. Most species grow quickly, mature early, and are short-lived. In most species, the male uses a specially-ada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Octopuses
An octopus (: octopuses or octopodes) is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed Mollusca, mollusc of the order (biology), order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is symmetry in biology, bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a cephalopod beak, beaked mouth at the centre point of the eight limbs. An octopus can radically deform its shape, enabling it to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their appendages behind them as they swim. The Siphon (mollusc), siphon is used for aquatic respiration, respiration and aquatic locomotion, locomotion (by jet propulsion#Jet-propelled animals, water jet propulsion). Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various ocean habitats, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Octopus
An octopus (: octopuses or octopodes) is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other cephalopods, an octopus is bilaterally symmetric with two eyes and a beaked mouth at the centre point of the eight limbs. An octopus can radically deform its shape, enabling it to squeeze through small gaps. They trail their appendages behind them as they swim. The siphon is used for respiration and locomotion (by water jet propulsion). Octopuses have a complex nervous system and excellent sight, and are among the most intelligent and behaviourally diverse invertebrates. Octopuses inhabit various ocean habitats, including coral reefs, pelagic waters, and the seabed; some live in the intertidal zone and others at abyssal depths. Most species grow quickly, mature early, and are short-lived. In most species, the male uses a speciall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Virion
A virion (plural, ''viria'' or ''virions'') is an inert virus particle capable of invading a Cell (biology), cell. Upon entering the cell, the virion disassembles and the genetic material from the virus takes control of the cell infrastructure, thus enabling the virus to Replication (virus), replicate. The genetic material (''Viral core, core'', either DNA or RNA, along with occasionally present virus core protein) inside the virion is usually enclosed in a protection shell, known as the capsid. While the terms "virus" and "virion" are occasionally confused, recently "virion" is used solely to describe the virus structure outside of cells, while the terms "virus/viral" are broader and also include biological properties such as the infectivity of a virion. Components A virion consists of one or more nucleic acid genome molecules (single-stranded or double-stranded RNA or DNA) and coatings (a capsid and possibly a viral envelope). The virion may contain other proteins (for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hypercorrection
In sociolinguistics, hypercorrection is the nonstandard use of language that results from the overapplication of a perceived rule of language-usage prescription. A speaker or writer who produces a hypercorrection generally believes through a misunderstanding of such rules that the form or phrase they use is more "correct", standard, or otherwise preferable, often combined with a desire to appear formal or educated. Linguistic hypercorrection occurs when a real or imagined grammatical rule is applied in an inappropriate context, so that an attempt to be "correct" leads to an incorrect result. It does not occur when a speaker follows "a natural speech instinct", according to Otto Jespersen and Robert J. Menner. Hypercorrection can be found among speakers of less prestigious language varieties who attempt to produce forms associated with high-prestige varieties, even in situations where speakers of those varieties would not. Some commentators call such production ''hyperurba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Perl
Perl is a high-level, general-purpose, interpreted, dynamic programming language. Though Perl is not officially an acronym, there are various backronyms in use, including "Practical Extraction and Reporting Language". Perl was developed by Larry Wall in 1987 as a general-purpose Unix scripting language to make report processing easier. Since then, it has undergone many changes and revisions. Perl originally was not capitalized and the name was changed to being capitalized by the time Perl 4 was released. The latest release is Perl 5, first released in 1994. From 2000 to October 2019 a sixth version of Perl was in development; the sixth version's name was changed to Raku. Both languages continue to be developed independently by different development teams which liberally borrow ideas from each other. Perl borrows features from other programming languages including C, sh, AWK, and sed. It provides text processing facilities without the arbitrary data-length limits of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Proto-Indo-European Nominals
Proto-Indo-European nominals include nouns, adjectives, and pronouns. Their grammatical forms and meanings have been reconstructed by modern linguists, based on similarities found across all Indo-European languages. This article discusses nouns and adjectives; Proto-Indo-European pronouns are treated elsewhere. The Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) had eight or nine cases, three numbers (singular, dual and plural) and probably originally two genders (animate and neuter), with the animate later splitting into the masculine and the feminine. Nominals fell into multiple different declensions. Most of them had word stems ending in a consonant (called athematic stems) and exhibited a complex pattern of accent shifts and/or vowel changes (ablaut) among the different cases. Two declensions ended in a vowel (The asterisk (*) indicates that the form is not directly attested but has been reconstructed on the basis of other linguistic material.) and are called ''thematic''; they we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |