|
Planck Star
In loop quantum gravity theory, a Planck star is a hypothetical astronomical object, theorized as a compact, exotic star, that exists within a black hole's event horizon, created when the energy density of a collapsing star reaches the Planck energy density. Under these conditions, assuming gravity and spacetime are quantized, a repulsive "force" arises from Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. The accumulation of mass–energy inside the Planck star cannot collapse beyond this limit because it violates the uncertainty principle for spacetime itself. The key feature of this theoretical object is that this repulsion arises from the energy density, not the Planck length, and starts taking effect far earlier than might be expected. This repulsive "force" is strong enough to stop the star's collapse well before a singularity is formed and, indeed, well before the Planck scale for distance: for a stellar mass black hole the Planck star would be of the order of - for a primordial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loop Quantum Gravity
Loop quantum gravity (LQG) is a theory of quantum gravity that incorporates matter of the Standard Model into the framework established for the intrinsic quantum gravity case. It is an attempt to develop a quantum theory of gravity based directly on Albert Einstein's geometric formulation rather than the treatment of gravity as a mysterious mechanism (force). As a theory, LQG postulates that the structure of space and time is composed of finite loops woven into an extremely fine fabric or network. These networks of loops are called spin networks. The evolution of a spin network, or spin foam, has a scale on the order of a Planck length, approximately 10−35 meters, and smaller scales are meaningless. Consequently, not just matter, but space itself, prefers an atomic structure. The areas of research, which involve about 30 research groups worldwide, share the basic physical assumptions and the mathematical description of quantum space. Research has evolved in two directions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
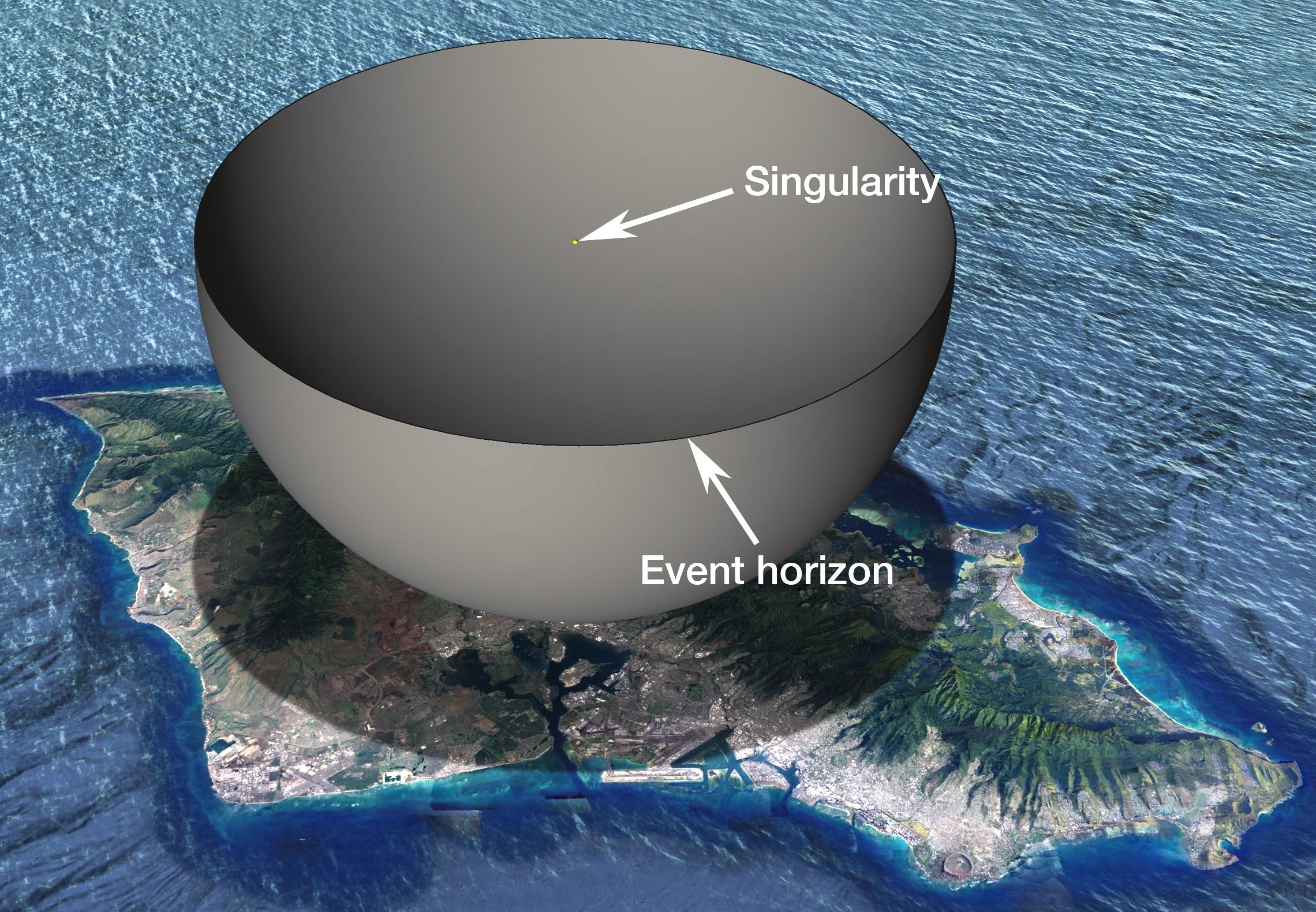
Gravitational Singularity
A gravitational singularity, spacetime singularity, or simply singularity, is a theoretical condition in which gravity is predicted to be so intense that spacetime itself would break down catastrophically. As such, a singularity is by definition no longer part of the regular spacetime and cannot be determined by "where" or "when”. Gravitational singularities exist at a junction between general relativity and quantum mechanics; therefore, the properties of the singularity cannot be described without an established theory of quantum gravity. Trying to find a complete and precise definition of singularities in the theory of general relativity, the current best theory of gravity, remains a difficult problem. A singularity in general relativity can be defined by the scalar invariant curvature becoming infinite or, better, by a geodesic being incomplete. General relativity predicts that any object collapsing beyond its Schwarzschild radius would form a black hole, inside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsingular Black Hole Models
A nonsingular black hole model is a mathematical theory of black holes that avoids certain theoretical problems with the standard black hole model, including information loss and the unobservable nature of the black hole event horizon. Avoiding paradoxes in the standard black hole model For a black hole to physically exist as a solution to Einstein's equation, it must form an event horizon in finite time relative to outside observers. This requires an accurate theory of black hole formation, of which several have been proposed. In 2007, Shuan Nan Zhang of Tsinghua University proposed a model in which the event horizon of a potential black hole only forms (or expands) after an object falls into the existing horizon, or after the horizon has exceeded the critical density. In other words, an infalling object causes the horizon of a black hole to expand, which only occurs after the object has fallen into the hole, allowing an observable horizon in finite time. This solution does n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuzzball (string Theory)
Fuzzballs are hypothetical objects in superstring theory, intended to provide a fully quantum description of the black holes predicted by general relativity. The fuzzball hypothesis dispenses with the singularity at the heart of a black hole by positing that the entire region within the black hole's event horizon is actually an extended object: a ball of strings, which are advanced as the ultimate building blocks of matter and light. Under string theory, strings are bundles of energy vibrating in complex ways in both the three familiar dimensions of space as well as in extra dimensions.Jennifer Ouellette"The Fuzzball Fix for a Black Hole Paradox" ''Quanta Magazine'', (June 23, 2015). Fuzzballs provide resolutions to two major open problems in black hole physics. First, they avoid the gravitational singularity that exists within the event horizon of a black hole. General relativity predicts that at the singularity, the curvature of spacetime becomes infinite, and it cannot determi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Theory
In physics, string theory is a theoretical framework in which the point-like particles of particle physics are replaced by one-dimensional objects called strings. String theory describes how these strings propagate through space and interact with each other. On distance scales larger than the string scale, a string acts like a particle, with its mass, charge, and other properties determined by the vibrational state of the string. In string theory, one of the many vibrational states of the string corresponds to the graviton, a quantum mechanical particle that carries the gravitational force. Thus, string theory is a theory of quantum gravity. String theory is a broad and varied subject that attempts to address a number of deep questions of fundamental physics. String theory has contributed a number of advances to mathematical physics, which have been applied to a variety of problems in black hole physics, early universe cosmology, nuclear physics, and condensed matter ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Hole
In general relativity, a white hole is a hypothetical region of spacetime and Gravitational singularity, singularity that cannot be entered from the outside, although energy, matter, light and information can escape from it. In this sense, it is the reverse of a black hole, from which energy, matter, light and information cannot escape. White holes appear in the theory of Wormhole#Schwarzschild wormholes, eternal black holes. In addition to a black hole region in the future, such a solution of the Einstein field equations has a white hole region in its past. This region does not exist for black holes that have formed through gravitational collapse, however, nor are there any observed physical processes through which a white hole could be formed. Supermassive black holes (SMBHs) are theoretically predicted to be at the center of every galaxy and may be essential for their formation. Stephen Hawking and others have proposed that these supermassive black holes could Black hole cosmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hole Firewall
A black hole firewall is a hypothetical phenomenon where an observer falling into a black hole encounters high-energy quanta at (or near) the event horizon. The "firewall" phenomenon was proposed in 2012 by physicists Ahmed Almheiri, Donald Marolf, Joseph Polchinski, and James Sully as a possible solution to an apparent inconsistency in black hole complementarity. The proposal is sometimes referred to as the AMPS firewall, an acronym for the names of the authors of the 2012 paper. The potential inconsistency pointed out by AMPS had been pointed out earlier by Samir Mathur who used the argument in favour of the fuzzball proposal. The use of a firewall to resolve this inconsistency remains controversial, with physicists divided as to the solution to the paradox. The motivating paradox According to quantum field theory in curved spacetime, a single emission of Hawking radiation involves two mutually entangled particles. The outgoing particle escapes and is emitted as a quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesca Vidotto
Francesca Vidotto (born November 22, 1980) is an Italian theoretical physicist. Biography She earned her UG/ MA in theoretical physics at the University of Padova and the PhD as double-degree at the University of Pavia and the Aix-Marseille Université. Afterwards, she was a postdoc researcher at the universities of Grenoble, Nijmegen and Bilbao. She was awarded a Rubicon (2012) and a Veni (2014) fellowship by the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research. From 2019, she has been an Assistant Professor of Physics & Astronomy and Philosophy at the University of Western Ontario, where she held a Canada Research Chair in Foundations of Physics. She has been also a core member and associate director oWestern's Rotman Institute of Philosophy Her research explores the quantum aspects of the gravitational field, in the framework of Loop Quantum Gravity. Her work covers topics from the cosmological and astrophysical applications of quantum gravity to the reflections on the nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlo Rovelli
Carlo Rovelli (born 3 May 1956) is an Italian theoretical physicist and writer who has worked in Italy, the United States, France, and Canada. He is currently Emeritus Professor at the Centre de Physique Theorique of Marseille in France, a Distinguished Visiting Research Chair at the Perimeter Institute, core member of the Rotman Institute of Philosophy of Western University in Canada, and Fractal Faculty of the Santa Fe Institute in The United States. Rovelli works mainly in the field of quantum gravity and is a founder of the theory of loop quantum gravity. He has also worked in the history and philosophy of science, formulating the relational quantum mechanics and the notion of thermal time. He collaborates with several Italian newspapers, including the cultural supplements of the '' Corriere della Sera'', ''Il Sole 24 Ore'', and ''La Repubblica''. His popular science book, '' Seven Brief Lessons on Physics'', was originally published in Italian in 2014. It has sold over t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Dilation
Time dilation is the difference in elapsed time as measured by two clocks, either because of a relative velocity between them (special relativity), or a difference in gravitational potential between their locations (general relativity). When unspecified, "time dilation" usually refers to the effect due to velocity. The dilation compares "wristwatch" clock readings between events measured in different inertial frames and is not observed by visual comparison of clocks across moving frames. These predictions of the theory of relativity have been repeatedly confirmed by experiment, and they are of practical concern, for instance in the operation of satellite navigation systems such as GPS and Galileo. Invisibility Time dilation is a relationship between clock readings. Visually observed clock readings involve delays due to the propagation speed of light from the clock to the observer. Thus there is no direct way to observe time dilation. As an example of time dilation, two expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawking Radiation
Hawking radiation is black-body radiation released outside a black hole's event horizon due to quantum effects according to a model developed by Stephen Hawking in 1974. The radiation was not predicted by previous models which assumed that once electromagnetic radiation is inside the event horizon, it cannot escape. Hawking radiation is predicted to be extremely faint and is many orders of magnitude below the current best telescopes' detecting ability. Hawking radiation would reduce the mass and rotational energy of black holes and consequently cause black hole evaporation. Because of this, black holes that do not gain mass through other means are expected to shrink and ultimately vanish. For all except the smallest black holes, this happens extremely slowly. The radiation temperature, called Hawking temperature, is inversely proportional to the black hole's mass, so micro black holes are predicted to be larger emitters of radiation than larger black holes and should dissipat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
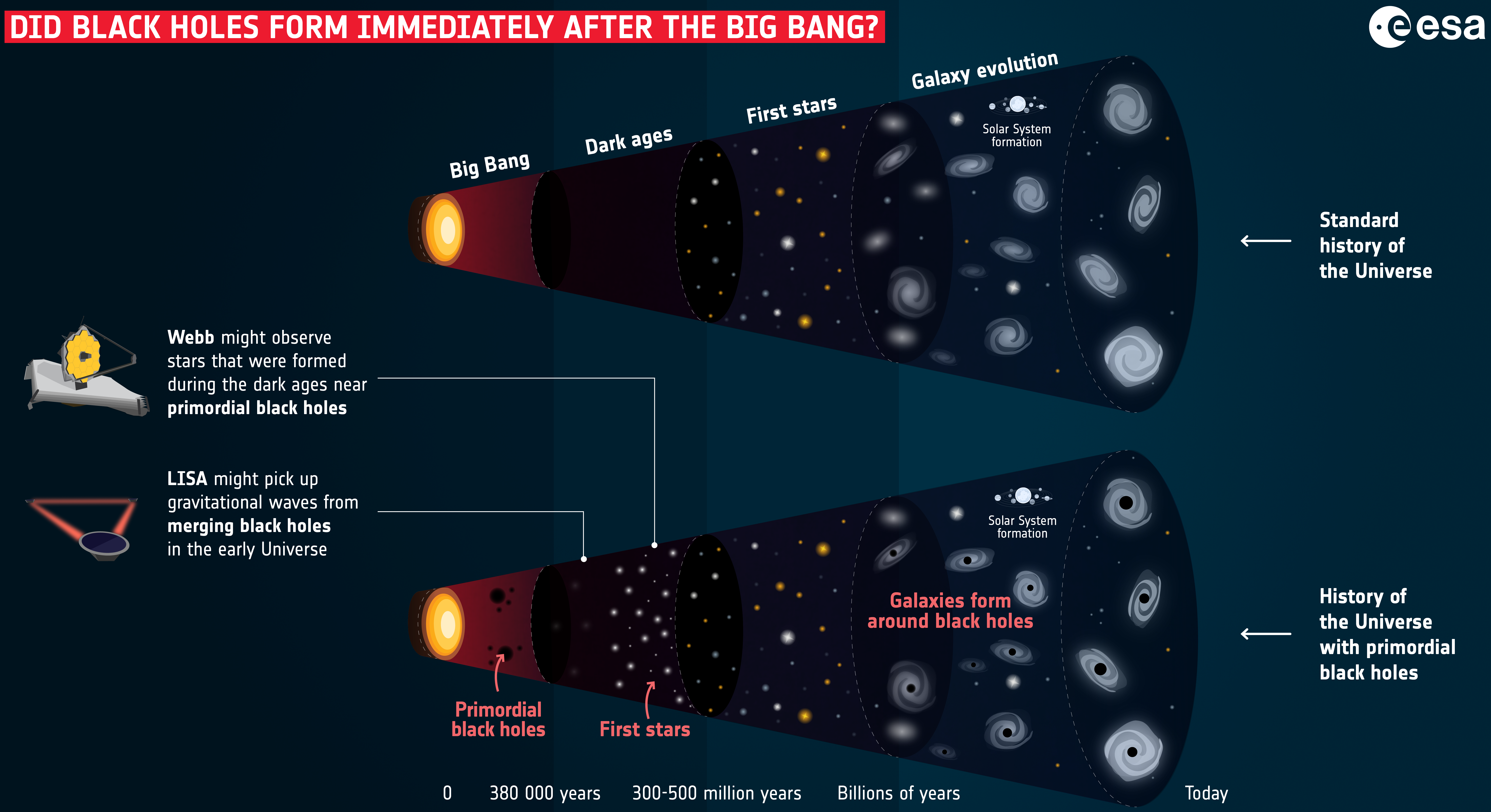
Primordial Black Hole
In cosmology, primordial black holes (PBHs) are hypothetical black holes that formed soon after the Big Bang. In the inflationary era and early radiation-dominated universe, extremely dense pockets of subatomic matter may have been tightly packed to the point of gravitational collapse, creating primordial black holes without the supernova compression typically needed to make black holes today. Because the creation of primordial black holes would pre-date the first stars, they are not limited to the narrow mass range of stellar black holes. In 1966, Yakov Zeldovich and Igor Novikov first proposed the existence of such black holes, while the first in-depth study was conducted by Stephen Hawking in 1971. However, their existence remains hypothetical. In September 2022, primordial black holes were proposed by some researchers to explain the unexpected very large early galaxies discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). PBHs have long been considered possibly important i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |