|
Piper (Indigenous Australian Explorer)
Piper (c.1810 – ?), also known as John Piper and Jemmy Piper, was a Wiradjuri man from the Bathurst region of New South Wales who led Sir Thomas Mitchell's 1836 expedition along the Lachlan, Murrumbidgee and Murray Rivers and into what is now known as the State of Victoria. Early life Details of Piper's early life are unclear, except that he was born around 1810 into a Wiradjuri clan near to the site what soon after became the British military outpost of Bathurst. As a boy he survived the Bathurst War between the colonists and his people. It appears that he obtained the name of Piper during adolescence after becoming associated, probably as servant, with the military officer John Piper who was granted the estate of Alloway Bank near Bathurst in the mid-1820s. Mitchell's 1836 expedition In 1836, the chief surveyor of the colony of New South Wales, Thomas Mitchell, was tasked with exploring the major rivers to the south-west of Sydney. He arrived in Bathurst in March of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiradjuri
The Wiradjuri people (; ) are a group of Aboriginal Australian people from central New South Wales, united by common descent through kinship and shared traditions. They survived as skilled hunter-fisher-gatherers, in family groups or clans, and many still use knowledge of hunting and gathering techniques as part of their customary life. In the 21st century, major Wiradjuri groups live in Condobolin, Peak Hill, Narrandera and Griffith. There are significant populations at Wagga Wagga and Leeton and smaller groups at West Wyalong, Parkes, Dubbo, Forbes, Cootamundra, Darlington Point, Cowra and Young. Name The Wiradjuri autonym is derived from , meaning "no" or "not", with the comitative suffix or meaning "having". That the Wiradjuri said , as opposed to some other word for "no", was seen as a distinctive feature of their speech, and several other tribes in New South Wales, to the west of the Great Dividing Range, are similarly named after their own words for "no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darling River
The Darling River (or River Darling; Paakantyi: ''Baaka'' or ''Barka''), is the third-longest river in Australia, measuring from its source in northern New South Wales to its confluence with the Murray River at Wentworth. Including its longest contiguous tributaries, it is long, making it the longest river system in Australia. The Darling River is the outback's most famous waterway. As of the early 2020s, the Darling is in poor health, suffering from over-allocation of its waters to irrigation, pollution from pesticide runoff, and prolonged drought. During drought periods in 2019 it barely flowed at all. The river has a high salt content and declining water quality. Increased rainfall in its catchment in 2010 improved its flow, but the health of the river will depend on long-term management. The Division of Darling, Division of Riverina-Darling, Electoral district of Darling and Electoral district of Lachlan and Lower Darling were named after the river. History Aborig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-barrelled Shotgun
A double-barreled shotgun, also known as a double shotgun, is a break-action shotgun with two parallel barrels, allowing two single shots that can be fired simultaneously or sequentially in quick succession. Construction Modern double-barreled shotguns, often known as ''doubles'', are almost universally break action, with the barrels hinge down at the rear to expose the breech ends for unloading and reloading. Since there is no reciprocating action needed to eject and reload the shells, doubles are more compact than repeating designs such as pump action, lever action, bolt action, or self-loading shotguns. Barrel configuration Double-barreled shotguns (specifically break-action), come in two basic configurations: * side-by-side (S×S) — the two barrels are arranged horizontally; * over-and-under (O/U) — the two barrels are arranged vertically. The original double-barreled guns were commonly all side-by-side designs, which was a more practical design for muzzleloaders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunter Region
The Hunter Region, also commonly known as the Hunter Valley, Newcastle Region, or simply Hunter, spans the region in northern New South Wales, Australia, extending from approximately to north of Sydney. It contains the Hunter River (New South Wales), Hunter River and its tributaries with highland areas to the north and south. Situated at the northern end of the Sydney Basin bioregion, the Hunter Valley is one of the largest river valleys on the NSW coast, and is most commonly known for its wineries and coal industry. Most of the population of the Hunter Region lives within of the coast, with 55% of the entire population living in the cities of Newcastle, New South Wales, Newcastle and City of Lake Macquarie, Lake Macquarie. There are numerous other towns and villages scattered across the region in the eleven Local government in Australia, local government areas (LGAs) that make up the region. At the the combined population of the region was 682,465, and is expected to reach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moreton Bay
Moreton Bay is a bay located on the eastern coast of Australia from central Brisbane, Queensland. It is one of Queensland's most important coastal resources. The waters of Moreton Bay are a popular destination for recreational anglers and are used by commercial operators who provide seafood to market. The Port of Brisbane coordinates large traffic along the shipping channel which crosses the northern section of the bay. The bay serves as a safe approach to the airport and reduces noise pollution over the city to the west of the runway. A number of barge, ferry and water-taxi services also travel over the bay. Moreton Bay was the site of conflict between the Quandamooka people and early European settlers. It contains environmentally significant habitats and large areas of sandbanks. The bay is the only place in Australia where dugong gather into herds. Many parts of the mainland foreshore and southern islands are settled. The waters of Moreton Bay are relatively calm, bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
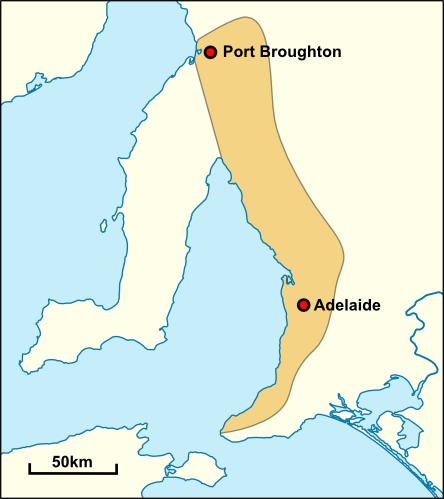
Adelaide
Adelaide ( , ; ) is the list of Australian capital cities, capital and most populous city of South Australia, as well as the list of cities in Australia by population, fifth-most populous city in Australia. The name "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre; the demonym ''Adelaidean'' is used to denote the city and the residents of Adelaide. The Native title in Australia#Traditional owner, traditional owners of the Adelaide region are the Kaurna, with the name referring to the area of the city centre and surrounding Adelaide Park Lands, Park Lands, in the Kaurna language. Adelaide is situated on the Adelaide Plains north of the Fleurieu Peninsula, between the Gulf St Vincent in the west and the Mount Lofty Ranges in the east. Its metropolitan area extends from the coast to the Adelaide Hills, foothills of the Mount Lofty Ranges, and stretches from Gawler in the north to Sellicks Beach in the south. Named in ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Cunningham (botanist)
Richard Cunningham (12 February 1793 – April 1835) was an English botanist who became Colonial Botanist of New South Wales and superintendent of the Sydney Botanic Gardens. Early life He was born in Wimbledon, Surrey, England, the second son of gardener Allan Cunningham, who came from Renfrewshire, Scotland, and his English wife Sarah. Cunningham was educated at a Rev. John Adams Academy at Putney and then went to work for William Townsend Aiton on ''Hortus Kewensis'' for six years. For the next 18 years, he worked at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, England, cataloguing specimens sent from Australia by his brother Allan. Australia After being recommended for the position by both his brother Allan and botanist Robert Brown, Cunningham sailed to Australia to take up the position of Colonial Botanist of New South Wales and superintendent of Sydney Botanic Gardens, arriving in January 1833. Later that year he made an expedition to New Zealand, on . He was dropped off in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Darling
General Sir Ralph Darling, GCH (1772 – 2 April 1858) was a British Army officer who served as Governor of New South Wales from 1825 to 1831. His period of governorship was unpopular, with Darling being broadly regarded as a tyrant. He introduced austere policies that resulted in croneyism, prisoner abuse, curtailment of press freedoms, discrimination against emancipists, obstruction of representative government, theatrical entertainment bans and injustices toward Indigenous Australians. During his time as Governor, a significant area of eastern Australia was explored by the British with local geographical features being named after him including the Darling River and the Darling Downs, along with Darling Harbour in Sydney. Early life Born in Ireland around 1772, Ralph Darling was the eldest son of Christopher Darling, an English sergeant, and later military adjutant, in the 45th Regiment of Foot of the British Army. While his father was away on service during the Amer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broken River (Victoria)
The Broken River, a minor inland perennial river of the Goulburn River, Goulburn Broken catchment, part of the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Alpine and Northern Country/North Central regions of the Australian state of Victoria (Australia), Victoria. The headwaters of the Broken River rise in the western slopes of the Victorian Alps, near Bald Hill and descend to flow into the Goulburn River near Shepparton. The river is impounded by the Nillahcootie Dam to create Lake Nillahcootie and Benalla Dam to create Lake Benalla. Location and features The river rises below Bald Hill on the western slopes of the Victorian Alps, within the Shire of Mansfield. The river flow generally west, then north, then west passing through or adjacent to the regional cities of and , joined by ten minor tributaries, before reaching its confluence with the Goulburn River within Shepparton. The river descends over its watercourse, course. When at maximum capacity, the Broken River is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ironbark
Ironbark is a common name of a number of species in three taxonomic groups within the genus ''Eucalyptus'' that have dark, deeply furrowed bark. Instead of being shed annually as in many of the other species of ''Eucalyptus'', the dead bark accumulates on the trees, forming the fissures. It becomes rough after drying out and becomes impregnated with kino (red gum), a dark red tree sap exuded by the tree. The tree is so named for the apparent resemblance of its bark to iron slag. The bark is resistant to fire and heat and protects the living tissue within the trunk and branches from fire. In cases of extreme fire, where leaves and shoots are removed, the protective bark aids in protecting epicormic buds which allow the tree to reshoot. Being a very dense, hard wood, a length of ironbark is often used as a bug shoe on the bottom of a ship's skeg to protect it from shipworms. Ironbark was widely used in the piles of 19th and early 20th century bridges and wharves in New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wimmera River
The Wimmera River, an inland intermittent river of the Wimmera catchment, is located in the Grampians and Wimmera regions of the Australian state of Victoria. Rising in the Pyrenees, on the northern slopes of the Great Dividing Range, the Wimmera River flows generally north by west and drains into Lake Hindmarsh and Lake Albacutya, a series of ephemeral lakes that, whilst they do not directly empty into a defined watercourse, form part of the Murray River catchment of the Murray-Darling basin. Course and features The Wimmera River rises in the Great Dividing Range below , between and , and flows generally north and west, through , , and , also forming the eastern boundary of the Little Desert National Park. It is joined by fourteen minor tributaries, including the Mackenzie River, before reaching its mouth at Lake Hindmarsh, near Jeparit. The river descends over its course. On the rare occasions that Lake Hindmarsh overflows, water flows via Outlet Creek to Lake Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Boga (Victoria)
Lake Boga (), a freshwater endorheic lake that is managed by Goulburn–Murray Water as a water storage, is part of the Victorian Mid Murray Storages, is located near in The Mallee region of Victoria, in southeastern Australia. The lake is situated about southeast of Swan Hill and adjacent to the town of the same name. During World War II, Lake Boga was used as a repair and service depot for flying boats at the Lake Boga Flying Boat Base which was established in June 1942 and closed in November 1947. Water storage Lake Boga has a capacity of at the full supply level of and a surface area of . Under normal operation, water levels in Lake Boga vary between levels of and . At the level of , there is a depth of up to of water in the deepest parts of the lake. Although operation and lake levels will vary from season to season, in general water will be harvested into Lake Boga during the winter and spring months. Subject to sufficient water to harvest, the lake generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |