|
Pinzón Brothers
The Pinzón brothers were Spanish sailors, pirates, explorers and fishermen, natives of Palos de la Frontera, Huelva, Spain. Martín Alonso, Francisco Martín and Vicente Yáñez, who participated in Christopher Columbus's first expedition to the New World (generally considered to constitute the discovery of the Americas by Europeans) and in other voyages of discovery and exploration in the late 15th and early 16th centuries.A document in the Archivo de Simancas in the ''Registro general del Sello'', dated March 1505, gives the terms of the inheritance of the estate of the Pinzón brothers' mother. This document is the source for the parents of the brothers being Martín Alonso Pinzón (father) and Mayor Vicente (mother), who left them some houses in the Barrero neighborhood of Palos, indicating that the family had been in Palos for at least one generation before the brothers.Cited in: * * Dentro del proceso de apelación de la sentencia de Dueñas -pleito iniciado por Diego Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of The Castilian Succession
The War of the Castilian Succession was the military conflict contested from 1475 to 1479 for the succession of the Crown of Castile fought between the supporters of Joanna 'la Beltraneja', reputed daughter of the late monarch Henry IV of Castile, and those of Henry's half-sister, Isabella, who was ultimately successful. The war had a marked international character, as Isabella was married to Ferdinand, heir apparent to the Crown of Aragon, while Joanna was strategically married to King Afonso V of Portugal, her uncle, after the suggestion of her supporters. France intervened in support of Portugal, as they were rivals with Aragon for territory in Italy and Roussillon. Despite a few initial successes by the supporters of Joanna, a lack of military aggressiveness by Afonso V and the stalemateAs noted by Spanish scholars Luis Suárez Fernández, Juan de Mata Carriazo and by Manuel F. Álvarez: "Not a military victory, but a political victory, the battle of Toro is in itself, a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plus Ultra (flying Boat)
''Plus Ultra'' is a Dornier Do J flying boat which completed the first transatlantic flight between Spain and South America in January 1926 with a crew of Spanish aviators, that included: the major Ramón Franco, the captain Julio Ruiz de Alda, Julio Ruiz de Alda Miqueleiz, the sub-lieutenant Juan Manuel Durán, and the mechanic Pablo Rada. The flight The ''Plus Ultra'' departed from Palos de la Frontera, in Province of Huelva, Huelva, Spain on January 22 and arrived in Buenos Aires, Argentina on January 26. It stopped over at Gran Canaria, Cape Verde, Fernando de Noronha, Pernambuco (Recife), Rio de Janeiro and Montevideo. The journey was completed in 59 hours and 39 minutes. The flight of the ''Plus Ultra'' followed approximately the route taken, in 1922, by the Portuguese aviators Artur de Sacadura Cabral, Sacadura Cabral and Carlos Viegas Gago Coutinho, Gago Coutinho, in the First aerial crossing of the South Atlantic, first Trans-Atlantic flight over the South Atlant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodrigo De Triana
Rodrigo de Triana (1469 in Lepe, Huelva, Spain – 1535 in Maluku Islands) was a Spanish sailor, believed to be the first European from the Age of Exploration to have seen the Americas. Born as Juan Rodríguez Bermejo, Triana was the son of hidalgo and potter Vicente Bermejo and Sereni Betancour. On October 12, 1492, while on Christopher Columbus' ship '' La Pinta'', he sighted a land that was called Guanahani by the natives. "'" �The Diary of Christopher Columbusref name="diary"> After spotting the Bahamian island at approximately two o'clock in the morning, he is reported to have shouted "'" (Land! Land!). Columbus claims in his journal that he saw a light "like a little wax candle rising and falling" four hours earlier, "but it was so indistinct that he did not dare to affirm it was land." Rodrigo had spotted a small island in the Lucayas archipelago (known today as the Bahamas), in the Caribbean Sea. The island was named by Christopher Columbus as San Salvador, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Rodriguez Bermejo
Rodrigo de Triana (1469 in Lepe, Huelva, Spain – 1535 in Maluku Islands) was a Spanish sailor, believed to be the first European from the Age of Exploration to have seen the Americas. Born as Juan Rodríguez Bermejo, Triana was the son of Hidalgo (nobility), hidalgo and pottery, potter Vicente Bermejo and Sereni Betancour. On October 12, 1492, while on Christopher Columbus' ship ''Pinta (ship), La Pinta'', he sighted a land that was called Guanahani by the natives. "'" �The Diary of Christopher Columbusref name="diary"> After spotting the Bahamian island at approximately two o'clock in the morning, he is reported to have shouted "'" (Land! Land!). Columbus claims in his journal that he 1492 light sighting, saw a light "like a little wax candle rising and falling" four hours earlier, "but it was so indistinct that he did not dare to affirm it was land." Rodrigo had spotted a small island in the Lucayas archipelago (known today as the Bahamas), in the Caribbean Sea. The is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
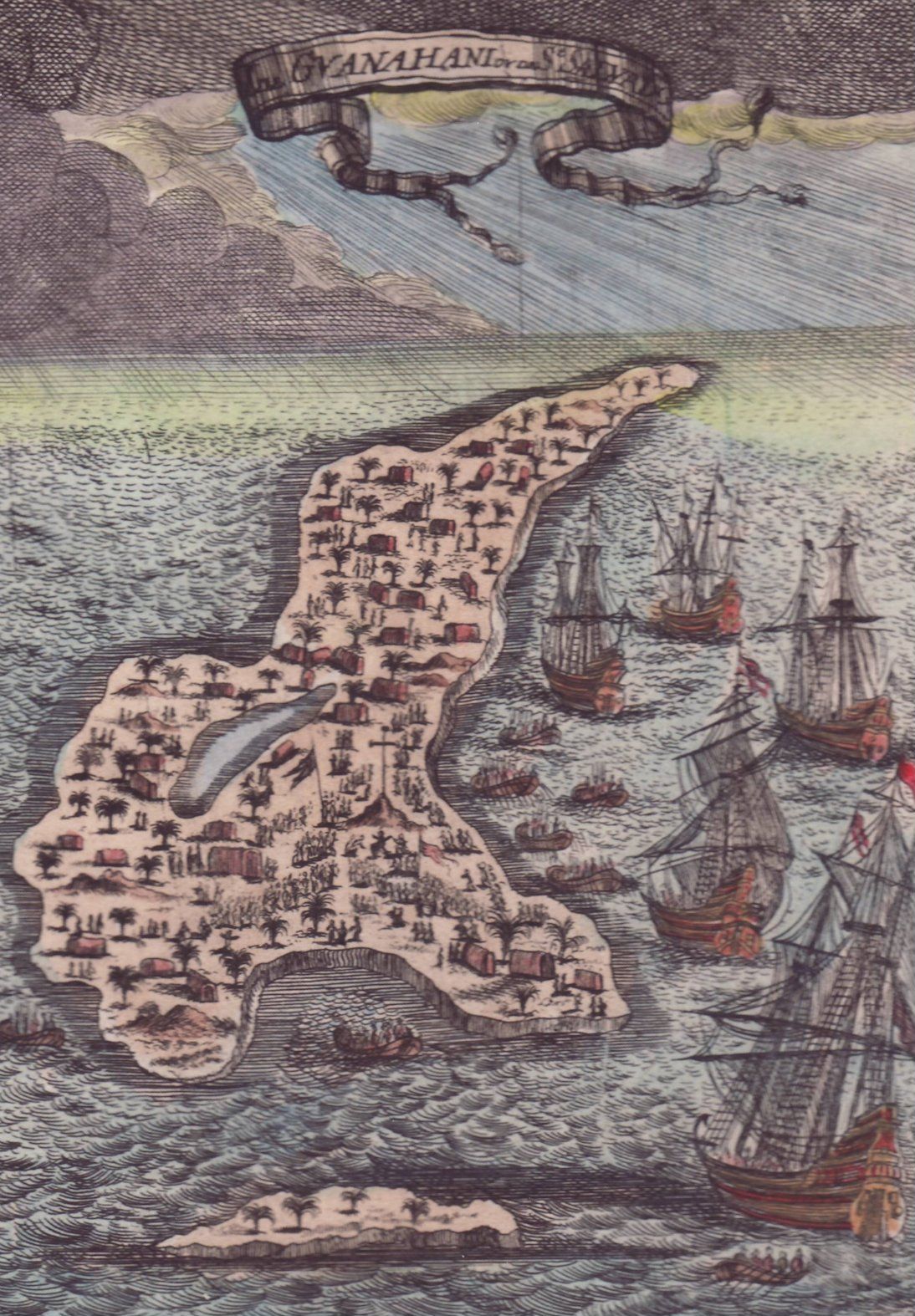
Guanahani
Guanahaní (meaning "small upper waters land") was the Taíno language, Taíno name of an island in the Bahamas that was the first land in the New World sighted and visited by Christopher Columbus' Voyages of Christopher Columbus#First voyage (1492–1493), first voyage, on 12 October 1492. It is a bean-shaped island that Columbus called San Salvador. Guanahaní has traditionally been identified with Watlings Island, which was officially renamed San Salvador Island in 1925 as a result, but modern scholars are divided on the accuracy of this identification and several alternative candidates in and around the southern Bahamas have been proposed as well. Primary sources Letter from Columbus himself Upon his return to Spain in the spring of 1493, Columbus Columbus Letter on the First Voyage, wrote a letter to Luis de Santangel, one of his patrons at the Royal Court of Kingdom of Castile, Castile. The letter was printed widely and translated into many languages, spreading the news of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
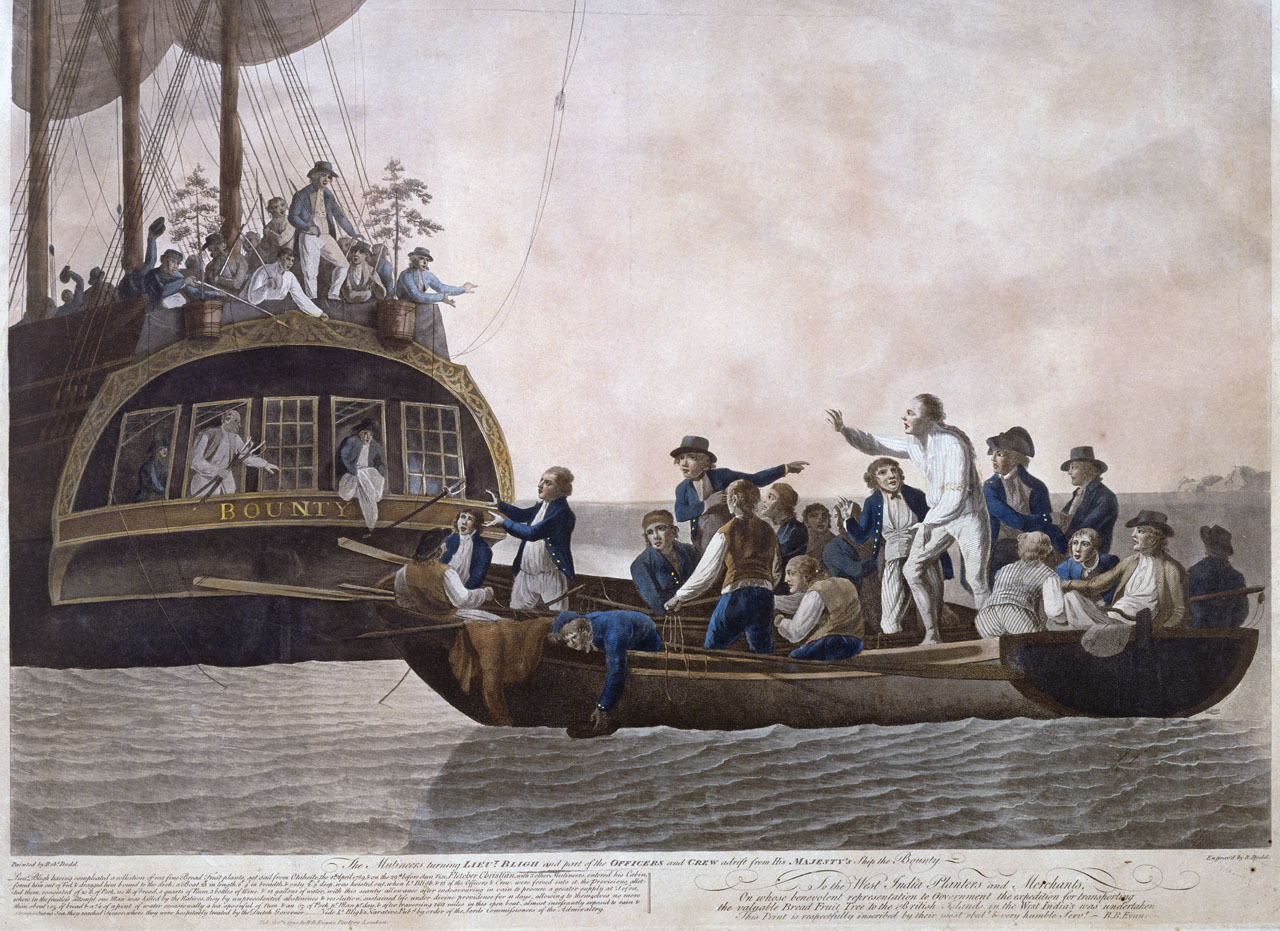
Mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military or a crew) to oppose, change, or remove superiors or their orders. The term is commonly used for insubordination by members of the military against an officer or superior, but it can also sometimes mean any type of rebellion against any force. Mutiny does not necessarily need to refer to a military force and can describe a political, economic, or power structure in which subordinates defy superiors. During the Age of Discovery, mutiny particularly meant open rebellion against a ship's captain. This occurred, for example, during Ferdinand Magellan's journeys around the world, resulting in the killing of one mutineer, the execution of another, and the marooning of others; on Henry Hudson's '' Discovery'', resulting in Hudson and others being set adrift in a boat; and the famous mutiny on the ''Bounty''. Mutiny is widely considered a serious crime, punishable by imprisonment, penal labour or death. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population, seventh-largest by population, with over 212 million people. The country is a federation composed of 26 Federative units of Brazil, states and a Federal District (Brazil), Federal District, which hosts the capital, Brasília. List of cities in Brazil by population, Its most populous city is São Paulo, followed by Rio de Janeiro. Brazil has the most Portuguese-speaking countries, Portuguese speakers in the world and is the only country in the Americas where Portuguese language, Portuguese is an Portuguese-speaking world, official language. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazil, coastline of . Covering roughly half of South America's land area, it Borders of Brazil, borders all other countries and ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odiel
The Odiel () is a river in the Atlantic basin in southern Spain, more precisely in the province of Huelva, Andalusia. It originates at Marimateos in the Sierra de Aracena at an elevation of above sea level. At the Punta del Sebo, it joins the Rio Tinto to form the Huelva Estuary. Its principal tributaries are the Escalada, Meca, Olivargas, Oraque, Santa Eulalia, and El Villar. Its basin covers . In Roman times it was known as the ''Urius'', although some scholars have proposed to identify the Odiel with another ancient name normally associated with the Río Tinto (''Luxia''). Even before the Romans, its mouth was an important place of commerce, as can be seen by archaeological remnants from Phoenicians and Ancient Greeks, known as the "Huelva Estuary Deposit" (), dated 1000 BCE. , ''Arte e historia''. Accessed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Río Tinto (river)
The Río Tinto (, ''red river'' or Tinto River) is a highly toxic river in southwestern Spain that rises in the Sierra Morena mountains of Andalusia. It flows generally south-southwest, reaching the Gulf of Cádiz at Huelva. The Río Tinto river has a unique red and orange colour derived from its chemical makeup that is extremely acidic and with very high levels of iron and heavy metals. The name ''río tinto'' means "coloured river" in Spanish, in contrast to most rivers, which are clear. However, "tinto" is also an expression for red wine in Spain, so it is also related to this second meaning. The river maintains its colour for an approximate length of 50 kilometres. After the 50 kilometre mark, the chemistry that makes the Río Tinto river so unique appears to slowly decline, as does the odd colouring. The location where the chemistry of the river is altered is near the town of Niebla. The river's chemistry begins to significantly change following the town of Niebla as the R� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niña (ship)
''La Niña'' (Spanish for ''The Girl'') was one of the three Spanish ships used by Italian explorer Christopher Columbus in his first voyage to the West Indies in 1492. As was tradition for Spanish ships of the day, she bore a female saint's name, ''Santa Clara''. However, she was commonly referred to by her nickname, ''La Niña'' ('The Little Girl'), which was probably a pun on the name of her owner, Juan Niño of Moguer ('Niño', his surname, meaning 'Little Boy'). She was a standard caravel-type vessel. The other ships of the Columbus expedition were the caravel-type and the carrack-type . ''Niña'' was by far Columbus's favorite. She was originally lateen sail rigged ''caravela latina'', but she was re-rigged as a ''caravela redonda'' at Las Palmas, in the Canary Islands, with square sails for better ocean performance. There is no authentic documentation on the specifics of ''Niña''s design, although Michele de Cuneo, who accompanied Columbus on his second voyage, mention ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |