|
Pigafetta's Dictionary
Pigafetta's dictionary is the first Italian–Malay vocabulary written by the chronicler Antonio Pigafetta. These are the list words of the languages of various natives he met during his journey with Ferdinand Magellan. Background The Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan led about 270 men on five ships from Spain to look for the Spice Islands of Maluku. The Venetian chronicler Antonio Pigafetta participated in the expedition and served as an assistant to Magellan. He kept a detailed, daily journal of the voyage. He was one of only 18 men who returned to Spain in 1522. One of his notable works in the voyage was his narrative and the list of words of various languages of natives during the long journey which includes: Brazilian native language – 8 words, Patagonian language – 90 words, Philippine language – 160 words, Malay – more than 400 words, which Pigafetta calls "Moorish." In Pigafetta's book, (), he takes care to record as many words as he can. The chronicle of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Pigafetta
Antonio Pigafetta (; – c. 1531) was a Venetian scholar and explorer. In 1519, he joined the Spanish expedition to the Spice Islands led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan, the world's first Magellan's circumnavigation, circumnavigation, and is best known for being the chronicler of the voyage. During the expedition, he served as Magellan's assistant until Magellan's death in the Philippine Islands, and kept an accurate journal, which later assisted him in translating the Cebuano language. It is the Pigafetta's dictionary, first recorded document concerning the language. Pigafetta was one of the Magellan's circumnavigation#Survivors, 18 men who made the complete trip, returning to Spain in 1522, under the command of Juan Sebastián Elcano, out of the approximately 240 who set out three years earlier. These men completed the first circumnavigation of the world while others mutinied and returned in the first year. Pigafetta's surviving journal is the source for much of what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
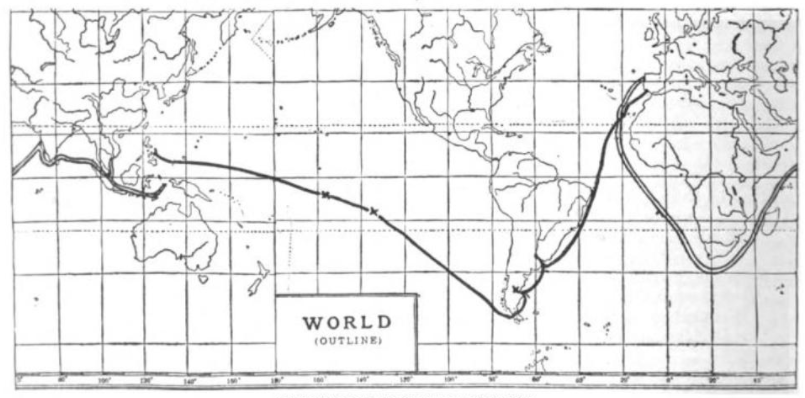
Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer best known for having planned and led the 1519–22 Spanish expedition to the East Indies. During this expedition, he also discovered the Strait of Magellan, allowing his fleet to pass from the Atlantic into the Pacific Ocean and perform the first European navigation to Asia via the Pacific. Magellan was killed in battle in the Philippines and his crew, commanded by the Spanish Juan Sebastián Elcano, completed the return trip to Spain in 1522 achieving the first circumnavigation of Earth in history. Born around 1480 into a family of minor Portuguese nobility, Magellan became a skilled sailor and naval officer in service of the Portuguese Crown in Asia. King Manuel I refused to support Magellan's plan to reach the Moluccas, or Spice Islands, by sailing westwards around the American continent. Magellan then proposed the same plan to King Charles I of Spain, who approved it. In Seville, he married, fathere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malay Language
Malay ( , ; , Jawi alphabet, Jawi: ) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken primarily by Malays (ethnic group), Malays in several islands of Maritime Southeast Asia and the Malay Peninsula on the mainland Asia. The language is an official language of Brunei, Malaysia, and Singapore. Indonesian language, Indonesian, a standardized variety of Malay, is the official language of Indonesia and one of the working languages of East Timor. Malay is also spoken as a regional language of Malays (ethnic group), ethnic Malays in Indonesia and the Thai Malays, southern part of Thailand. Altogether, it is spoken by 60 million people across Maritime Southeast Asia. The language is pluricentric and a ISO 639 macrolanguage, macrolanguage, i.e., a group of Mutual intelligibility, mutually intelligible speech varieties, or dialect continuum, that have no traditional name in common, and which may be considered distinct languages by their speakers. Several varieties of it ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primer Viaje En Torno Del Globo (1922)
Primer may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Primer'' (film), a 2004 feature film written and directed by Shane Carruth * ''Primer'' (video), a documentary about the funk band Living Colour Literature * Primer (textbook), a textbook used in primary education to teach the alphabet and other basic subjects * Primer (prayer book), a common name for English prayer books used from the 13th to 16th centuries * '' The New England Primer'' (1688), a Puritan book from Colonial America with morality-themed rhymes Music * ''Primer'' (album), a 1995 music album by the musical group Rockapella * Primer 55, an American alternative metal band Firearms * Primer (firearms), a firearm powder charge-ignition mechanism ** Centerfire ammunition, Boxer or Berdan primers used in modern centerfire cartridges ** Detonator, a small explosive device also known as an explosive primer or blasting cap ** Friction primer, an ignition device for muzzle-loading cannon ** Percussion cap, a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visayan Languages
The Bisayan languages or Visayan languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken in the Philippines. They are most closely related to Tagalog and the Bikol languages, all of which are part of the Central Philippine languages. Most Bisayan languages are spoken in the whole Visayas section of the country, but they are also spoken in the southern part of the Bicol Region (particularly in Masbate and Sorsogon where several dialects of Waray are spoken), islands south of Luzon, such as those that make up Romblon, most of the areas of Mindanao and the province of Sulu located southwest of Mindanao. Some residents of Metro Manila also speak one of the Bisayan languages. Over 30 languages constitute the Bisayan language family. The Bisayan language with the most speakers is Cebuano, spoken by 20 million people as a native language in Central Visayas, parts of Eastern Visayas, and most of Mindanao. Two other well-known and widespread Bisayan languages are Hili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebuano Language
Cebuano ( )Cebuano on Merriam-Webster.com is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken in the southern Philippines by Cebuano people and other Ethnic groups in the Philippines, ethnic groups as a secondary language. It is natively, though informally, called by the generic name Bisayâ (), or Binisayâ () (both terms are translated into English as ''Visayan'', though this should not be confused with other Bisayan languages) and sometimes referred to in English sources as Cebuan ( ). It is spoken by the Visayans, Visayan ethnolinguistic groups native to the islands of Cebu, Bohol, Siquijor, the eastern half of Negros Island, Negros, the western half of Leyte, the northern coastal areas of Northern Mindanao and the eastern part of Zamboanga del Norte due to Captaincy General of the Philippines, Spanish settlements during the 18th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Cebuano
Classical Cebuano, or Spanish-Era Cebuano, (, ''Binisayâ sa Katuigan sa Katsilà''; Badlit: pre-virama: , post-virama: ) was a form of the Cebuano language spoken during the Spanish colonial era of the Philippines. It was the primary language spoken in Cebu, Bohol, and other parts of Visayas and Mindanao. History The earliest surviving record of Cebuano was from a wordlist collected by Antonio Pigafetta during the Magellan expedition in 1521. The wordlist contains about 160 Cebuano words (some of which are in Malay) written in an Italian-influenced orthography, which is considered problematic due to its inconsistent and unphonetic spelling system. The oldest reliable glimpse of Cebuano's grammar and vocabulary was from Domingo Ezguerra's ''Arte de la Lengua Bisaya de la Provincia de Leyte'', a Waray grammar book written in 1663. The first dedicated grammar book for Cebuano, Francisco Encina's ''Arte de la Lengua Zebuana'', was compiled in 1801 (40 years after his death). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Langaige Du Bresil
is a vocabulary produced in the 1540s, considered the oldest substantial record of a Languages of Brazil, Brazilian language, specifically of Tupi language, Old Tupi. It is contained in a manuscript in the Bibliothèque nationale de France, cataloged as "Ms. Fr. 24269", from folio 53Recto and verso, r to 54r, and presents 88 entries. Little is known about its compiler, a sea captain or voyage organizer, probably from Bordeaux or Rouen, named Jehan Lamy. is important as it demonstrates social relations between the French and Indigenous peoples in Brazil, Brazilian indigenous people were not merely limited to commercial interactions, but, on the contrary, both peoples maintained intimate social contacts with each other. Context The tribes that spoke Old Tupi were first mentioned during the discovery of Brazil in 1500, on the occasion of 2nd Portuguese India Armada (Cabral, 1500), the voyage of Pedro Álvares Cabral, but such accounts did not include records of this language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocabulary
A vocabulary (also known as a lexicon) is a set of words, typically the set in a language or the set known to an individual. The word ''vocabulary'' originated from the Latin , meaning "a word, name". It forms an essential component of language and communication, helping convey thoughts, ideas, emotions, and information. Vocabulary can be oral, written, or signed and can be categorized into two main types: active vocabulary (words one uses regularly) and passive vocabulary (words one recognizes but does not use often). An individual's vocabulary continually evolves through various methods, including direct instruction, independent reading, and natural language exposure, but it can also shrink due to forgetting, trauma, or disease. Furthermore, vocabulary is a significant focus of study across various disciplines, like linguistics, education, psychology, and artificial intelligence. Vocabulary is not limited to single words; it also encompasses multi-word units known as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictionaries
A dictionary is a listing of lexemes from the lexicon of one or more specific languages, often arranged Alphabetical order, alphabetically (or by Semitic root, consonantal root for Semitic languages or radical-and-stroke sorting, radical and stroke for Logogram, logographic languages), which may include information on definitions, usage, etymologies, pronunciations, Bilingual dictionary, translation, etc.Webster's New World College Dictionary, Fourth Edition, 2002 It is a Lexicography, lexicographical reference that shows inter-relationships among the data. A broad distinction is made between general and specialized dictionaries. Specialized dictionaries include words in specialist fields, rather than a comprehensive range of words in the language. Lexical items that describe concepts in specific fields are usually called terms instead of words, although there is no consensus whether lexicology and terminology are two different fields of study. In theory, general dictionarie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Philippines (900–1565)
The recorded pre-colonial history of the Philippines, sometimes also referred to as its "protohistoric period" begins with the creation of the Laguna Copperplate Inscription in 900 CE and ends with the beginning of Spanish colonization in 1565. The inscription on the Laguna Copperplate Inscription itself dates its creation to 822 Saka (900 CE). The creation of this document marks the end of the prehistory of the Philippines at 900 AD, and the formal beginning of its recorded history. During this historical time period, the Philippine archipelago was home to numerous kingdoms and sultanates and was a part of the Indosphere and Sinosphere. Sources of precolonial history include archeological findings; records from contact with the Song dynasty, the Brunei Sultanate, Korea, Japan, and Muslim traders; the genealogical records of Muslim rulers; accounts written by Spanish chroniclers in the 16th and 17th centuries; and cultural patterns that at the time had not yet been repla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |