|
Phuang Malai
''Phuang malai'' (, ) or ''malai'' (, ) are a Thai form of floral garland. They are often given as offerings or kept for good luck. Origins Phuang malai may be derived from the Tamil term “poo maalai” which has the same meaning. It is a combination of two Tamil terms: “poo” (flowers) and “maalai” (garland). There is historical evidence that the Chola kings from Tamil Nadu (South India) had captured parts of what is currently Thailand, Java and Sumatra, Indonesia, and Sri Lanka. Rock inscriptions mention these victories. In general, the Tamil people are skillful garland makers and celebrate every special life event with flowers and garlands- from birth to death. Chola kings were known for patronising temples in Tamil Nadu and abroad and, in doing so, disseminated these traditions. Because of their strong presence in Thailand, the Cholas came to be known as “Chulalongarn” in Thai. The first record of ''phuang malai'' was found during the reign of King Chulalong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kuchinarai District
Kuchinarai (, ; , ) is a district (''amphoe'') in the eastern part of Kalasin province, northeastern Thailand. Geography Neighboring districts are (from the west clockwise): Don Chan, Na Mon, Huai Phueng, Na Khu, and Khao Wong of Kalasin Province; Khamcha-i and Nong Sung of Mukdahan province; Moei Wadi, Phon Thong, and Pho Chai of Roi Et province. Economy A traditional sugarcane product that used to be common in Thailand is now made only in this district, and specifically, in Lao Hai Ngam Subdistrict. It is called 'sugarcane cake' (, ) or 'sugar cake' (, ). It is made from indigenous cane grown for more than eight months. Rice farmers produce it as a secondary money-earner. The sugar cakes are made only in February and are quickly bought up and disappear from the market until the following year. Administration The district is divided into 12 sub-districts (''tambons''), which are further subdivided into 142 villages (''mubans''). There are two sub-district municipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
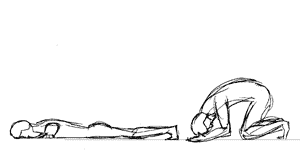
Pranāma
''Pranāma'' (Sanskrit: प्रणाम; IAST: praṇāma; meaning: "obeisance, prostration or bowing forward") is a form of respectful or reverential salutation (or reverential bowing) before something or another person – usually one's elders, spouse or teachers – as well as anyone deeply respected such as a deity, found in Indian culture and Hindu, Buddhist, Jain and Sikh traditions. The gesture, also known as the apology hand gesture, is also used as an apology in certain situations. Etymology ''Pranama'' is derived from ''pra'' (Sanskrit: प्र) and ''ānama'' (Sanskrit: आनम); ''pra'' as prefix means "forward, in front, before, very, or very much", while ''ānama'' means "bending or stretching". Combined ''pranama'' means "bending, bowing in front" or "bending much" or "prostration". In cultural terms, it means "respectful salutation" or "reverential bowing" before another, usually elders or teachers or someone deeply respected such as a deity. Types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Namaste
''Namaste'' (, Devanagari: नमस्ते), sometimes called ''namaskār'' and ''namaskāram'', is a customary Hindu manner of respectfully greeting and honouring a person or group, used at any time of day. It is used worldwide among the Hindu, Buddhist and Jain traditions. ''Namaste'' is usually spoken with a slight bow and hands pressed together, palms touching and fingers pointing upwards, thumbs close to the chest. This gesture is called ''añjali mudrā''; the standing posture incorporating it is ''pranāmāsana''. Etymology, meaning and origins ''Namaste'' (''Namas'' + ''te'') is derived from Sanskrit and is a combination of the word ''namas'' and the second person dative pronoun in its enclitic form, '' te''.Thomas Burrow, ''The Sanskrit Language'', pp. 263–268 The word ''namaḥ'' takes the sandhi form ''namas'' before the sound ''te''.Thomas Burrow, ''The Sanskrit Language'', pp. 100–102 It is found in the Vedic literature. ''Namas-krita'' and related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lei (garland)
A lei () is a garland or wreath common in The Pacific Islands of Polynesia and also in Asia (Philippines). More loosely defined, a lei is any series of objects strung together with the intent to be worn. Lei of various styles are given as gifts to honour people throughout the Pacific, being presented, for example, to visiting dignitaries, graduates, or to loved ones who are departing. Lei gained popularity in the United States due to the common practice of presenting one to arriving or leaving tourists in Hawaiʻi. Sampaguita leis are also used in the Philippines for religious reasons, typically worn to their Anito or religious statues. Symbolism A lei can be given to someone for a variety of reasons. Most commonly, these reasons include peace, love, honor, or friendship. Common events during which leis may be distributed include graduations, weddings, and school dances. Often the composition of a lei determines its significance. A lei made using a hala fruit, for instance, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Garland
A garland is a decorative braid, knot or wreath of flowers, leaves, or other material. Garlands can be worn on the head or around the neck, hung on an inanimate object, or laid in a place of cultural or religious importance. In contemporary times, Garlands are used to decorate, especially around holidays Etymology From the French language, French , itself from the Italian language, Italian , a braid. Types *Bead garland *Flower garland **Lei (garland), Lei – The traditional garland of Hawaiʻi. **Daisy chain – A garland created from the Bellis, daisy flower (generally as a children's game) is called a daisy chain. One method of creating a daisy chain is to pick daisies and create a hole towards the base of the stem (such as with fingernails or by tying a Overhand knot, knot). The stem of the next flower can be threaded through until stopped by the head of the flower. By repeating this with many daisies, it is possible to build up long chains and to form them into simple bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hindu Prayer Beads
A japamala, , or simply Japay mala (; , meaning 'garland') is a loop of prayer beads commonly used in Indian religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism. It is used for counting recitations (''japa'') of mantras, prayers or other sacred phrases. It is also worn to ward off evil, to count repetitions within some other form of '' sadhana'' (spiritual practice) such as prostrations before a holy icon. They are also used as symbols of religious identification. The main body of a mala usually consists of 108 beads of roughly the same size and material as each other, although smaller versions, often factors of 108 such as 54 or 27, exist. A distinctive 109th "guru bead" or mother bead, which is not counted, is very common. Mala beads have traditionally been made of a variety of materials such as wood, stone, gems, seeds, bone and precious metals—with various religions often favouring certain materials—and strung with natural fibres such as cotton, silk, or animal h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rainy Season
The rainy season is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Rainy Season may also refer to: * ''Rainy Season'' (short story), a 1989 short horror story by Stephen King * "Rainy Season", a 2018 song by Monni * '' The Rainy Season'', a 1993 album by Marc Cohn * ''The Rainy Season'', a 1999 novel by James Blaylock * ''Rainy Seasons'' (film), a 2010 Iranian film {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Buddhist Lent
''Vassa'' (, , both "rain") is the three-month annual retreat observed by Theravada Buddhists. Taking place during the wet season, Vassa lasts for three lunar months, usually from July (the Burmese month of Waso, ) to October (the Burmese month of Thadingyut, ).Vassa at In English, Vassa is also called Rains Retreat. While Vassa is sometimes casually called "Buddhist Lent
Lent (, 'Fortieth') is the solemn Christianity, Christian religious moveable feast#Lent, observance in the liturgical year in preparation for Easter. It echoes the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in th ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Phu Thai
Phu Thai (Phuu Thai; Thai, Phu Thai: ''Phasa Phu Thai'', ภาษาผู้ไท or ภูไท) is a Southwestern Tai language spoken in Laos, Thailand and Vietnam. Although it appears different from the Isan and the Lao languages, it is spoken in areas where these languages are predominant and has been influenced by them. Comparisons of Phu Thai with other Tai languages such as Tay Khang have not yet been done systematically enough to yield convincing results. Another aspect of Phu Thai is its contact with the Katuic languages, a branch of the Austroasiatic languages. Whether in the Phu Thai areas of Central Laos or in more recent locations of Northeastern Thailand, one can find, along with Phu Thai, a few Katuic dialects known locally as Bru, So or Katang. James R. Chamberlain (2012) focusing on anthropological issues describes “the Phou Thay – Brou relationship” as a “symbiosis” and states that “the Phou Thay – Brou relationship has never evolved into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |