|
Photographers' Abbreviations
During most of the 20th century photography depended mainly upon the photochemical technology of silver halide emulsions on glass plates or roll film.Langford, Michael. ''Story of Photography''. Focal Press, 1998, pp. 224. . Early in the 21st century this technology was displaced by the electronic technology of digital cameras. The development of digital image sensors, microprocessors, memory cards, miniaturised devices and image editing software enabled these cameras to offer their users a much wider range of operating options than was possible with the older silver halide technology.Busch, David D. ''Digital SLR Cameras and Photography For Dummies''. For Dummies, Wiley 2009. .Kelby, Scott. ''The Digital Photography Book''. Peachpit Press, 2006, pp. 240. . This has led to a proliferation of new abbreviations, acronyms and initialisms. The commonest of these are listed below. Some are used in related fields of optics and electronics but many are specific to digital phot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Plate
Photographic plates preceded film as the primary medium for capturing images in photography. These plates, made of metal or glass and coated with a light-sensitive emulsion, were integral to early photographic processes such as heliography, daguerreotypes, and photogravure. Glass plates, thinner than standard window glass, became widely used in the late 19th century for their clarity and reliability. Although largely replaced by film during the 20th century, plates continued to be used for specialised scientific and medical purposes until the late 20th century. History Glass plates were far superior to film for research-quality imaging because they were stable and less likely to bend or distort, especially in large-format frames for wide-field imaging. Early plates used the wet collodion process. The wet plate process was replaced late in the 19th century by gelatin dry plates. A view camera nicknamed "The Mammoth" weighing was built by George R. Lawrence in 1899, sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Speed
Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on various numerical scales, the most recent being the ISO system introduced in 1974. A closely related system, also known as ISO, is used to describe the relationship between exposure and output image lightness in digital cameras. Prior to ISO, the most common systems were ASA in the United States and DIN in Europe. The term ''speed'' comes from the early days of photography. Photographic emulsions that were more sensitive to light needed less time to generate an acceptable image and thus a complete exposure could be finished faster, with the subjects having to hold still for a shorter length of time. Emulsions that were less sensitive were deemed "slower" as the time to complete an exposure was much longer and often usable only for still life photography. Exposure times for photographic emulsions shortened from hours to fractions of a second by the late 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss ", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type semiconductor, p-type and n-type semiconductor, n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips (including Nonvolatile BIOS memory, CMOS BIOS), and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensors), data conversion, data converters, RF circuits (RF CMOS), and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1948, Bardeen and Brattain patented an insulated-gate transistor (IGFET) with an inversion layer. Bardeen's concept forms the basis of CMOS technology today. The CMOS process was presented by Fairchild Semico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camera Left
Screen direction is the direction that actors or objects appear to be moving on the screen from the point of view of the camera or audience. A rule of film editing and film grammar is that movement from one edited shot to another must maintain the consistency of screen direction in order to avoid audience confusion. Continuity Editing is an essential rule that filmmakers follow to push their narrative forward in a navigable manner. "Camera left" or "frame left" indicates movement towards the left side of the screen, while "camera right" or "frame right" refers to movement towards the right side of the screen. "Foreground" refers to the apparent space close to the camera (and thus to the audience), and "background" refers to the apparent space in the distance away from the camera and the audience. A majority of films will track from left-to-right rather than right-to-left. Some theorists believe simply controlling the direction of the shot can control the reactions of the audience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. Overview In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by Doping (semiconductor), p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion, color aberration, color fringing, or purple fringing, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the lens elements varies with the wavelength of light. The refractive index of most transparent materials decreases with increasing wavelength. Since the focal length of a lens depends on the refractive index, this variation in refractive index affects focusing. Since the focal length of the lens varies with the color of the light different colors of light are brought to focus at different distances from the lens or with different levels of magnification. Chromatic aberration manifests itself as "fringes" of color along boundaries that separate dark and bright parts of the image. Types There are two types of chromatic aberration: ''axial'' (''longitudinal''), and ''transverse'' (''lateral''). Axial aberration occurs when different wavelengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture One
Capture One is a photography software suite. It includes custom support for Raw image format, RAW files from over 650 cameras and tethering support (remote camera control via USB, network cable or Wifi) for over 200 cameras. Originally produced by camera maker Phase One (company), Phase One, the software department was split off into its own company, called Capture One A/S, in 2019. Both companies are majority-owned by the private equity firm Axcel. Before Axcel, Phase One including the software department was majority-owned by Silverfleet Capital. In 2022, Capture One released its iPad app with a sub-set of features from the desktop app and Capture One Live, a cloud-based collaboration platform for getting feedback in real-time. In 2023, Capture One was also released for iPhone, compatible with iOS 15 and newer. Capture One Pro is available as subscription or one-time purchase ("perpetual license") Other product variants like Studio and Enterprise are only available as subscrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Balance
In photography and image processing, color balance is the global adjustment of the intensities of the colors (typically red, green, and blue primary colors). An important goal of this adjustment is to render specific colors – particularly neutral colors like white or grey – correctly. Hence, the general method is sometimes called gray balance, neutral balance, or white balance. Color balance changes the overall mixture of colors in an image and is used for color correction. Generalized versions of color balance are used to correct colors other than neutrals or to deliberately change them for effect. White balance is one of the most common kinds of balancing, and is when colors are adjusted to make a white object (such as a piece of paper or a wall) appear white and not a shade of any other colour. Image data acquired by sensors – either photographic film, film or electronic image sensors – must be transformed from the acquired values to new values that are appropriate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organization also coordinates U.S. standards with international standards so that American products can be used worldwide. ANSI accredits standards that are developed by representatives of other standards organizations, government agencies, consumer groups, companies, and others. These standards ensure that the characteristics and performance of products are consistent, that people use the same definitions and terms, and that products are tested the same way. ANSI also accredits organizations that carry out product or personnel certification in accordance with requirements defined in international standards. The organization's headquarters are in Washington, D.C. ANSI's operations office is located in New York City. The ANSI annual operating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Photo System
Advanced Photo System (APS) is a film format for consumer still photography first marketed in 1996 and discontinued in 2011. It was sold by various manufacturers under several brand names, including Eastman Kodak (Advantix), FujiFilm (Nexia), Agfa (Futura) and Konica (Centuria). Development was led by Kodak starting in the mid-1980s. Like prior attempts to displace 135 film from the amateur photography market, including 126 film (Instamatic), 110, and disc, APS used a film cartridge to reduce loading errors. APS also could reduce camera and lens size and weight by using a smaller image format; unlike the older amateur formats, image quality would be maintained by using newly-developed films, featuring emulsions with finer grain size and a flatter base material. The other major innovation delivered by APS was the "information exchange" process in which the camera recorded data directly on the film; this would simplify cropping prints to a desired aspect ratio and potentially cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APS-C
Advanced Photo System type-C (APS-C) is an image sensor format approximately equivalent in size to the Advanced Photo System film negative in its C ("Classic") format, of 25.1×16.7 mm, an aspect ratio of 3:2 and Ø 30.15 mm field diameter. It is therefore also equivalent in size to the Super 35 motion picture film format, which has the dimensions of 24.89 mm × 18.66 mm (0.980 in × 0.735 in) and Ø 31.11 mm field diameter. Sensors approximating these dimensions are used in many digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs), mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras (MILCs), and a few large-sensor live-preview digital cameras. APS-C size sensors are also used in a few digital rangefinder camera, rangefinders. Such sensors exist in many different variants depending on the manufacturer and camera model. All APS-C variants are considerably smaller than 35 mm standard film which measures 36×24 mm. Because of this, devices with APS-C sensors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
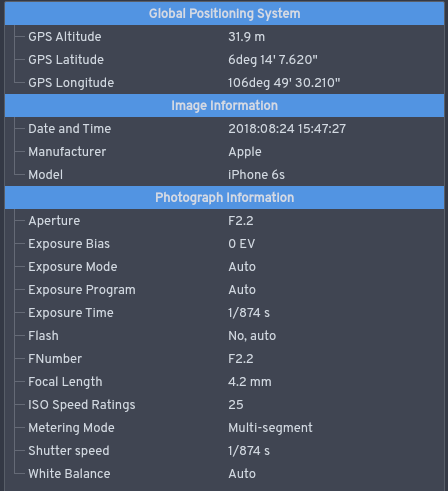
Exif
Exchangeable image file format (officially Exif, according to JEIDA/JEITA/CIPA specifications) is a standard that specifies formats for images, sound, and ancillary tags used by digital cameras (including smartphones), scanners and other systems handling image and sound files recorded by digital cameras. The specification uses the following existing encoding formats with the addition of specific metadata tags: JPEG lossy coding for compressed image files, TIFF Rev. 6.0 ( RGB or YCbCr) for uncompressed image files, and RIFF WAV for audio files (linear PCM or ITU-T G.711 μ-law PCM for uncompressed audio data, and IMA-ADPCM for compressed audio data). It does not support JPEG 2000 or GIF encoded images. This standard consists of the Exif image file specification and the Exif audio file specification. Background Exif is supported by almost all digital camera manufacturers. The metadata tags defined in the Exif standard cover a broad spectrum: * Camera settings: This includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |