|
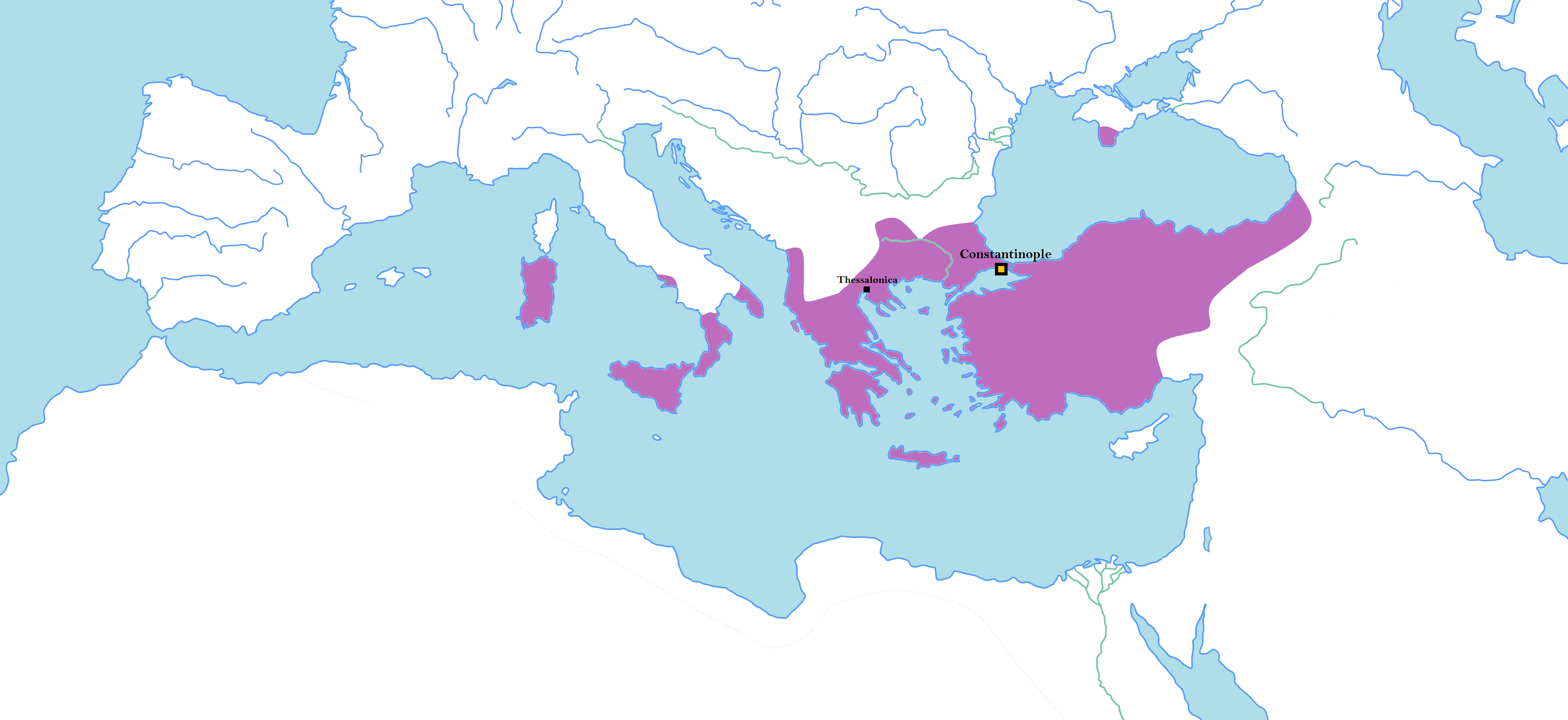
Photios I Of Constantinople
Photius I of Constantinople (, ''Phōtios''; 815 – 6 February 893), also spelled ''Photius''Fr. Justin Taylor, essay "Canon Law in the Age of the Fathers" (published in Jordan Hite, T.O.R., and Daniel J. Ward, O.S.B., "Readings, Cases, Materials in Canon Law - A Textbook for Ministerial Students, Revised Edition" ollegeville, Minn., The Liturgical Press, 1990, p. 61 (), was the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 858 to 867 and from 877 to 886. He is recognized in the Eastern Orthodox Church as Saint Photius the Great. Photius I is widely regarded as the most powerful and influential church leader of Constantinople subsequent to John Chrysostom's archbishopric around the turn of the fifth century. He is also viewed as the most important intellectual of his time – "the leading light of the ninth-century renaissance". He was a central figure in both the conversion of the Slavs to Christianity and the Photian schism, and is considered " e great systematic compiler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denomination. In Anglican Communion, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheranism, Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but a selected few are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official Ecclesiastical polity, ecclesiastical recognition, and veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. In many Protestant denominations, and following from Pauline usage, ''saint'' refers broadly to any holy Christian, without special recognition or selection. While the English word ''saint'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gratian (jurist)
The , also known as the or or simply as the , is a collection of Catholic canon law compiled and written in the 12th century as a legal textbook by the jurist known as Gratian. It forms the first part of the collection of six legal texts, which together became known as the . It was used as the main source of law by canonists of the Catholic Church until the ''Decretals'', promulgated by Pope Gregory IX in 1234, obtained legal force, after which it was the cornerstone of the , in force until 1917. Overview In the first half of the 12th century Gratian, ''clusinus episcopus'',Reali, Francesco (ed.), , 2009, pp. 63-73 and p. 244 has found and re-evaluated a Kalendarium of the Sienese Church owned by the Library of the Intronati of Siena (Ms FI2, f. 5v) in which, in Carolina minuscule writing with a date that at most can be placed in the mid-12th century, reads the following (after ): ; Reali observes that the text conforms to another reliable source of the 12th century, in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iconoclasm (Byzantine)
The Byzantine Iconoclasm () are two periods in the history of the Byzantine Empire when the use of religious images or icons was opposed by religious and imperial authorities within the Ecumenical Patriarchate (at the time still comprising the Roman-Latin and the Eastern-Orthodox traditions) and the temporal imperial hierarchy. The First Iconoclasm, as it is sometimes called, occurred between about 726 and 787, while the Second Iconoclasm occurred between 814 and 842. According to the traditional view, Byzantine Iconoclasm was started by a ban on religious images promulgated by the Byzantine Emperor Leo III the Isaurian, and continued under his successors. It was accompanied by widespread destruction of religious images and persecution of supporters of the veneration of images. The Papacy remained firmly in support of the use of religious images throughout the period, and the whole episode widened the growing divergence between the Byzantine and Carolingian traditions in what wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikephoros I
Nikephoros I (; 750 – 26 July 811), also known as Nicephorus I, was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. He was General Logothete (finance minister) under Empress Irene, but later overthrew her to seize the throne for himself. Prior to becoming emperor, he was sometimes referred to as "the Logothete" () and "Genikos" or "Genicus" (), in recognition of his previous role as General Logothete. During his reign, Nikephoros engaged in military campaigns against both the Arabs and the Bulgarians, although the outcomes were varied. While leading an invasion into Bulgaria, he suffered a defeat and was killed at the Battle of Pliska. Background According to several sources outside the Byzantine context, such as Michael the Syrian, al-Tabari, and Mas'udi, there is a tradition that suggests Nikephoros had Ghassanid Arab origins and that he descended from the final Ghassanid ruler Jabala ibn al-Ayham. Al-Tabari assets that he obtained this information from Byzantine sources, althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irene Of Athens
Irene of Athens (, ; 750/756 – 9 August 803), surname Sarantapechaena (, ), was Byzantine empress consort to Emperor Leo IV from 775 to 780, regent during the childhood of their son Constantine VI from 780 until 790, co-ruler from 792 until 797, and finally empress regnant and sole ruler of the Eastern Roman Empire from 797 to 802. A member of the politically prominent Sarantapechos family, she was selected as Leo IV's bride for unknown reasons in 768. Even though her husband was an iconoclast, she harbored iconophile sympathies. During her rule as regent, she called the Second Council of Nicaea in 787, which condemned iconoclasm as heretical and brought an end to the first iconoclast period (730–787). During her 5 year sole reign, her public figure was polarizing, due to the setbacks faced by the Empire and her iconophilic stances, often attributed to her gender and the influence of her retinue. Her reign as sole ruler made her the first ever empress regnant, ruling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niketas David Paphlagon
Niketas David Paphlagon (), also known as Nicetas the Paphlagonian or Nicetas of Paphlagonia, was a prolific Byzantine Greek writer of the late 9th and early 10th century. Older scholarship dated Niketas' death to about 890, but more recent research suggests that he was born around 885 and was active as late as 963. He was a disciple of Arethas of Caesarea. In a letter, Arethas calls him a ''scholastikos'', meaning lawyer. "David" appears to be a religious name, which he may have taken later in life. When Arethas, under pressure from Pope Nicholas I, moved to support the tetragamy of the Emperor Leo VI, Niketas distributed all his master's goods to the poor and fled to Thrace. He was arrested and imprisoned in Constantinople. The Patriarch Euthymios I secured his release, but forced him to live in seclusion for two years. Niketas was a prolific author on Christian topics. He wrote about fifty hagiographies, a treatise on calculating the end times, a commentary on the ''Psalms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Seven Ecumenical Councils
In the history of Christianity, the first seven ecumenical councils include the following: the First Council of Nicaea in 325, the First Council of Constantinople in 381, the Council of Ephesus in 431, the Council of Chalcedon in 451, the Second Council of Constantinople in 553, the Third Council of Constantinople from 680 to 681 and finally, the Second Council of Nicaea in 787. All of the seven councils were convened in what is now the country of Turkey. These seven events represented an attempt by Church leaders to reach an orthodox consensus, restore peace and develop a unified Christendom. Among Eastern Christians the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Church of the East (Assyrian) churches and among Western Christians the Roman Catholic, Anglican, Utrecht and Polish National Old Catholic, and some Scandinavian Lutheran churches all trace the legitimacy of their clergy by apostolic succession back to this period and beyond, to the earlier period referred to as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Council Of Constantinople (Eastern Orthodox)
The Fourth Council of Constantinople was held in 879–880. It confirmed the reinstatement of Photius I as patriarch of Constantinople. The result of this council is accepted by the Eastern Orthodox as having the authority of an ecumenical council. Eastern Orthodox sometimes call it the eighth ecumenical council. Background The Council settled the dispute that had broken out after the deposition of Ignatius as Patriarch of Constantinople in 858. Ignatius, himself appointed to his office in an uncanonical manner, opposed Caesar Bardas, who had deposed the regent Theodora. In response, Bardas' nephew, the youthful Emperor Michael III engineered Ignatius's deposition and confinement on the charge of treason. The patriarchal throne was filled with Photius, a renowned scholar and kinsman of Bardas. The deposition of Ignatius without a formal ecclesiastical trial and the sudden promotion of Photius caused scandal in the church. Pope Nicholas I and the western bishops took up the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Council Of Constantinople (Catholic Church)
The Fourth Council of Constantinople was the eighth ecumenical council of the Catholic Church held in Constantinople from 5 October 869, to 28 February 870. It was poorly attended, the first session by only 12 bishops and the number of bishops later never exceeded 103. In contrast, the pro-Photian council of 879–80 was attended by 383 bishops. The Council met in ten sessions from October 869 to February 870 and issued 27 canons. The council was called by Emperor Basil I the Macedonian, with the support of Pope Hadrian II."Photius", in Cross, F. L., ed. ''The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church''. New York: Oxford University Press. 2005 It deposed and anathematized Photius, a layman who had been appointed as Patriarch of Constantinople, and reinstated his predecessor Ignatius. The Council also reaffirmed the decisions of the Second Council of Nicaea in support of icons and holy images and required the image of Christ to have veneration equal with that of the gospel bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope John VIII
Pope John VIII (; died 16 December 882) was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 14 December 872 to his death. He is often considered one of the most able popes of the 9th century. John devoted much of his papacy to attempting to halt and reverse the Muslim gains in southern Italy and their march northwards. When his efforts to obtain assistance from either the Franks or the Byzantines failed, John strengthened the defences of Rome. He supported Methodius of Thessalonica in his mission to the Slavs, defended him against the Carolingian rulers and Bavarian clergy, and authorized the translation of the Bible into Old Church Slavonic. John also extended diplomatic recognition to the Duchy of Croatia and resolved the Photian schism. John's pontificate ended with his assassination, and the papacy became significantly weaker in the aftermath. Slavonic liturgy Pope Adrian II consecrated Methodius of Thessalonica as archbishop and supported his mission to the Slav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael III
Michael III (; 9/10 January 840 – 24 September 867), also known as Michael the Drunkard, was Byzantine emperor from 842 to 867. Michael III was the third and traditionally last member of the Amorian dynasty, Amorian (or Phrygian) dynasty. He was given the disparaging epithet ''the Drunkard'' () by the hostile historians of the succeeding Macedonian dynasty, but modern historical research has rehabilitated his reputation to some extent, demonstrating the vital role his reign played in the resurgence of Byzantine power in the 9th century. He was also the youngest person to bear the imperial title, as well as the youngest to succeed as senior emperor. Life Early life and regency Michael was the youngest child of the emperor Theophilos (emperor), Theophilos and his empress Theodora (wife of Theophilos), Theodora. His precise date of birth is uncertain, but the balance of available evidence supports a birthdate in early 840, probably on 9 or 10 January. He was coronation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarasios Of Constantinople
Tarasios of Constantinople (also ''Saint Tarasius'' and ''Saint Tarasios''; ; 730 – 25 February 806) was the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople from 25 December 784 until his death on 25 February 806. Background Tarasios was born and raised in the city of Constantinople. A son of a high-ranking judge, Tarasios was related to important families, including that of the later Patriarch Photios I of Constantinople. He had an elder brother, Sisinnios, who was captured during the invasion of Calabria in 788–789. Tarasios had embarked on a career in the secular administration and had attained the rank of senator, eventually becoming imperial secretary ('' asekretis'') to the Emperor Constantine VI and his mother, the Empress Irene of Athens. When Patriarch Paul IV of Constantinople retired to a monastery, he recommended the lay administrator Tarasios as his successor. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |