|
Photic
The photic zone (or euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone) is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes that supply nutrients into the upper water column. The photic zone is home to the majority of aquatic life due to the activity (primary production) of the phytoplankton. The thicknesses of the photic and euphotic zones vary with the intensity of sunlight as a function of season and latitude and with the degree of water turbidity. The bottommost, or aphotic, zone is the region of perpetual darkness that lies beneath the photic zone and includes most of the ocean waters. Photosynthesis in photic zone In the photic zone, the photosynthesis rate exceeds the respiration rate. This is due to the abundant solar energy which is used as an energy source for photosynthesis by primary producers such as phytoplankton. These phytoplankton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
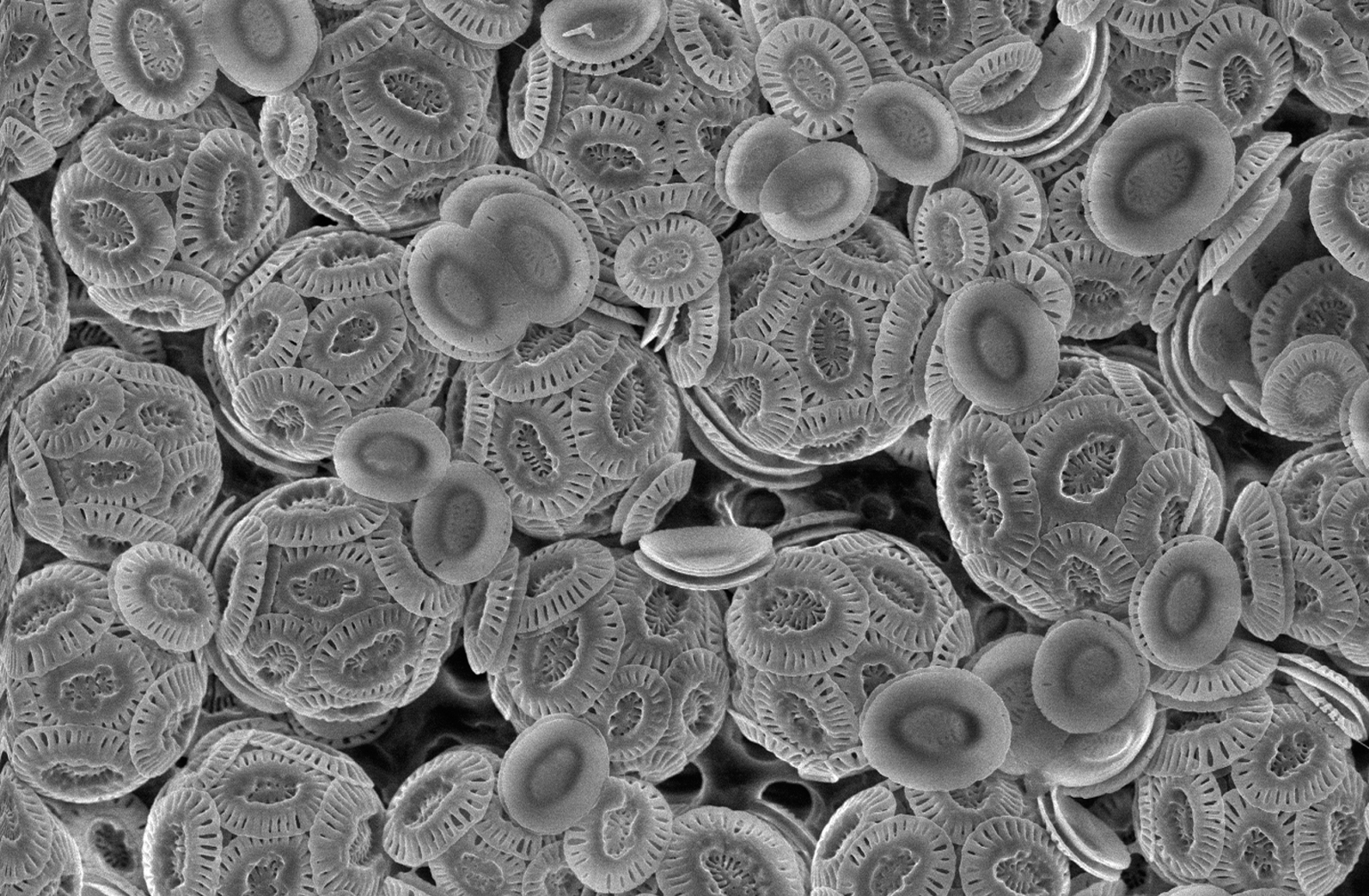
Coccolithophore
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single-celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdom Protista, according to Robert Whittaker (ecologist), Robert Whittaker's five-kingdom system, or clade Hacrobia, according to a newer biological classification system. Within the Hacrobia, the coccolithophores are in the phylum or division (botany), division Haptophyta, class Prymnesiophyceae (or Coccolithophyceae). Coccolithophores are almost exclusively Marine (ocean), marine, are photosynthesis, photosynthetic and mixotrophic, and exist in large numbers throughout the Photic zone, sunlight zone of the ocean. Coccolithophores are the most productive calcifying organisms on the planet, covering themselves with a calcium carbonate shell called a ''coccosphere''. However, the reasons they calcify remain elusive. One key function may be that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
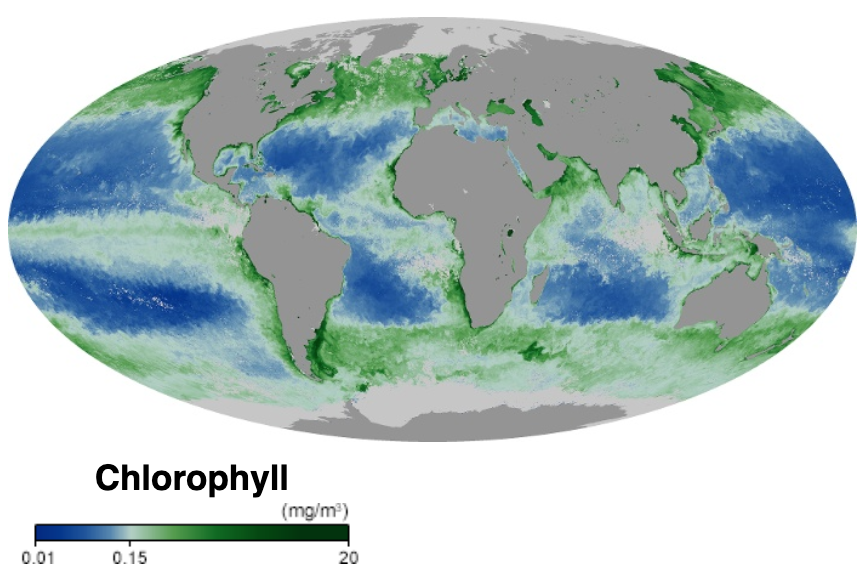
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as trees and other plants do on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrared (typically perceived by humans as warmth) and ultraviolet (which can have physiological effects such as sunburn) lights. However, according to the American Meteorological Society, there are "conflicting conventions as to whether all three [...] are referred to as light, or whether that term should only be applied to the visible portion of the spectrum." Upon reaching the Earth, sunlight is light scattering by particles, scattered and attenuation, filtered through the atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere as daylight when the Sun is above the horizon. When direct solar radiation is not blocked by clouds, it is experienced as sunshine, a combination of bright light and radiant heat (atmospheric). When cloud cover, blocked by clouds or dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma'') is any member of a large group comprising several Genus, genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of Earth's Biomass (ecology), biomass. They generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion tonnes of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The Protist shell, shells of dead diatoms are a significant component of marine sediment, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of fresh-water lakes. Diatoms are unicellular organisms: they occur either as solitary cells or in Colony (biology), colonies, which can take the shape of ribb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Column
The (oceanic) water column is a concept used in oceanography to describe the physical (temperature, salinity, light penetration) and chemical ( pH, dissolved oxygen, nutrient salts) characteristics of seawater at different depths for a defined geographical point. Generally, vertical profiles are made of temperature, salinity, chemical parameters at a defined point along the water column. The water column is the largest, yet one of the most under-explored, habitats on the planet; it is explored to better understand the ocean as a whole, including the huge biomass that lives there and its importance to the global carbon and other biogeochemical cycles. Studying the water column also provides understanding on the links between living organisms and environmental parameters, large-scale water circulation and the transfer of matter between water masses. Water columns are used chiefly for environmental studies evaluating the stratification or mixing of thermal or chemically stratif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Primary Production
Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of organic compounds from atmospheric or dissolved carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are called primary producers or autotrophs. Most marine primary production is generated by a diverse collection of marine microorganisms called algae and cyanobacteria. Together these form the principal primary producers at the base of the ocean food chain and produce half of the world's oxygen. Marine primary producers underpin almost all marine animal life by generating nearly all of the oxygen and food marine animals need to exist. Some marine primary producers are also ecosystem eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nekton
Nekton or necton (from the ) is any aquatic organism that can actively and persistently propel itself through a water column (i.e. swimming) without touching the bottom. Nektons generally have powerful tails and appendages (e.g. fins, pleopods, flippers or jet propulsion) that make them strong enough swimmers to counter ocean currents, and have mechanisms for sufficient lift and/or buoyancy to prevent sinking. Examples of extant nektons include most fish (especially pelagic fish like tuna and sharks), marine mammals (cetaceans, sirenias and pinnipeds) and reptiles (specifically sea turtles), penguins, coleoid cephalopods (squids and cuttlefish) and several species of decapod crustaceans (specifically prawns, shrimps and krills). The term was proposed by German biologist Ernst Haeckel to differentiate between the active swimmers in a body of water, and the planktons that were passively carried along by the current. As a guideline, nektonic organisms have a high Reynolds numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically evolved to feed on plants, especially upon vascular tissues such as foliage, fruits or seeds, as the main component of its diet. These more broadly also encompass animals that eat non-vascular autotrophs such as mosses, algae and lichens, but do not include those feeding on decomposed plant matters (i.e. detritivores) or macrofungi (i.e. fungivores). As a result of their plant-based diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouth structures ( jaws or mouthparts) well adapted to mechanically break down plant materials, and their digestive systems have special enzymes (e.g. amylase and cellulase) to digest polysaccharides. Grazing herbivores such as horses and cattles have wide flat- crowned teeth that are better adapted for grinding grass, tree bark and other tougher lignin-containing materials, and many of them evolved rumination or cecotropic behaviors to better extract nutrients from plants. A large per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sediments), several species have Parasitism, parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as Ecological indicator, biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a Crustacean larvae#Nauplius, nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthropods including decapods (shrimps, prawns, crabs, lobsters and crayfish), seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, opossum shrimps, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods (insects and entognathans) emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed pan-group referred to as Pancrustacea. The three classes Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda and Remipedia are more closely related to the hexapods than they are to any of the other crustaceans ( oligostracans and multicrustaceans). The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Of Water
A body of water or waterbody is any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth or another planet. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as ponds, wetlands, or more rarely, puddles. A body of water does not have to be still or contained; rivers, streams, canals, and other Landform, geographical features where water moves from one place to another are also considered bodies of water. Most are naturally occurring and massive geographical features, but some are artificial. There are types that can be either. For example, most reservoirs are created by engineering dams, but some natural lakes are used as reservoirs. Similarly, most harbors are naturally occurring bays, but some harbors have been created through construction. Bodies of water that are Navigability, navigable are known as waterways. Some bodies of water collect and move water, such as rivers and streams, and others primarily hold water, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Distribution
A spatial distribution in statistics is the arrangement of a phenomenon across the Earth's surface and a graphical display of such an arrangement is an important tool in geographical and environmental statistics. A graphical display of a spatial distribution may summarize raw data directly or may reflect the outcome of a more sophisticated data analysis. Many different aspects of a phenomenon can be shown in a single graphical display by using a suitable choice of different colours to represent differences. One example of such a display could be observations made to describe the geographic patterns of features, both physical and human across the earth. The information included could be where units of something are, how many units of the thing there are per units of area, and how sparsely or densely packed they are from each other. Patterns of spatial distribution Usually, for a phenomenon that changes in space, there is a pattern that determines the location of the subject o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |