|
Phonetic Form
In the field of linguistics, specifically in syntax, phonetic form (PF), also known as phonological form or the articulatory-perceptual (A-P) system, is a certain level of mental representation of a linguistic expression, derived from surface structure, and related to Logical Form. Phonetic form is the level of representation wherein expressions, or sentences, are assigned a phonetic representation, which is then pronounced by the speaker. Phonetic form takes surface structure as its input, and outputs an audible (or visual, in the case of sign languages), pronounced sentence. This is part of the Y- or T-model of grammar within minimalist grammar, wherein the syntactic structure is constructed and then transferred (called spell-out) to both the Phonetic Form and the Logical Form. Operations in this branch of the model (between spell-out and pronunciation), the syntax-phonology interface, affect the pronunciation of the utterance but not its meaning. Within distributed morpho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Representation
A mental representation (or cognitive representation), in philosophy of mind, cognitive psychology, neuroscience, and cognitive science, is a hypothetical internal cognitive symbol that represents external reality or its abstractions. Mental representation is the mental imagery of things that are not actually present to the senses. In contemporary philosophy, specifically in fields of metaphysics such as philosophy of mind and ontology, a mental representation is one of the prevailing ways of explaining and describing the nature of ideas and concepts. Mental representations (or mental imagery) enable representing things that have never been experienced as well as things that do not exist. Our brains and mental imageries allow us to imagine things have either never happened or are impossible and do not exist. Although visual imagery is more likely to be recalled, mental imagery may involve representations in any of the sensory modalities, such as hearing, smell, or taste. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Structure And Surface Structure
Deep structure and surface structure (also D-structure and S-structure although those abbreviated forms are sometimes used with distinct meanings) are concepts used in linguistics, specifically in the study of syntax in the Chomskyan tradition of transformational generative grammar. The deep structure of a linguistic expression is a theoretical construct that seeks to unify several related structures. For example, the sentences "Pat loves Chris" and "Chris is loved by Pat" mean roughly the same thing and use similar words. Some linguists, Chomsky in particular, have tried to account for this similarity by positing that these two sentences are distinct ''surface forms'' that derive from a common (or very similar) deep structure. Origin Chomsky coined and popularized the terms "deep structure" and "surface structure" in the early 1960s. American linguist Sydney Lamb wrote in 1975 that Chomsky "probably orrowedthe term from Hockett". American linguist Charles Hockett first use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
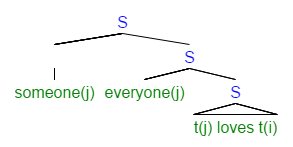
Logical Form (linguistics)
In generative grammar and related approaches, the logical form (LF) of a linguistic expression is the variant of its syntactic structure which undergoes formal semantics (linguistics), semantic interpretation. It is distinguished from ''phonetic form'', the structure which corresponds to a sentence's pronunciation. These separate mental representation, representations are postulated in order to explain the ways in which an expression's meaning can be partially independent of its pronunciation, e.g. scope (formal semantics)#Scope ambiguity, scope ambiguities. LF is the cornerstone of the classic generative view of the syntax-semantics interface. However, it is not used in Lexical Functional Grammar and Head-Driven Phrase Structure Grammar, as well as some modern variants of the generative approach. Syntax interfacing with semantics The notion of Logical Form was originally invented for the purpose of determining Quantifier (linguistics), quantifier scope. As the theory around t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimalism (syntax)
In linguistics, the minimalist program is a major line of inquiry that has been developing inside generative grammar since the early 1990s, starting with a 1993 paper by Noam Chomsky. Following Imre Lakatos's distinction, Chomsky presents minimalism as a program, understood as a mode of inquiry that provides a conceptual framework which guides the development of linguistic theory. As such, it is characterized by a broad and diverse range of research directions. For Chomsky, there are two basic minimalist questions—What is language? and Why does it have the properties it has?—but the answers to these two questions can be framed in any theory.Boeckx, Cedric ''Linguistic Minimalism. Origins, Concepts, Methods and Aims'', pp. 84 and 115. Conceptual framework Goals and assumptions Minimalism is an approach developed with the goal of understanding the nature of language. It models a speaker's knowledge of language as a computational system with one basic operation, namely M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Morphology
In generative linguistics, Distributed Morphology is a theoretical framework introduced in 1993 by Morris Halle and Alec Marantz.Halle, Morris & Alec Marantz. 1993. 'Distributed Morphology and the Pieces of Inflection.' In The View from Building 20, ed. Kenneth Hale and S. Jay Keyser. MIT Press, Cambridge, 111–176. The central claim of Distributed Morphology is that there is no divide between the construction of words and sentences. The syntax is the single generative engine that forms sound-meaning correspondences, both complex phrases and complex words. This approach challenges the traditional notion of the lexicon as the unit where derived words are formed and idiosyncratic word-meaning correspondences are stored. In Distributed Morphology there is no unified lexicon, as in earlier generative treatments of word-formation; rather, the functions that other theories ascribe to the lexicon are distributed among other components of the grammar. Overview of Distributed Morpholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology is the study of words, including the principles by which they are formed, and how they relate to one another within a language. Most approaches to morphology investigate the structure of words in terms of morphemes, which are the smallest units in a language with some independent meaning. Morphemes include roots that can exist as words by themselves, but also categories such as affixes that can only appear as part of a larger word. For example, in English the root ''catch'' and the suffix ''-ing'' are both morphemes; ''catch'' may appear as its own word, or it may be combined with ''-ing'' to form the new word ''catching''. Morphology also analyzes how words behave as parts of speech, and how they may be inflected to express grammatical categories including number, tense, and aspect. Concepts such as productivity are concerned with how speakers create words in specific contexts, which evolves over the history of a language. The basic fields of ling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosody (linguistics)
In linguistics, prosody () is the study of elements of speech, including intonation, stress, rhythm and loudness, that occur simultaneously with individual phonetic segments: vowels and consonants. Often, prosody specifically refers to such elements, known as ''suprasegmentals'', when they extend across more than one phonetic segment. Prosody reflects the nuanced emotional features of the speaker or of their utterances: their obvious or underlying emotional state, the form of utterance (statement, question, or command), the presence of irony or sarcasm, certain emphasis on words or morphemes, contrast, focus, and so on. Prosody displays elements of language that are not encoded by grammar, punctuation or choice of vocabulary. Attributes of prosody In the study of prosodic aspects of speech, it is usual to distinguish between auditory measures ( subjective impressions produced in the mind of the listener) and objective measures (physical properties of the sound wave and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constituent (linguistics)
In syntactic analysis, a constituent is a word or a group of words that function as a single unit within a hierarchical structure. The constituent structure of sentences is identified using ''tests for constituents''. These tests apply to a portion of a sentence, and the results provide evidence about the constituent structure of the sentence. Many constituents are phrases. A phrase is a sequence of one or more words (in some theories two or more) built around a head lexical item and working as a unit within a sentence. A word sequence is shown to be a phrase/constituent if it exhibits one or more of the behaviors discussed below. The analysis of constituent structure is associated mainly with phrase structure grammars, although dependency grammars also allow sentence structure to be broken down into constituent parts. Tests for constituents in English Tests for constituents are diagnostics used to identify sentence structure. There are numerous tests for constituents that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Structure
In linguistics, information structure, also called information packaging, describes the way in which information is Formal semantics (natural language), formally packaged within a Sentence (linguistics), sentence.Lambrecht, Knud. 1994. ''Information structure and sentence form.'' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. This generally includes only those aspects of information that "respond to the temporary state of the addressee's mind", and excludes other aspects of linguistic information such as references to background (encyclopedic/common) knowledge, choice of style, politeness, and so forth. For example, the difference between an active clause (e.g., ''the police want him'') and a corresponding passive (e.g., ''he is wanted by police'') is a syntactic difference, but one motivated by information structuring considerations. Other structures motivated by information structure include preposing (e.g., ''that one I don't like'') and inversion (e.g., ''"the end", said the man''). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonology
Phonology (formerly also phonemics or phonematics: "phonemics ''n.'' [''obsolescent''] 1. Any procedure for identifying the phonemes of a language from a corpus of data. 2. (formerly also phonematics) A former synonym for phonology, often preferred by the American Structuralists and reflecting the importance in structuralist work of phonemics in sense 1.": "phonematics ''n.'' 1. [''obsolete''] An old synonym for phonemics (sense 2).") is the branch of linguistics that studies how languages systematically organize their phonemes or, for sign languages, their constituent parts of signs. The term can also refer specifically to the sound or sign system of a particular language variety. At one time, the study of phonology related only to the study of the systems of phonemes in spoken languages, but now it may relate to any Linguistic description, linguistic analysis either: Sign languages have a phonological system equivalent to the system of sounds in spoken languages. The buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |