|
Philosophical Zombie
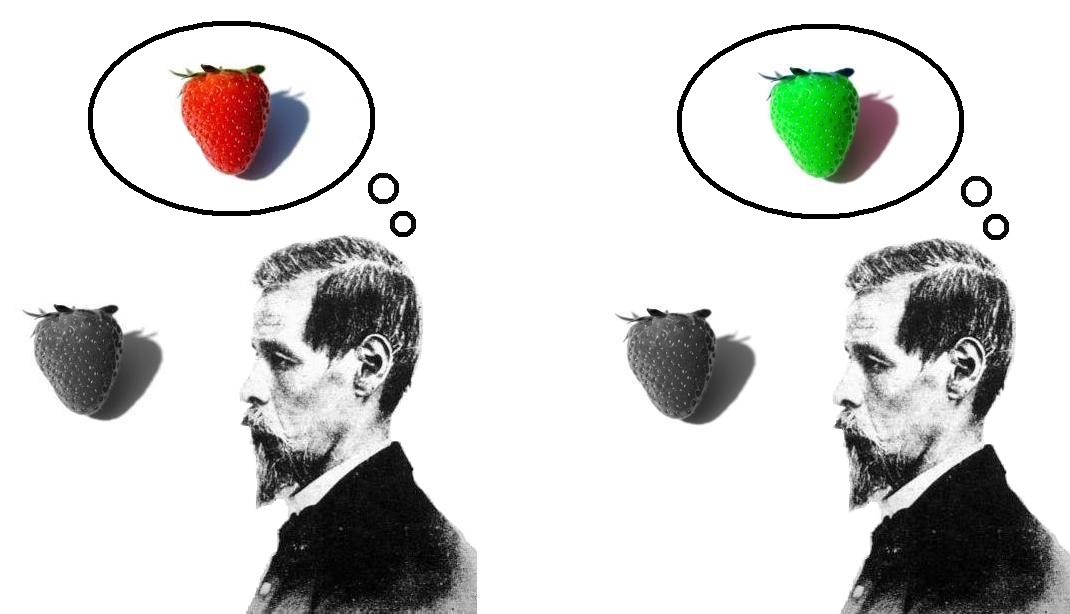
A philosophical zombie (or "p-zombie") is a being in a thought experiment in the philosophy of mind that is physically identical to a normal human being but does not have conscious experience. For example, if a philosophical zombie were poked with a sharp object, it would not feel any pain, but it would react exactly the way any conscious human would. Philosophical zombie arguments are used against forms of physicalism and in defense of the hard problem of consciousness, which is the problem of accounting in physical terms for subjective, intrinsic, first-person, what-it's-like-ness experiences. Proponents of philosophical zombie arguments, such as the philosopher David Chalmers, argue that since a philosophical zombie is by definition physically identical to a conscious person, even its logical possibility refutes physicalism. This is because it establishes the existence of conscious experience as a further fact.Chalmers, D. (1996): The Conscious Mind, Oxford University Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thought Experiment
A thought experiment is an imaginary scenario that is meant to elucidate or test an argument or theory. It is often an experiment that would be hard, impossible, or unethical to actually perform. It can also be an abstract hypothetical that is meant to test our intuitions about morality or other fundamental philosophical questions. History The ancient Greek , "was the most ancient pattern of mathematical proof", and existed before Euclidean geometry, Euclidean mathematics, where the emphasis was on the conceptual, rather than on the experimental part of a thought experiment. Johann Witt-Hansen established that Hans Christian Ørsted was the first to use the equivalent German term . Ørsted was also the first to use the equivalent term in 1820. By 1883, Ernst Mach used in a different sense, to denote exclusively the conduct of a experiment that would be subsequently performed as a by his students. Physical and mental experimentation could then be contrasted: Mach asked hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Encyclopedia Of Philosophy
The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (''SEP'') is a freely available online philosophy resource published and maintained by Stanford University, encompassing both an online encyclopedia of philosophy and peer-reviewed original publication. Each entry is written and maintained by an expert in the field, including professors from many academic institutions worldwide. Authors contributing to the encyclopedia give Stanford University the permission to publish the articles, but retain the copyright to those articles. Approach and history As of August 5, 2022, the ''SEP'' has 1,774 published entries. Apart from its online status, the encyclopedia uses the traditional academic approach of most encyclopedias and academic journals to achieve quality by means of specialist authors selected by an editor or an editorial committee that is competent (although not necessarily considered specialists) in the field covered by the encyclopedia and peer review. The encyclopedia was created i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Conscious Mind
''The Conscious Mind: In Search of a Fundamental Theory'' was published in 1996, and is the first book written by David Chalmers, an Australian philosopher specialising in philosophy of mind. Although the book has been greatly influential, Chalmers maintains that it is "far from perfect", as most of it was written as part of his PhD dissertation after "studying philosophy for only four years". Summary Thesis In ''The Conscious Mind'', Chalmers argues that (1) the physical does not exhaust the actual, so materialism is false; (2) consciousness is a fundamental fact of nature; (3) science and philosophy should strive towards discovering a fundamental law of consciousness. Definitions *Psychological consciousness: publicly accessible descriptions of consciousness, such as its neurochemical correlates or role in influencing behaviour. *Phenomenal consciousness: experience; something is phenomenologically conscious if it feels like something to be it. Every mental state can be describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Nagel
Thomas Nagel (; born July 4, 1937) is an American philosopher. He is the University Professor of Philosophy and Law Emeritus at New York University, where he taught from 1980 until his retirement in 2016. His main areas of philosophical interest are political philosophy, ethics and philosophy of mind. Nagel is known for his critique of material reductionist accounts of the mind, particularly in his essay " What Is It Like to Be a Bat?" (1974), and for his contributions to liberal moral and political theory in ''The Possibility of Altruism'' (1970) and subsequent writings. He continued the critique of reductionism in '' Mind and Cosmos'' (2012), in which he argues against the neo-Darwinian view of the emergence of consciousness. Life and career Nagel was born on July 4, 1937, in Belgrade, Yugoslavia (now Serbia), to German Jewish refugees Carolyn () and Walter Nagel. He arrived in the US in 1939, and was raised in and around New York. He had no religious upbringing, but regard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saul Kripke
Saul Aaron Kripke (; November 13, 1940 – September 15, 2022) was an American analytic philosophy, analytic philosopher and logician. He was Distinguished Professor of Philosophy at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York and emeritus professor at Princeton University. From the 1960s until his death, he was a central figure in a number of fields related to mathematical logic, mathematical and modal logic, philosophy of language and philosophy of mathematics, mathematics, metaphysics, epistemology, and recursion theory. Kripke made influential and original contributions to logic, especially modal logic. His principal contribution is a semantics for modal logic involving possible worlds, now called Kripke semantics. He received the 2001 Schock Prize in Logic and Philosophy. Kripke was also partly responsible for the revival of metaphysics and Scientific essentialism, essentialism after the decline of logical positivism, claiming Metaphysical necessity, necessity is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modal Logic
Modal logic is a kind of logic used to represent statements about Modality (natural language), necessity and possibility. In philosophy and related fields it is used as a tool for understanding concepts such as knowledge, obligation, and causality, causation. For instance, in epistemic modal logic, the well-formed_formula, formula \Box P can be used to represent the statement that P is known. In deontic modal logic, that same formula can represent that P is a moral obligation. Modal logic considers the inferences that modal statements give rise to. For instance, most epistemic modal logics treat the formula \Box P \rightarrow P as a Tautology_(logic), tautology, representing the principle that only true statements can count as knowledge. However, this formula is not a tautology in deontic modal logic, since what ought to be true can be false. Modal logics are formal systems that include unary operation, unary operators such as \Diamond and \Box, representing possibility and necessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Property (philosophy)
In logic and philosophy (especially metaphysics), a property is a characteristic of an object; for example, a red object is said to have the property of redness. The property may be considered a form of object in its own right, able to possess other properties. A property, however, differs from individual objects in that it may be instantiated, and often in more than one object. It differs from the logical and mathematical concept of class by not having any concept of extensionality, and from the philosophical concept of class in that a property is considered to be distinct from the objects which possess it. Understanding how different individual entities (or particulars) can in some sense have some of the same properties is the basis of the problem of universals. Terms and usage A property is any member of a class of entities that are capable of being attributed to objects. Terms similar to ''property'' include ''predicable'', ''attribute'', ''quality'', ''feature'', ''chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Theory
Substance theory, or substance–attribute theory, is an ontological theory positing that objects are constituted each by a ''substance'' and properties borne by the substance but distinct from it. In this role, a substance can be referred to as a ''substratum'' or a '' thing-in-itself''. ''Substances'' are particulars that are ontologically independent: they are able to exist all by themselves. Another defining feature often attributed to substances is their ability to ''undergo changes''. Changes involve something existing ''before'', ''during'' and ''after'' the change. They can be described in terms of a persisting substance gaining or losing properties. ''Attributes'' or ''properties'', on the other hand, are entities that can be exemplified by substances. Properties characterize their bearers; they express what their bearer is like. ''Substance'' is a key concept in ontology, the latter in turn part of metaphysics, which may be classified into monist, dualist, or plural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualia
In philosophy of mind, qualia (; singular: quale ) are defined as instances of subjective, conscious experience. The term ''qualia'' derives from the Latin neuter plural form (''qualia'') of the Latin adjective '' quālis'' () meaning "of what sort" or "of what kind" in relation to a specific instance, such as "what it is like to taste a specific this particular apple now". Examples of qualia include the perceived sensation of ''pain'' of a headache, the ''taste'' of wine, and the ''redness'' of an evening sky. As qualitative characteristics of sensations, qualia stand in contrast to propositional attitudes, where the focus is on beliefs about experience rather than what it is directly like to be experiencing. C.S. Peirce introduced the term ''quale'' in philosophy in 1866, and in 1929 C. I. Lewis was the first to use the term "qualia" in its generally agreed upon modern sense. Frank Jackson later defined qualia as "...certain features of the bodily sensations especially, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soul
The soul is the purported Mind–body dualism, immaterial aspect or essence of a Outline of life forms, living being. It is typically believed to be Immortality, immortal and to exist apart from the material world. The three main theories that describe the relationship between the soul and the body are Interactionism (philosophy of mind), interactionism, Psychophysical parallelism, parallelism, and epiphenomenalism. Anthropology, Anthropologists and Psychology, psychologists have found that most humans are naturally inclined to believe in the existence of the soul and that they have interculturally distinguished between souls and bodies. The soul has been the central area of interest in philosophy since Ancient history, ancient times. Socrates envisioned the soul to possess a rational faculty, its practice being man's most godlike activity. Plato believed the soul to be the person's real self, an immaterial and immortal dweller of our lives that continues and thinks even after d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modal Logic
Modal logic is a kind of logic used to represent statements about Modality (natural language), necessity and possibility. In philosophy and related fields it is used as a tool for understanding concepts such as knowledge, obligation, and causality, causation. For instance, in epistemic modal logic, the well-formed_formula, formula \Box P can be used to represent the statement that P is known. In deontic modal logic, that same formula can represent that P is a moral obligation. Modal logic considers the inferences that modal statements give rise to. For instance, most epistemic modal logics treat the formula \Box P \rightarrow P as a Tautology_(logic), tautology, representing the principle that only true statements can count as knowledge. However, this formula is not a tautology in deontic modal logic, since what ought to be true can be false. Modal logics are formal systems that include unary operation, unary operators such as \Diamond and \Box, representing possibility and necessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |