|
Philipp Lenard
Philipp Eduard Anton von Lenard (; ; 7 June 1862 – 20 May 1947) was a Hungarian-German physicist who received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1905 "for his work on cathode rays" and the discovery of many of their properties. One of his most important contributions was the experimental realization of the photoelectric effect. He discovered that the energy (speed) of the electrons ejected from a cathode depends only on the frequency, and not the intensity, of the incident light. Lenard was a nationalist and antisemite; as an active proponent of the Nazi ideology, he supported Adolf Hitler in the 1920s and was an important role model for the movement during the Nazi period. Notably, he labeled Albert Einstein's contributions to science as "Jewish physics". Early life and work Philipp Lenard was born in Pressburg (''Pozsony'', today's Bratislava), on 7 June 1862 in the Kingdom of Hungary. The Lenard family had originally come from Tyrol in the 17th century, while his mother' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. Officially, the population of the city is about 475,000; however, some sources estimate daily number of people moving around the city based on mobile phone SIM cards is more than 570,000. Bratislava is in southwestern Slovakia at the foot of the Little Carpathians, occupying both banks of the Danube and the left bank of the Morava (river), River Morava. Bordering Austria and Hungary, it is the only national capital to border two sovereign states. The city's history has been influenced by people of many nations and religions, including Austrians, Bulgarians, Croats, Czechs, Germans, Hungarian people, Hungarians, Jews and Slovaks. It was the coronation site and legislative center and capital of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1536 to 1783; elev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wrocław
The University of Wrocław (, UWr; ) is a public research university in Wrocław, Poland. It is the largest institution of higher learning in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship, with over 100,000 graduates since 1945, including some 1,900 researchers, among whom many have received the highest awards for their contributions to the development of scientific scholarship. The university was reconstituted in its current form in 1945, as a direct successor to the previous German University of Breslau. Following the territorial changes of Poland's borders, academics primarily from the Jan Kazimierz University of Lwów restored the university building, which had been heavily damaged in the 1945 Battle of Breslau. History Leopoldina The oldest mention of a university in Wrocław comes from the foundation deed signed on 20 July 1505 for the ''Generale litterarum Gymnasium'' in Wrocław by King Vladislaus II of Hungary () of the Polish Jagiellonian dynasty. However, the new academic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intensity (physics)
In physics and many other areas of science and engineering the intensity or flux of radiant energy is the Power (physics), power transferred per unit area, where the area is measured on the plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the energy. In the SI system, it has units watts per square metre (W/m2), or kilogram, kg⋅second, s−3 in SI base unit, base units. Intensity is used most frequently with waves such as acoustic waves (sound), matter waves such as electrons in electron microscopes, and electromagnetic waves such as light or radio waves, in which case the time averaging, ''average'' power transfer over one Period (physics), period of the wave is used. ''Intensity'' can be applied to other circumstances where energy is transferred. For example, one could calculate the intensity of the kinetic energy carried by drops of water from a garden sprinkler. The word "intensity" as used here is not synonymous with "wikt:strength, strength", "wikt:amplitude, amplitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. The interval of time between events is called the period. It is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times per minute (2 hertz), its period is one half of a second. Special definitions of frequency are used in certain contexts, such as the angular frequency in rotational or cyclical properties, when the rate of angular progress is measured. Spatial frequency is defined for properties that vary or cccur repeatedly in geometry or space. The unit of measurement of frequency in the International System of Units (SI) is the hertz, having the symbol Hz. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode
A cathode is the electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device such as a lead-acid battery. This definition can be recalled by using the mnemonic ''CCD'' for ''Cathode Current Departs''. Conventional current describes the direction in which positive charges move. Electrons, which are the carriers of current in most electrical systems, have a negative electrical charge, so the movement of electrons is ''opposite'' to that of the conventional current flow: this means that electrons flow ''into'' the device's cathode from the external circuit. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a + (plus) is the cathode. The electrode through which conventional current flows the other way, into the device, is termed an anode. Charge flow Conventional current flows from cathode to anode outside the cell or device (with electrons moving in the opposite direction), regardless of the cell or device type and operating mode. Cathode polarity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up quark, up and down quark, down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall electric charge#Charge neutrality, neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electron, valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of Phenomenon, phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. They work across a wide range of Physics#Research fields, research fields, spanning all length scales: from atom, sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to physical cosmology, cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: Experimental physics, experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and Theoretical physics, theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. Physicists can apply their k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Genealogy Project
The Mathematics Genealogy Project (MGP) is a web-based database for the academic genealogy of mathematicians.. it contained information on 300,152 mathematical scientists who contributed to research-level mathematics. For a typical mathematician, the project entry includes graduation year, thesis title (in its Mathematics Subject Classification), '' alma mater'', doctoral advisor, and doctoral students.. Origin of the database The project grew out of founder Harry Coonce's desire to know the name of his advisor's advisor.. Coonce was Professor of Mathematics at Minnesota State University, Mankato, at the time of the project's founding, and the project went online there in the autumn of 1997.Mulcahy, Colm;The Mathematics Genealogy Project Comes of Age at Twenty-one(PDF) AMS Notices (May 2017) Coonce retired from Mankato in 1999, and in the autumn of 2002 the university decided that it would no longer support the project. The project relocated at that time to North Dakota State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
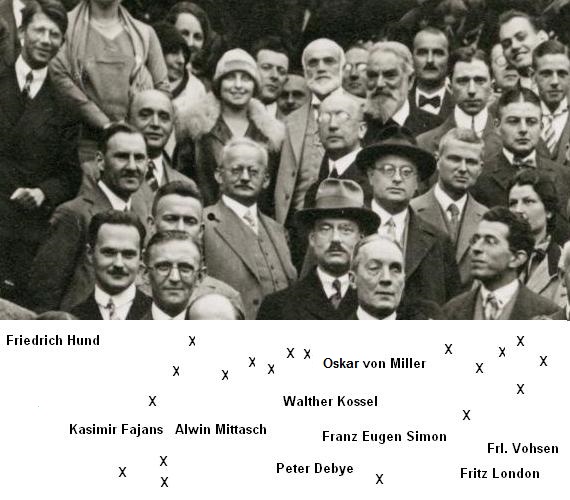
Walther Kossel
Walther Ludwig Julius Kossel (; 4 January 1888 – 22 May 1956) was a German chemist and physicist known for his theory of the chemical bond (ionic bond/octet rule), Sommerfeld–Kossel displacement law of atomic spectra, the Kossel–Stranski model for crystal growth, and the Kossel effect. Walther was the son of Albrecht Kossel who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1910. Career Kossel was born in Berlin, and began studies at the University of Heidelberg in 1906, but was at the University of Berlin during 1907 and 1908. In 1910, he became assistant to Philipp Lenard, who was also his thesis advisor. Kossel was awarded his Ph.D. in 1910, and he stayed on as assistant to Leonard until 1913. In 1913, the year in which Niels Bohr introduced the Bohr model of the atom, Kossel went to the University of Munich as assistant to Arnold Sommerfeld, under whom he did his Habilitation. Under Sommerfeld, Munich was a theoretical center for the developing atomic theory, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Crystallography
The International Union of Crystallography (IUCr) is an organisation devoted to the international promotion and coordination of the science of crystallography. The IUCr is a member of the International Council for Science (ICSU). Objectives The objectives of the IUCr are to promote international cooperation in crystallography and to contribute to all aspects of crystallography, to promote international publication of crystallographic research, to facilitate standardization of methods, units, nomenclatures and symbols, and to form a focus for the relations of crystallography to other sciences. The IUCr fulfils these objectives by publishing in print and electronically primary scientific journals through the ''Acta Crystallographica'' journal series, as well as '' Journal of Applied Crystallography'', '' Journal of Synchrotron Radiation'', '' IUCrJ'', the series of reference volumes ''International Tables for Crystallography'', distributing the quarterly ''IUCr Newsletter'', mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Andrade
Edward Neville da Costa Andrade FRS ( 27 December 1887 – 6 June 1971) was an English physicist, writer, and poet. He told ''The Literary Digest'' his name was pronounced "as written, i.e., like ''air raid'', with ''and'' substituted for ''air''." In the scientific world Andrade is best known for work (with Ernest Rutherford) that first determined the wavelength of a type of gamma radiation, proving it was far higher in energies than X-rays known at the time. Also, a rheological model suggested by him and bearing his name is still widely employed in continuum mechanics and its geophysical applications. In popular culture he was best known for his appearances on The Brains Trust. Life Edward Neville Andrade was a Sephardi Jew, his family having arrived in London from Portugal during the Napoleonic era, and was a descendant of Moses da Costa Andrade (not Moses da Costa as is sometimes stated). da Costa Andrade was his 2nd great-grandfather, a feather merchant in London's Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bunsen
Robert Wilhelm Eberhard Bunsen (; 30 March 1811 – 16 August 1899) was a German chemist. He investigated emission spectra of heated elements, and discovered caesium (in 1860) and rubidium (in 1861) with the physicist Gustav Kirchhoff. The Bunsen–Kirchhoff Award for spectroscopy is named after Bunsen and Kirchhoff. Bunsen also developed several gas-analytical methods, was a pioneer in photochemistry, and did early work in the field of organic arsenic chemistry. With his laboratory assistant Peter Desaga, he developed the Bunsen burner, an improvement on the laboratory burners then in use. Early life and education Bunsen was born in Göttingen, Germany, in 1811, in what is now the state of Lower Saxony in Germany. Bunsen was the youngest of four sons of the University of Göttingen's chief librarian and professor of modern philology, Christian Bunsen (1770–1837). After attending school in Holzminden, Bunsen matriculated at Göttingen in 1828 and studied chemistry wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |