|
Philip IV Of France
Philip IV (April–June 1268 – 29 November 1314), called Philip the Fair (), was King of France from 1285 to 1314. Jure uxoris, By virtue of his marriage with Joan I of Navarre, he was also King of Navarre and Count of Champagne as Philip I from 1284 to 1305. Although Philip was known to be handsome, hence the epithet ''le Bel'', his rigid, autocratic, imposing, and inflexible personality gained him (from friend and foe alike) other nicknames, such as the Iron King (). His fierce opponent Bernard Saisset, Roman Catholic Diocese of Pamiers, bishop of Pamiers, said of him: "He is neither man nor beast. He is a statue." Philip, seeking to reduce the wealth and power of the nobility and clergy, relied instead on skilful civil servants, such as Guillaume de Nogaret and Enguerrand de Marigny, to govern Kingdom of France, the kingdom. The king, who sought an uncontested monarchy, compelled his vassals by wars and restricted their feudal privileges, paving the way for the tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of France
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions. Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I, king of the Franks (), as the first king of France. However, historians today consider that such a kingdom did not begin until the establishment of West Francia, after the fragmentation of the Carolingian Empire in the 9th century. Titles The kings used the title "King of the Franks" () until the late twelfth century; the first to adopt the title of "King of France" (Latin: ''Rex Franciae''; French language, French: ''roi de France'') was Philip II of France, Philip II in 1190 (r. 1180–1223), after which the title "King of the Franks" gradually lost ground. However, ''Francorum Rex'' continued to be sometimes used, for example by Louis XII in 1499, by Francis I of France, Francis I in 1515, and by Henry II of France, Henry II in about 1550; it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jure Uxoris
''Jure uxoris'' (a Latin phrase meaning "by right of (his) wife"), citing . describes a title of nobility used by a man because his wife holds the office or title '' suo jure'' ("in her own right"). Similarly, the husband of an heiress could become the legal possessor of her lands. For example, married women in England and Wales were legally prohibited from owning real estate until the Married Women's Property Act 1882. Middle Ages During the feudal era, the husband's control over his wife's real property, including titles, was substantial. On marriage, the husband gained the right to possess his wife's land during the marriage, including any acquired after the marriage. Whilst he did not gain the formal legal title to the lands, he was able to spend the rents and profits of the land and sell his right, even if the wife protested. The concept of ''jure uxoris'' was standard in the Middle Ages even for queens regnant. In the Kingdom of Jerusalem, Fulk V of Anjou, Guy of Lusig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
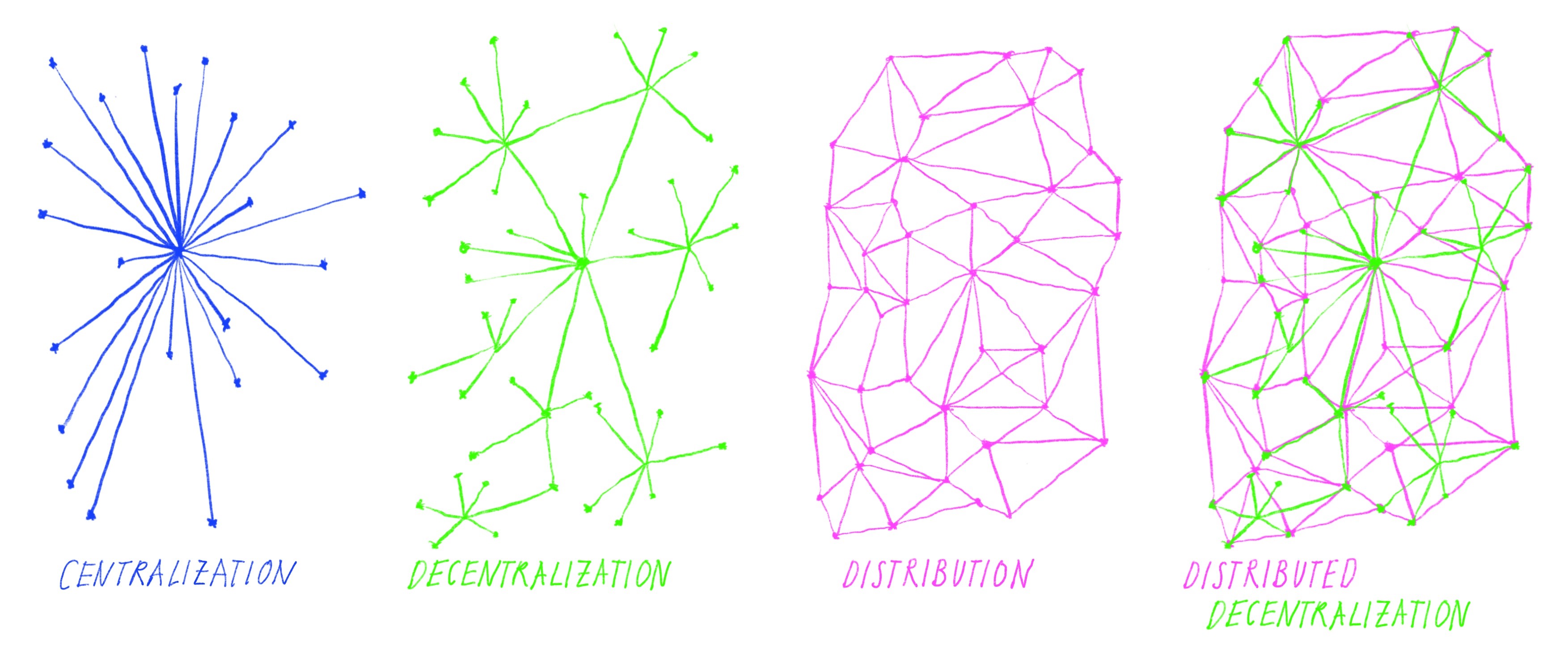
Centralisation
Centralisation or centralization (American English) is the process by which the activities of an organisation, particularly those regarding planning, decision-making, and framing strategies and policies, become concentrated within a particular group within that organisation. This creates a power structure where the said group occupies the highest level of hierarchy and has significantly more authority and influence over the other groups, who are considered its subordinates. An antonym of ''centralisation'' is ''decentralisation'', where authority is shared among numerous different groups, allowing varying degree of autonomy for each. The term has a variety of meanings in several fields. In political science, centralisation refers to the concentration of a government's power—both geographically and politically—into a centralized government, centralised government, which has sovereignty over all its administrative divisions. Conversely, a decentralized system, decentralised s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was a combination of legal, economic, military, cultural, and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe from the 9th to 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour. The classic definition, by François Louis Ganshof (1944),François Louis Ganshof (1944). ''Qu'est-ce que la féodalité''. Translated into English by Philip Grierson as ''Feudalism'', with a foreword by F. M. Stenton, 1st ed.: New York and London, 1952; 2nd ed: 1961; 3rd ed.: 1976. describes a set of reciprocal legal and Medieval warfare, military obligations of the warrior nobility and revolved around the key concepts of lords, vassals, and fiefs. A broader definition, as described by Marc Bloch (1939), includes not only the obligations of the warrior nobility but the obligations of all three estates of the realm: the nobility, the cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. The rights and obligations of a vassal are called vassalage, while the rights and obligations of a suzerain are called suzerainty. The obligations of a vassal often included military support by knights in exchange for certain privileges, usually including land held as a tenant or fief. The term is also applied to similar arrangements in other feudal societies. In contrast, fealty (''fidelitas'') was sworn, unconditional loyalty to a monarch. European vassalage In fully developed vassalage, the lord and the vassal would take part in a commendation ceremony composed of two parts, the Homage (feudal), homage and the fealty, including the use of Christian sacraments to show its sacred importance. According to Eginhard's brief description, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of France
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the Middle Ages, medieval and Early modern France, early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from the High Middle Ages to 1848 during its dissolution. It was also an early French colonial empire, colonial power, with colonies in Asia and Africa, and the largest being New France in North America geographically centred around the Great Lakes. The Kingdom of France was descended directly from the West Francia, western Frankish realm of the Carolingian Empire, which was ceded to Charles the Bald with the Treaty of Verdun (843). A branch of the Carolingian dynasty continued to rule until 987, when Hugh Capet was elected king and founded the Capetian dynasty. The territory remained known as ''Francia'' and its ruler as ('king of the Franks') well into the High Middle Ages. The first king calling himself ('King of France') was Philip II of Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enguerrand De Marigny
Enguerrand de Marigny, Baron Le Portier (c. 126030 April 1315) was a French chamberlain and minister of Philip IV. Early life He was born at Lyons-la-Forêt in Normandy, of an old Norman family of the lesser baronage called Le Portier, which took the name of Marigny about 1200. Enguerrand entered the service of Hugues II de Bouville, chamberlain and secretary of king Philip IV, as a squire, and then was attached to the household of Queen Jeanne, who made him one of the executors of her will. He married her god-daughter, Jeanne de St Martin. In 1298 he received the custody of the castle of Issoudun. Ministry After the death of Pierre Flotte at Courtrai in 1302 and de Bouville at the Battle of Mons-en-Pévèle in 1304, he became Philip's Grand Chamberlain and chief minister. In 1306 he was sent to preside over the exchequer of Normandy. He received numerous gifts of land and money from Philip as well as a pension from Edward II of England. Possessed of an ingratiating mann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillaume De Nogaret
Guillaume de Nogaret (c. 1260 April 1313) was a French statesman, councilor and keeper of the seal to Philip IV of France. Early life Nogaret was born in Saint-Félix-Lauragais, Haute-Garonne. The family held a small ancestral property of servile origin at Nogaret, near Saint-Félix-de-Caraman (today's Saint-Félix-Lauragais), from which it took its name. In 1291 Guillaume was professor of jurisprudence at the university of Montpellier, and in 1296 he became a member of the Curia Regis at Paris. From 1306, he was a seigneur of Marsillargues, Calvisson, Aujargues and Congénies in Languedoc. Councilor to Philip IV His name is mainly connected with the quarrel between Philip IV and Pope Boniface VIII. In 1300 he was sent with an embassy to Boniface, of which he left a picturesque and highly coloured account. His influence over the king dates from February 1303, when he persuaded Philip to consent to the bold plan of seizing Boniface and bringing him forcibly from I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the terms used for individual clergy are clergyman, clergywoman, clergyperson, churchman, cleric, ecclesiastic, and vicegerent while clerk in holy orders has a long history but is rarely used. In Christianity, the specific names and roles of the clergy vary by denomination and there is a wide range of formal and informal clergy positions, including deacons, elders, priests, bishops, cardinals, preachers, pastors, presbyters, ministers, and the pope. In Islam, a religious leader is often known formally or informally as an imam, caliph, qadi, mufti, sheikh, mullah, muezzin, and ulema. In the Jewish tradition, a religious leader is often a rabbi (teacher) or hazzan (cantor). Etymology The word ''cleric'' comes from the ecclesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically hereditary and patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, but nobility also existed in such regimes as the Dutch Republic (1581–1795), the Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Pamiers
The Diocese of Pamiers, Couserans, and Mirepoix (Latin: ''Dioecesis Apamiensis, Couseranensis, et Mirapicensis''; French: ''Diocèse de Pamiers, Mirepoix, et Couserans'') is a Latin Church diocese of the Catholic Church in southern France. Erected in 1295, it was a historical diocese of county of Foix. The diocese was suppressed in 1801, it was restored in 1822. The diocese comprises the department of Ariège and is suffragan to the Archdiocese of Toulouse. The diocese of Pamiers is divided into five Deaneries: Pamiers, Foix, Haut-Ariège, Couserans, and Pays-d'Olmes-Mirapoix. The episcopal see is the Cathedral of Saint Antoninus in the city of Pamiers. In 2021, in the Diocese of Pamiers, Couserans, and Mirepoix there was one priest for every 5,082 Catholics. History The traditions of the diocese mention as its first apostle of Christianity St. Antoninus, born at Fredelacum (Frédélas) near Pamiers in the Rouergue, and martyred in his native country at a date uncertain. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |