|
Pharaohs In The Bible
The Bible makes reference to various pharaohs (, ''Parʿō'') of Egypt. These include unnamed pharaohs in events described in the Torah, as well as several later named pharaohs, some of whom were historical or can be identified with historical pharaohs. Unnamed pharaohs In the Book of Genesis tells of Abram moving to Egypt to escape a period of famine in Canaan. Abram worries that the unnamed pharaoh will kill him and take away his wife Sarai, so Abram tells her to say she is his sister. They are eventually summoned to meet the pharaoh, but God sends plagues against the pharaoh because of his intention to marry Sarai. After discovering that Sarai is Abram's wife, he releases her and orders Abram to take his belongings and return to Canaan. Abd al-Husayn Tayyib claimed this Pharaoh was Sanakht, while Al-Maqrizi regards his name as "Tutis". Egyptologist David Rohl argued that this pharaoh was Nebkaure Khety II. Rohl's claim has been rejected by the vast majority of Egyptologis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shoshenq I By Rosellini
Shoshenq (also commonly spelled Sheshonq, Sheshonk, Shoshenk, Shashank) was the name of many Ancient Egyptians with Ancient Libya, Libu ancestry since the Third Intermediate Period. People named Shoshenq Several pharaohs with this name are known, as well as many important state officials: Pharaohs *Shoshenq I, founder of the 22nd Dynasty, often identified as the ''Shishaq'' of the Hebrew Bible *Shoshenq IIa or simply Shoshenq II, of the 22nd Dynasty *Shoshenq IIb or Tutkheperre Shoshenq, of the 22nd Dynasty *Shoshenq III, of the 22nd Dynasty *Shoshenq IV, of the 22nd Dynasty *Shoshenq V, of the 22nd Dynasty *Shoshenq VI, of the 23rd Dynasty *Shoshenq VII (existence doubtful) Officials *Shoshenq A, grandfather of Shoshenq I *Shoshenq C, a Theban High Priests of Amun, Theban High Priest of Amun, son of pharaoh Osorkon I *Shoshenq D, a High Priest of Ptah, son of pharaoh Osorkon II *Shoshenq, Chief steward of the God's Wife of Amun Ankhnesneferibre, buried in TT27 Renderings of ''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
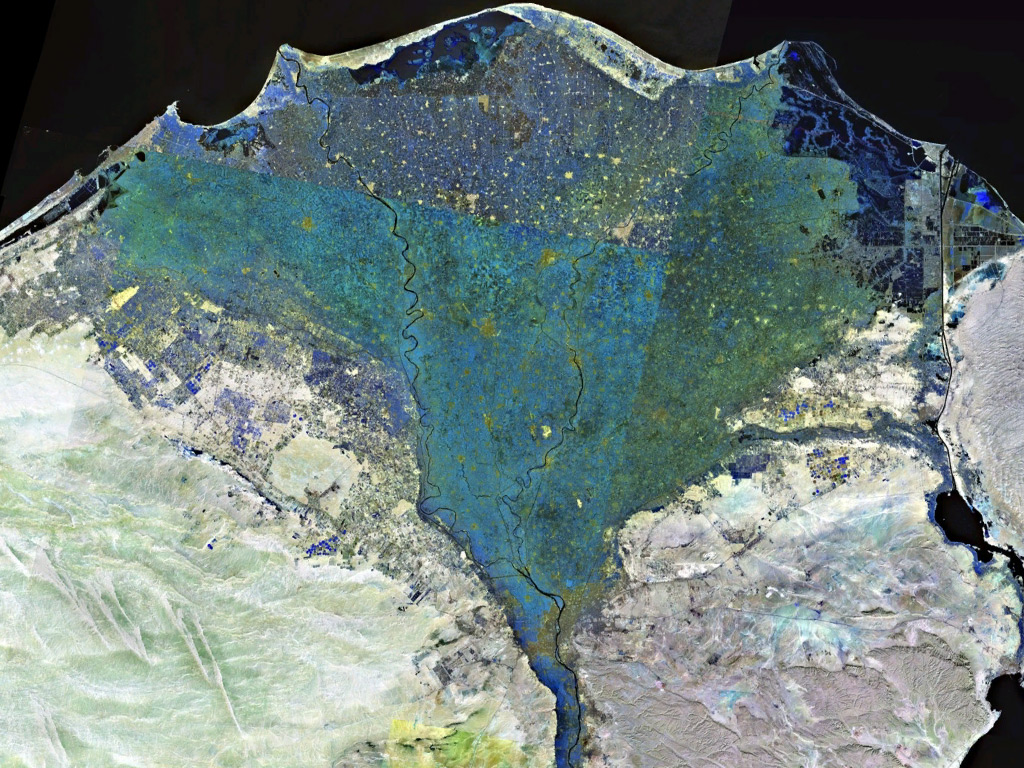
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east; it covers of the Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributary, distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same names. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood management, flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river systems by length, longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile has one of the lowest average annual flow rates. About long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt. In pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Levite
Levites ( ; ) or Levi are Jewish males who claim patrilineal descent from the Tribe of Levi. The Tribe of Levi descended from Levi, the third son of Jacob and Leah. The surname ''Halevi'', which consists of the Hebrew definite article "" ''Ha-'' ('the') plus ''Levi'' ('Levite'), is not conclusive regarding being a Levite; a titular use of HaLevi indicates being a Levite. The daughter of a Levite is a (''Bat'' being Hebrew for 'daughter'). The Tribe of Levi served particular religious duties for the Israelites and had political (administering cities of refuge) and educational responsibilities as well. In return, the landed tribes were expected to support the Levites with a tithe (), particularly the tithe known as the First tithe, ''ma'aser rishon''. The Kohanim, a subset of the Levites, were the priests, who performed the work of holiness in the Temple. The Levites, referring to those who were not Kohanim, were specifically assigned to: * Singing and/or playing music in the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritanism, and one of the most important prophets in Christianity, Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islam, the Manifestation of God (Baháʼí Faith)#Known messengers, Baháʼí Faith, and Table of prophets of Abrahamic religions, other Abrahamic religions. According to both the Bible and the Quran, God in Abrahamic religions, God dictated the Mosaic Law to Moses, which he Mosaic authorship, wrote down in the five books of the Torah. According to the Book of Exodus, Moses was born in a period when his people, the Israelites, who were an slavery, enslaved minority, were increasing in population; consequently, the Pharaohs in the Bible#In the Book of Exodus, Egyptian Pharaoh was worried that they might ally themselves with New Kingdom of Egypt, Eg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shiphrah And Puah
Shiphrah ( ') and Puah ( ') were two midwives who briefly prevented a genocide of children by the Egyptians, according to Exodus 1:15–21. According to the Exodus narrative, they were commanded by the King of Egypt, or Pharaoh, to kill all male Hebrew babies, but they refused to do so. When challenged by the Pharaoh, they told him Hebrew women's labour was short-lived because they were 'lively' or 'vigorous', and the babies had been born (and protected) before the midwives arrived. God "dealt well with the midwives" and "made them houses". Exodus 1:15–1:21 Interpretations The Talmud otah 11bidentifies Shiphrah with Jochebed, the mother of Moses, and Puah with Miriam, Moses' sister, making the two midwives mother and daughter respectively. "The midwives feared God" The Torah has no word for religion. The closest related concept found in the Torah is what it calls "the fear of God" (Exod. 1:17). The midwives apparently believed that God's moral demands outweighed Pharao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pi-Ramesses
Pi-Ramesses (; Ancient Egyptian: , meaning "House of Ramesses") was the new capital built by the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Nineteenth Dynasty Pharaoh Ramesses II (1279–1213 BC) at Qantir, near the old site of Avaris. The city had served as a summer palace under Seti I (c. 1290–1279 BC), and may have been founded by Ramesses I (c. 1292–1290 BC) while he served under Horemheb. Discovery In 1884, Flinders Petrie arrived in Egypt to begin his excavations there. His first dig was at Tanis, Egypt, Tanis, where he arrived with 170 workmen. Later in the 1930s, the ruins at Tanis were explored by Pierre Montet. The masses of broken Ramesside stonework at Tanis led archaeologists to identify it as Pi-Ramesses. Yet it eventually came to be recognised that none of these monuments and inscriptions originated at the site. In the 1960s, Manfred Bietak recognised that Pi-Ramesses was known to have been located on the then-easternmost branch of the Nile. He painstakingly mapped all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pithom
Pithom (; ; or , and ) was an ancient city of Egypt. References in the Hebrew Bible and ancient Greek and Roman sources exist for this city, but its exact location remains somewhat uncertain. Some scholars identified it as the later archaeological site of Tell el-Maskhuta (). Others identified it as the earlier archaeological site of Tell El Retabeh (). Etymology The English name comes from Hebrew which was taken from the Egyptian toponym ''pr-(j)tm'', "House of Atum". Atum's cult center was in Heliopolis.. Biblical Pithom Pithom is one of the cities which, according to the Book of Exodus , was built for the biblical Pharaoh of the oppression by the forced labour of the Israelites. The other city was Pi-Ramesses. The Septuagint adds a third, "''On'', which is Heliopolis." These cities are called by a term rendered in the Authorized Version "treasure cities" and in the Revised Version "store cities" (). The Septuagint renders it "strong r "fortified"cities." The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Book Of Exodus
The Book of Exodus (from ; ''Šəmōṯ'', 'Names'; ) is the second book of the Bible. It is the first part of the narrative of the Exodus, the origin myth of the Israelites, in which they leave slavery in Biblical Egypt through the strength of Yahweh, their deity, who according to the story Chosen people, chose them as his people. The Israelites then journey with the prophet Moses to biblical Mount Sinai, Mount Sinai, where Yahweh gives the Ten Commandments and they enter into a Mosaic covenant, covenant with Yahweh, who promises to make them a "holy nation, and a kingdom of priests" on condition of their faithfulness. He gives them laws and instructions to build the Tabernacle, the means by which he will come from heaven and dwell with them and lead them in a holy war to conquer Canaan (the "Promised Land"), which has earlier, according to the Book of Genesis, been promised to the "seed" of Abraham, the patriarch of the Israelites. Though traditionally Mosaic authorship, ascri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ankhu
Ankhu was an Egyptian vizier during the early 13th Dynasty in the late Middle Kingdom. He is believed to have resided in Thebes in Upper Egypt. Family Parentage Ankhu was the son of a vizier. Labib Habachi proposed that his father was the vizier Zamonth who served under king Amenemhat III in the Late Twelfth Dynasty. The mother of Ankhu is known as Henutpu, the name of Zamonth's wife is published as Henut. Habachi wonders whether ''Henut'' is a mistake or a short version of Henutpu. The name Henut is otherwise not attested. Detlef Franke agreed with this identification and calculates that Ankhu must have been 50 to 60 years old under king Khendjer. Wife and Children Ankhu was married to a woman called Mereret. Ankhu was the father of two further viziers: Resseneb and Iymeru. The family formed a strong dynasty of high court officials. One of the daughters of the couple was called Senebhenas. She was married to the ''overseer of the half domain'' Wepwawethotep (Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amenemhat III
:''See Amenemhat, for other individuals with this name.'' Amenemhat III (Ancient Egyptian: ''Ỉmn-m-hꜣt'' meaning 'Amun is at the forefront'), also known as Amenemhet III, was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the sixth king of the Twelfth Dynasty of the Middle Kingdom. He was elevated to throne as co-regent by his father Senusret III, with whom he shared the throne as the active king for twenty years. During his reign, Egypt attained its cultural and economic zenith of the Middle Kingdom. The aggressive military and domestic policies of Senusret III, which re-subjugated Nubia and wrested power from the nomarchs, allowed Amenemhat III to inherit a stable and peaceful Egypt. He directed his efforts towards an extensive building program with particular focus on Faiyum. Here he dedicated a temple to Sobek, a chapel to Renenutet, erected two colossal statues of himself in Biahmu, and contributed to excavation of Lake Moeris. He built for himself two pyramids at Dahshur and Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yuya
Yuya (sometimes Iouiya, or Yuaa, also known as Yaa, Ya, Yiya, Yayi, Yu, Yuyu, Yaya, Yiay, Yia, and Yuy) was a powerful ancient Egyptian courtier during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt ( 1390 BC). He was married to Thuya, an Egyptian noblewoman associated with the royal family, who held high offices in the governmental and religious hierarchies. Their daughter, Tiye, became the Great Royal Wife of Amenhotep III. Yuya and Thuya are known to have had a son named Anen, who carried the titles "Chancellor of Lower Egypt", "Second Prophet of Amun", "Sm-priest of Heliopolis", and "Divine Father". They may also have been the parents of Ay,Rice, p.222 an Egyptian courtier active during the reign of Akhenaten, who eventually became pharaoh as ''Kheperkheprure Ay''. There is no conclusive evidence, however, regarding the kinship of Yuya and Ay, although certainly both men came from the town of Akhmim. The tomb of Yuya and Thuya was, until the discovery of Tutankhamun's, one of the most s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |