|
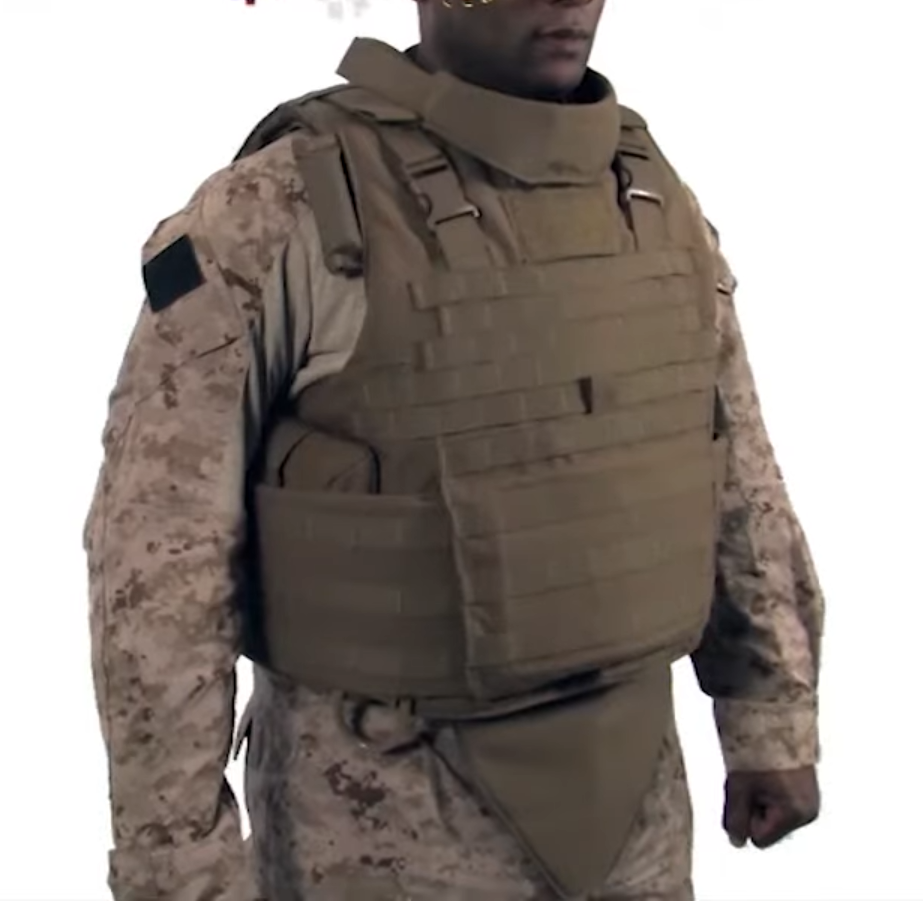
Personal Armor
Body armour, personal armour (also spelled ''armor''), armoured suit (''armored'') or coat of armour, among others, is armour for a person's body: protective clothing or close-fitting hands-free shields designed to absorb or deflect physical attacks. Historically used to protect military personnel, today it is also used by various types of police ( riot police in particular), private security guards, or bodyguards, and occasionally ordinary citizens. Today there are two main types: regular non-plated body armor for moderate to substantial protection, and hard-plate reinforced body armor for maximum protection, such as used by combatants. History Many factors have affected the development of personal armor throughout human history. Significant factors in the development of armor include the economic and technological necessities of armor production. For instance full plate armor first appeared in medieval Europe when water-powered trip hammers made the formation of plates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and Kuwait to the Iraq–Kuwait border, southeast, Jordan to Iraq–Jordan border, the southwest, and Syria to Iraq–Syria border, the west. The country covers an area of and has Demographics of Iraq, a population of over 46 million, making it the List of countries by area, 58th largest country by area and the List of countries by population, 31st most populous in the world. Baghdad, home to over 8 million people, is the capital city and the List of largest cities of Iraq, largest in the country. Starting in the 6th millennium BC, the fertile plains between Iraq's Tigris and Euphrates rivers, referred to as Mesopotamia, fostered the rise of early cities, civilisations, and empires including Sumer, Akkadian Empire, Akkad, and Assyria. Known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigandine
A brigandine (sometimes spelled "brigantine"), also called a brigander, is a form of body armour, in use from the late Middle Ages and up to the early modern era. It is a garment typically made of heavy cloth, canvas, or leather, featuring small oblong steel plates riveted to the fabric such that the fabric and rivets present on the outside, sometimes with a second layer of fabric on the inside. Origins Protective clothing and armour have been used by armies from earliest recorded history; the King James Version of the Bible (Jeremiah 46:4) translates the Hebrew , or , "coat of mail" as "brigandine". Medieval brigandines were essentially a refinement of the earlier coat of plates, which developed in the late 12th century. These were typically of simpler construction with larger metal plates. This new armour became very popular in Eastern Europe, especially in Hungary, towards the end of the 13th century and was adopted in western Europe several decades later. Early brigan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
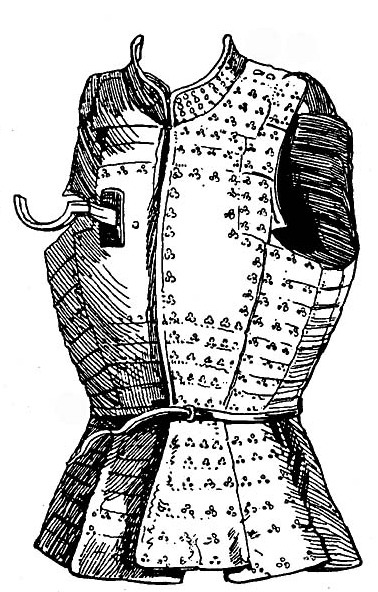
Coat Of Plates
A coat of plates is a form of segmented torso armour consisting of overlapping metal plates riveted inside a cloth or leather garment. The coat of plates is considered part of the era of transitional armour and was normally worn as part of a full knightly harness. The coat saw its introduction in Europe among the warring elite in the 1180s or 1220s and was well established by the 1250s. It was in very common usage by the 1290s. By the 1350s it was universal among infantry militias as well. After about 1340, the plates covering the chest were combined to form an early breastplate, replacing the coat of plates. After 1370, the breastplate covered the entire torso. Different forms of the coat of plates, known as the brigandine and jack of plates, remained in use until the late 16th century. Construction The plates number anywhere from eight or ten to the hundreds depending on their size. The plates overlap, usually enough to guarantee full coverage even when moving around and fig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellar Armour
Lamellar armour is a type of body armour made from small rectangular plates (scales or ''lamellae'') of iron, steel, leather ( rawhide), bone, or bronze laced into horizontal rows. Lamellar armour was used over a wide range of time periods in Central Asia, Eastern Asia (especially in China, Japan, Korea, Mongolia, and Tibet), Western Asia, and Eastern Europe. The earliest evidence for lamellar armour comes from sculpted artwork of the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–609 BC) in the Near East. Lamellar armour should not be confused with laminar armour, a related form of plate armour which is made from horizontal overlapping rows or bands of solid armour plates (called lames) rather than scales. By comparison, lamellar armour is made from individual armour scales which are laced together to form a strip of armour which appears to be solid but is not. Description Lamellar armour consists of small platelets known as "lamellae" or "lames", which are punched and laced together, typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynasties In Chinese History
For most of its history, China was organized into various dynastic states under the rule of hereditary monarchs. Beginning with the establishment of dynastic rule by Yu the Great , and ending with the abdication of the Xuantong Emperor in AD 1912, Chinese historiography came to organize itself around the succession of monarchical dynasties. Besides those established by the dominant Han ethnic group or its spiritual Huaxia predecessors, dynasties throughout Chinese history were also founded by non-Han peoples. Dividing Chinese history into dynastic epochs is a convenient and conventional method of periodization. Accordingly, a dynasty may be used to delimit the era during which a family reigned, as well as to describe events, trends, personalities, artistic compositions, and artifacts of that period. For example, porcelain made during the Ming dynasty may be referred to as "Ming porcelain". The longest-reigning orthodox dynasty of China was the Zhou dynasty, ruling for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Armour
Chinese armour was predominantly lamellar from the Warring States period (481 BC–221 BC) until the Ming dynasty (1368–1644). Before lamellar, personal armour in China consisted of animal parts such as rhinoceros hide, rawhide, and turtle shells. Lamellar armour was supplemented by other forms of armour such as scale since the Warring States period or earlier. Large metal plates worn over the chest and back, known as "cord and plaque" armour, was used from the Northern and Southern dynasties (420–589) to the Tang dynasty (618–907). Evidence of mail and mountain pattern armour started appearing from the Tang dynasty onward, although they never supplanted lamellar as the primary type of body armour. Chain mail had been known since the Han dynasty (202 BC – 220 AD), but did not see widespread production. Mail was used infrequently and may have been seen as "exotic foreign armor" used to display the wealth of rich officers and soldiers. During the Ming dynasty (1368–1644), b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorica Squamata
The ''lorica squamata'' () is a type of scale armour used by the ancient Roman military during the Roman Republic and at later periods. It was made from small metal scales sewn to a fabric backing. No examples of an entire ''lorica squamata'' have been found, but there have been several archaeological finds of fragments of such shirts and individual scales are quite common finds—even in non-military contexts. Use in the Roman army It is typically seen on depictions of '' signiferes'' (standard bearers), '' aeneatores'', centurions, cavalry troops, and auxiliary infantry, as well as regular legionaries. On occasion the emperor The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ... would even be depicted wearing the ''lorica squamata''. During the Dacian Wars Trajan had to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorica Segmentata
The ''lorica segmentata'' (), also called ''lorica lamminata'', or ''banded armour'' is a type of personal armour that was used by soldiers of the Roman army, consisting of metal strips fashioned into circular bands, fastened to internal leather straps. The ''lorica segmentata'' has come to be viewed as symbolic of the Roman legions in popular culture. Name file:007 Conrad Cichorius, Die Reliefs der Traianssäule, Tafel VII (Ausschnitt 01).jpg, Roman legionaries marching across a pontoon bridge, a Roman sculpture, relief scene from Trajan's Column, the column of Emperor Trajan (r. 98-117 AD) in Rome, Italy (monochrome photography, monochrome photographs by Conrad Cichorius) In Latin, the name ''lorica segmentata'' translates to "segmented cuirass." However, this name was not given to the armor by the Romans. Instead, it was given by scholars in the 16th century. Despite the lack of knowledge on the Roman name for the armor, scholars can make educated guesses on the Roman n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorica Hamata
The ''lorica hamata'' (in Latin with normal elision: ) is a type of mail armor used by soldiers for over 600 years (3rd century BC to 4th century AD) from the Roman Republic to the Roman Empire. ''Lorica hamata'' comes from the Latin ''hamatus'' (hooked) from ''hamus'' which means "hook", as the rings hook into one another. Usage Modern historians believe that mail armor was invented by the Celts. With the idea for this form of mail possibly coming to Rome during conflicts with the Celts in the 3rd century BC, lorica hamata was used by both legionary and ''auxilia'' troops. The first documented use occurred during the Roman conquest of Hispania The romans ruled and occupied territories in the Iberian Peninsula that were previously under the control of native Celtic, Iberian, Celtiberian and Aquitanian tribes and the Carthaginian Empire. The Carthaginian territories in the south a .... There were several versions of this type of armor, specialized for different military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon James (archaeologist)
Simon James is an archeologist of the Iron Age and Ancient Rome, Roman period and an author. He is Professor of Archaeology at the University of Leicester in England. His research interests are the Roman world and its interactions with the Celts and Middle Eastern peoples. Education and academic career James obtained his PhD from University College London, and then moved to the British Museum, where he was an archaeological illustrator before becoming a museum educator. After several years as a Research Fellow at Durham University he joined the School of Archaeology and Ancient History at the University of Leicester in 2000. His research has focused on ancient warfare and especially the Roman military. He has studied the remarkably well-preserved Roman and Partho-Sasanian military remains from Dura-Europos, Syria. In reinterpreting the evidence for mine (military), mines and counter-mines dug beneath the city's walls during the Sasanian Persian siege which finally destroyed Dura a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celt
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century BC, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . "[T]he Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe." in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic languages and other cultural similarities.. "C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |