|
Pen
A pen is a common writing instrument that applies ink to a surface, typically paper, for writing or drawing. Early pens such as reed pens, quill pens, dip pens and ruling pens held a small amount of ink on a nib or in a small void or cavity that had to be periodically recharged by dipping the tip of the pen into an inkwell. Today, such pens find only a small number of specialized uses, such as in illustration and calligraphy. Reed pens, quill pens and dip pens, which were used for writing, have been replaced by ballpoint pens, rollerball pens, fountain pens and felt or ceramic tip pens. Ruling pens, which were used for technical drawing and cartography, have been replaced by technical pens such as the Rapidograph. All of these modern pens contain internal ink reservoirs, such that they do not need to be dipped in ink while writing. Types Modern Pens commonly used today can be categorized based on the mechanism of the writing tip and the type of ink: * A ballpoint pen di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porous Point Pen
A marker pen, fine liner, marking pen, felt-tip pen, felt pen, flow marker, sign pen (in South Korea), vivid (in New Zealand), flomaster (in East and South Slavic countries), texta (in Australia), sketch pen (in South Asia), koki (in South Africa) or simply marker is a pen which has its own ink source and a tip made of porous, pressed fibers such as felt. A marker pen consists of a container (glass, aluminum or plastic) and a core of an absorbent material that holds the ink. The upper part of the marker contains the nib that was made in earlier times of a hard felt material, and a cap to prevent the marker from drying out. Until the early 1990s, the most common solvents that were used for the ink in permanent markers were toluene and xylene. These two substances are both harmful and characterized by a very strong smell. Today, the ink is usually made on the basis of alcohols (e.g. 1-Propanol, 1-butanol, diacetone alcohol and cresols). Markers may be waterproof, dry-erase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
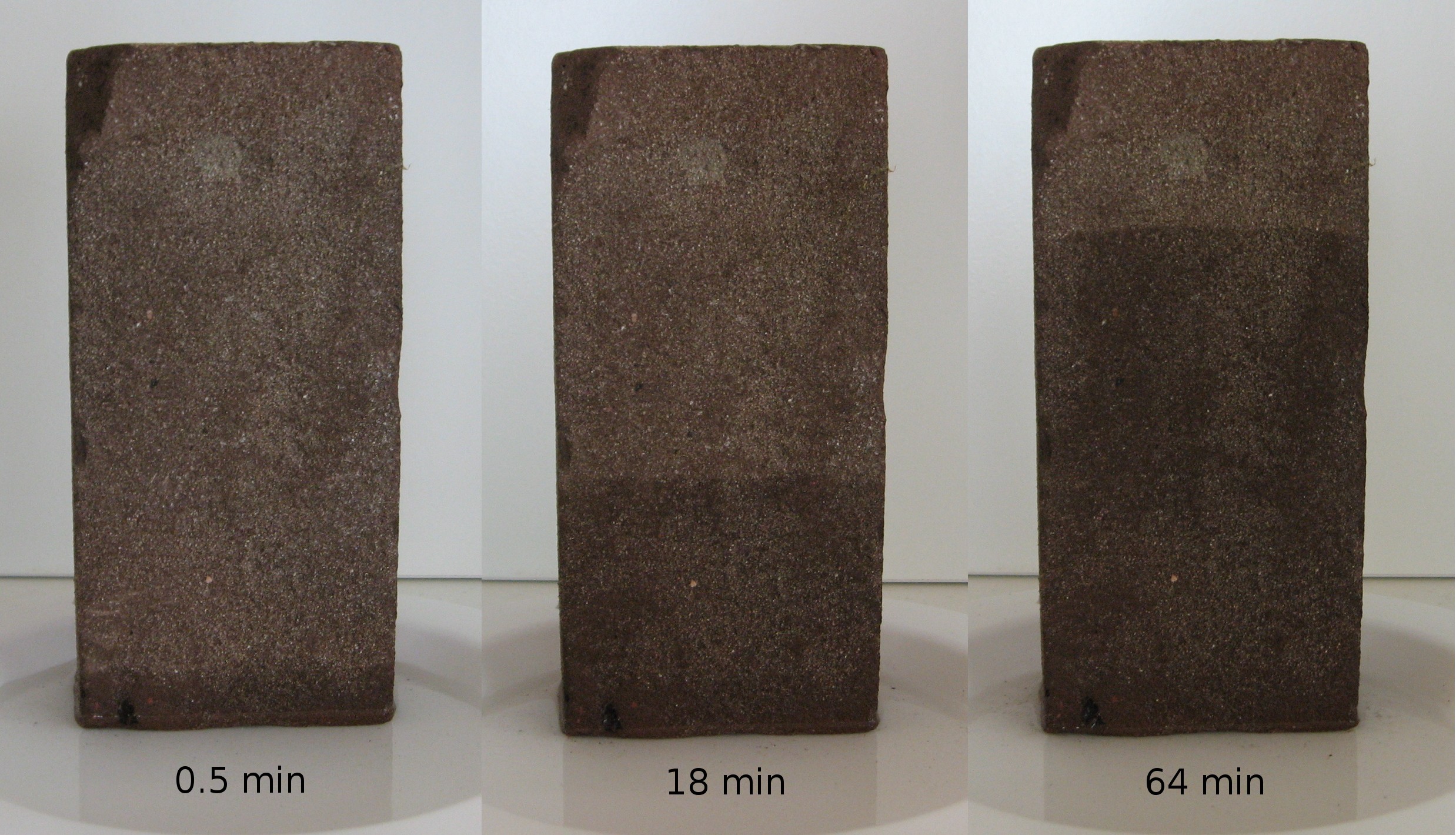
Capillary Action
Capillary action (sometimes called capillarity, capillary motion, capillary rise, capillary effect, or wicking) is the process of a liquid flowing in a narrow space without the assistance of external forces like Gravitation, gravity. The effect can be seen in the drawing up of liquids between the hairs of a paint-brush, in a thin tube such as a Drinking straw, straw, in porous materials such as paper and plaster, in some non-porous materials such as clay and liquefied carbon fiber, or in a biological cell. It occurs because of intermolecular forces between the liquid and surrounding solid surfaces. If the diameter of the tube is sufficiently small, then the combination of surface tension (which is caused by Cohesion (chemistry), cohesion within the liquid) and Adhesion, adhesive forces between the liquid and container wall act to propel the liquid. Etymology Capillary comes from the Latin word capillaris, meaning "of or resembling hair". The meaning stems from the tiny, hairl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permeation
In physics and engineering, permeation (also called imbuing) is the penetration of a wikt:permeate#English, permeate (a fluid such as a liquid, gas, or vapor) through a solid. It is directly related to the concentration gradient of the permeate, a material's intrinsic permeability, and the materials' mass diffusivity. Permeation is modeled by equations such as Fick's laws of diffusion, and can be measured using tools such as a minipermeameter. Description The process of permeation involves the diffusion of molecules, called the permeant, through a membrane or interface. Permeation works through diffusion; the permeant will move from high concentration to low concentration across the interface. A material can be semipermeable, with the presence of a semipermeable membrane. Only molecules or ions with certain properties will be able to diffuse across such a membrane. This is a very important mechanism in biology where fluids inside a blood vessel need to be regulated and controlle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: ) is a carbide containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into shapes through sintering for use in industrial machinery, engineering facilities, molding blocks, cutting tools, chisels, abrasives, armor-piercing bullets and jewelry. Tungsten carbide is approximately three times as stiff as steel, with a Young's modulus of approximately 530–700 GPa, and is twice as dense as steel. It is comparable with corundum (α- ) in hardness, approaching that of a diamond, and can be polished and finished only with abrasives of superior hardness such as cubic boron nitride and diamond. Tungsten carbide tools can be operated at cutting speeds much higher than high-speed steel (a special steel blend for cutting tools). Tungsten carbide powder was first synthesized by H. Moissan in 1893, and the industrial production of the cemented form starte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength and low raw material cost, steel is one of the most commonly manufactured materials in the world. Steel is used in structures (as concrete Rebar, reinforcing rods), in Bridge, bridges, infrastructure, Tool, tools, Ship, ships, Train, trains, Car, cars, Bicycle, bicycles, Machine, machines, Home appliance, electrical appliances, furniture, and Weapon, weapons. Iron is always the main element in steel, but other elements are used to produce various grades of steel demonstrating altered material, mechanical, and microstructural properties. Stainless steels, for example, typically contain 18% chromium and exhibit improved corrosion and Redox, oxidation resistance versus its carbon steel counterpart. Under atmospheric pressures, steels generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brass
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc, in proportions which can be varied to achieve different colours and mechanical, electrical, acoustic and chemical properties, but copper typically has the larger proportion, generally copper and zinc. In use since prehistoric times, it is a substitutional alloy: atoms of the two constituents may replace each other within the same crystal structure. Brass is similar to bronze, a copper alloy that contains tin instead of zinc. Both bronze and brass may include small proportions of a range of other Chemical element, elements including arsenic, lead, phosphorus, aluminium, manganese and silicon. Historically, the distinction between the two alloys has been less consistent and clear, and increasingly museums use the more general term "list of copper alloys, copper alloy". Brass has long been a popular material for its bright gold-like appearance and is still used for drawer pulls and door handle, doorknobs. It has also been widely used to ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
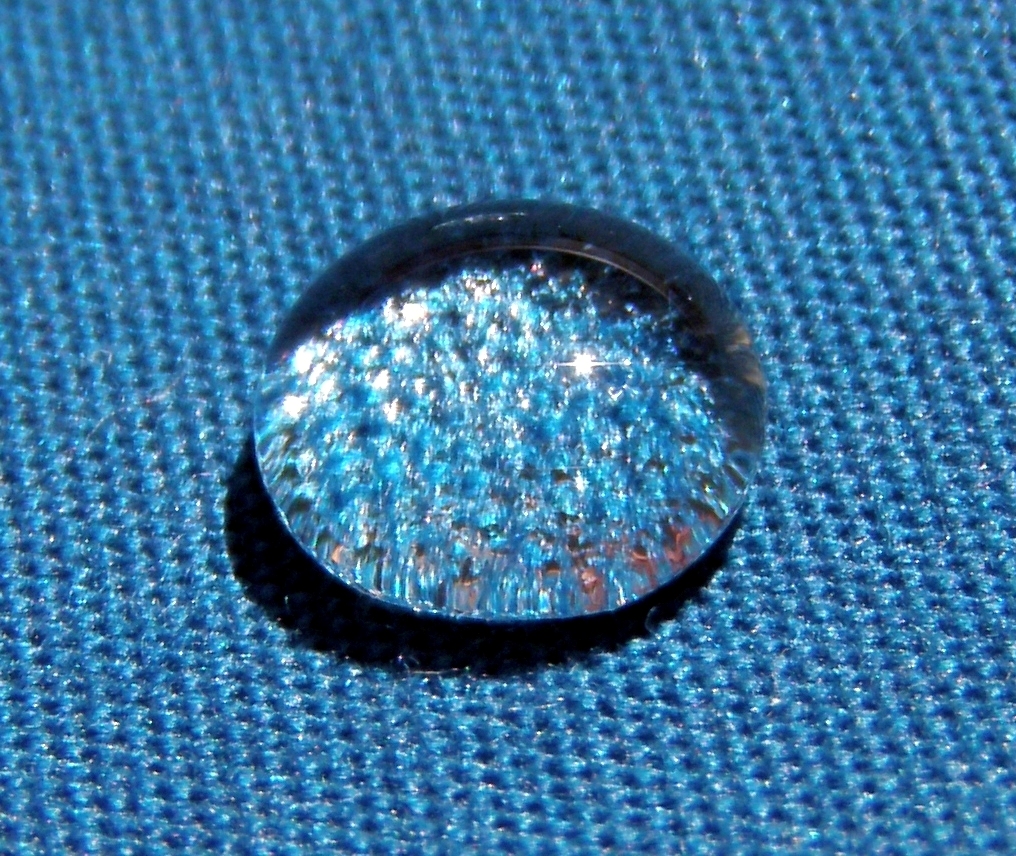
Wettability
Wetting is the ability of a liquid to displace gas to maintain contact with a solid surface, resulting from intermolecular interactions when the two are brought together. These interactions occur in the presence of either a gaseous phase or another liquid phase not miscible with the wetting liquid. The degree of wetting (wettability) is determined by a force balance between adhesive and cohesive forces. There are two types of wetting: non-reactive wetting and reactive wetting. Wetting is important in the bonding or adherence of two materials. The wetting power of a liquid, and surface forces which control wetting, are also responsible for related effects, including capillary effects. Surfactants can be used to increase the wetting power of liquids such as water. Wetting has gained increasing attention in nanotechnology and nanoscience research, following the development of nanomaterials over the past two decades (i.e., graphene, carbon nanotube, boron nitride nanomesh). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball Bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races. The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this by using at least two races to contain the balls and transmit the loads through the balls. In most applications, one race is stationary and the other is attached to the rotating assembly (e.g., a hub or shaft). As one of the bearing races rotates it causes the balls to rotate as well. Because the balls are rolling, they have a much lower coefficient of friction than if two flat surfaces were sliding against each other. Ball bearings tend to have lower load capacity for their size than other kinds of rolling-element bearings due to the smaller contact area between the balls and races. However, they can tolerate some misalignment of the inner and outer races. Common ball bearing designs include ''angular contact, axial, deep-groove,'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity is defined scientifically as a force multiplied by a time divided by an area. Thus its SI units are newton-seconds per metre squared, or pascal-seconds. Viscosity quantifies the internal friction, frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's center line than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (physics), stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macro Biro Tip
Macro (or MACRO) may refer to: Science and technology * Macroscopic, subjects visible to the eye * Macro photography, a type of close-up photography * Image macro, a picture with text superimposed * Monopole, Astrophysics and Cosmic Ray Observatory (MACRO), a particle physics experiment * Macronutrients, classes of chemical compounds humans consume in the largest quantities (i.e., proteins, fats, and carbohydrates) Sociology * Macrosociology, sociology at the national level * Macroeconomics, economics at a higher level, above individual markets * Macromanagement in business, the idea of "managing from afar" Computing * Macro (computer science), a set of instructions that is represented in an abbreviated format * Macro instruction, a statement, typically for an assembler, that invokes a macro definition to generate a sequence of instructions or other outputs * Macro key, a key found on some keyboards, particularly older keyboards. Media and entertainment * Macromanagement (gamepl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotring
Rotring (stylized rOtring) is a manufacturing company, manufacturer of technical drawing tools and writing implements. Established in Germany in 1928 as a fountain pen manufacturer, Rotring went on to be acquired by Newell Brands in 1998. The name "Rotring" directly translates to "red ring", which refers to the company's signature: a red band placed around the barrel of the pen. The company's name was changed to Rotring in the early 1970s to match the trademark. Since the Rotring factory and headquarters in Hamburg were shut down, production has been handled and distributed by Japanese manufacturer Holbein and other manufacturers. History The company was established in 1928 as "Tintenkuli Handels GmbH".Heritage on Rotring website, 25 Nov 2019 The company's first product was the "Tintenkuli", a type of pen with a narrow steel tube instead of a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |