|
Pauling's Rules
Pauling's rules are five rules published by Linus Pauling in 1929 for predicting and rationalizing the crystal structures of ionic compounds. First rule: the radius ratio rule For typical ionic solids, the cations are smaller than the anions, and each cation is surrounded by coordinated anions which form a polyhedron. The sum of the ionic radii determines the cation-anion distance, while the cation-anion radius ratio r_+ / r_- (or r_c / r_a) determines the coordination number (C.N.) of the cation, as well as the shape of the coordinated polyhedron of anions. For the coordination numbers and corresponding polyhedra in the table below, Pauling mathematically derived the ''minimum'' radius ratio for which the cation is in contact with the given number of anions (considering the ions as rigid spheres). If the cation is smaller, it will not be in contact with the anions which results in instability leading to a lower coordination number. The three diagrams at right cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling ( ; February 28, 1901August 19, 1994) was an American chemist and peace activist. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific topics. ''New Scientist'' called him one of the 20 greatest scientists of all time. For his scientific work, Pauling was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1954. For his peace activism, he was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1962. He is one of five people to have Nobel Prize#Multiple laureates, won more than one Nobel Prize. Of these, he is the only person to have been awarded two unshared Nobel Prizes, and one of two people to be awarded Nobel Prizes in different fields, the other being Marie Curie. Pauling was one of the founders of the fields of quantum chemistry and molecular biology. His contributions to the theory of the chemical bond include the concept of orbital hybridisation and the first accurate scale of electronegativity, electronegativities of the elements. Pauling also wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cube
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional space, three-dimensional solid object in geometry, which is bounded by six congruent square (geometry), square faces, a type of polyhedron. It has twelve congruent edges and eight vertices. It is a type of parallelepiped, with pairs of parallel opposite faces, and more specifically a rhombohedron, with congruent edges, and a rectangular cuboid, with right angles between pairs of intersecting faces and pairs of intersecting edges. It is an example of many classes of polyhedra: Platonic solid, regular polyhedron, parallelohedron, zonohedron, and plesiohedron. The dual polyhedron of a cube is the regular octahedron. The cube can be represented in many ways, one of which is the graph known as the cubical graph. It can be constructed by using the Cartesian product of graphs. The cube is the three-dimensional hypercube, a family of polytopes also including the two-dimensional square and four-dimensional tesseract. A cube with 1, unit s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
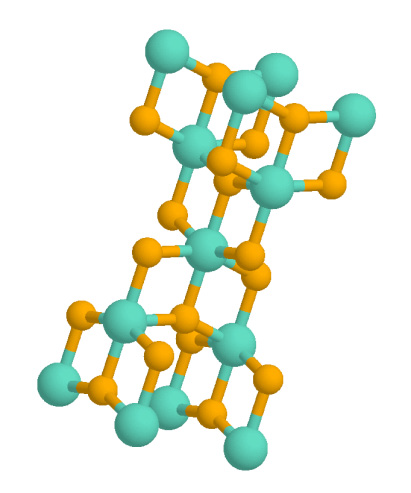
Rutile
Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite. Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at visible wavelengths of any known crystal and also exhibits a particularly large birefringence and high dispersion. Owing to these properties, it is useful for the manufacture of certain optical elements, especially polarization optics, for longer visible and infrared wavelengths up to about 4.5 micrometres. Natural rutile may contain up to 10% iron and significant amounts of niobium and tantalum. Rutile derives its name from the Latin ('red'), in reference to the deep red color observed in some specimens when viewed by transmitted light. Rutile was first described in 1803 by Abraham Gottlob Werner using specimens obtained in Horcajuelo de la Sierra, Madrid (Spain), which is consequently the type locality. Occurrence Rutile is a comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index International, CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble in water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structures of rutile and anatase are tetragonal in symmetry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthoclase
Orthoclase, or orthoclase feldspar ( endmember formula K Al Si3 O8), is an important tectosilicate mineral which forms igneous rock. The name is from the Ancient Greek for "straight fracture", because its two cleavage planes are at right angles to each other. It is a type of alkali feldspar, also known as potassium feldspar or K-spar. The gem known as moonstone (see below) is largely composed of orthoclase. Formation and subtypes left, Orthoclase Organ_Mountains.html" ;"title="crystal twinning from the Organ Mountains">crystal twinning from the Organ Mountains in New Mexico Orthoclase is a common constituent of most granites and other felsic igneous rocks and often forms huge crystals and masses in pegmatite. Typically, the pure potassium endmember of orthoclase forms a solid solution with albite, the sodium endmember (NaAlSi3O8) of plagioclase. While slowly cooling within the earth, sodium-rich albite lamellae form by exsolution, enriching the remaining orthocla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminosilicate
Aluminosilicate refers to materials containing anionic Si-O-Al linkages. Commonly, the associate cations are sodium (Na+), potassium (K+) and protons (H+). Such materials occur as minerals, coal combustion products and as synthetic materials, often in the form of zeolites. Both synthetic and natural aluminosilicates are of technical significance as structural materials, catalysts, and reagents. Important representatives Feldspar is a common tectosilicate aluminosilicate mineral made of potassium, sodium, and calcium cations surrounded by a negatively charged network of silicon, aluminium and oxygen atoms. Many aluminosilicates are synthesized by reactions of silicates, aluminates, and other compounds. They have the general formula where M+ is usually H+ and Na+. The Si/Al ratio is variable, which provides a means to tune the properties. Many of these materials are porous and exhibit properties of industrial value. Naturally occurring microporous, hydrous aluminosilicate m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Charge
Electric charge (symbol ''q'', sometimes ''Q'') is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative''. Like charges repel each other and unlike charges attract each other. An object with no net charge is referred to as neutral particle, electrically neutral. Early knowledge of how charged substances interact is now called classical electrodynamics, and is still accurate for problems that do not require consideration of quantum mechanics, quantum effects. In an isolated system, the total charge stays the same - the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge does not change over time. Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the atomic nucleus, nuclei of atoms. If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxide
An oxide () is a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. "Oxide" itself is the dianion (anion bearing a net charge of −2) of oxygen, an O2− ion with oxygen in the oxidation state of −2. Most of the Earth's crust consists of oxides. Even materials considered pure elements often develop an oxide coating. For example, aluminium foil develops a thin skin of (called a passivation layer) that protects the foil from further oxidation.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. . Stoichiometry Oxides are extraordinarily diverse in terms of stoichiometries (the measurable relationship between reactants and chemical equations of an equation or reaction) and in terms of the structures of each stoichiometry. Most elements form oxides of more than one stoichiometry. A well known example is carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs as the mineral halite. In its edible form, it is commonly used as a condiment and curing (food preservation), food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further Chemical synthesis, chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is deicing of roadways in sub-freezing weather. Uses In addition to the many familiar domestic uses of salt, more dominant applications of the approximately 250 million tonnes per year production (2008 data) include chemicals and de-icing.Westphal, Gisbert ''et al.'' (2002) "Sodium Chloride" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim . Chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CsCl Crystal
Caesium chloride or cesium chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula Cs Cl. This colorless salt is an important source of caesium ions in a variety of niche applications. Its crystal structure forms a major structural type where each caesium ion is coordinated by 8 chloride ions. Caesium chloride dissolves in water. CsCl changes to NaCl structure on heating. Caesium chloride occurs naturally as impurities in carnallite (up to 0.002%), sylvite and kainite. Less than 20 tonnes of CsCl is produced annually worldwide, mostly from a caesium-bearing mineral pollucite. Caesium chloride is widely used in isopycnic centrifugation for separating various types of DNA. It is a reagent in analytical chemistry, where it is used to identify ions by the color and morphology of the precipitate. When enriched in radioisotopes, such as 137CsCl or 131CsCl, caesium chloride is used in nuclear medicine applications such as treatment of cancer and diagnosis of myocardial infarction. Another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NaCl Polyhedra
Sodium chloride , commonly known as edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs as the mineral halite. In its edible form, it is commonly used as a condiment and food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is deicing of roadways in sub-freezing weather. Uses In addition to the many familiar domestic uses of salt, more dominant applications of the approximately 250 million tonnes per year production (2008 data) include chemicals and de-icing.Westphal, Gisbert ''et al.'' (2002) "Sodium Chloride" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim . Chemical functions Salt is used, directly or indirectly, in the prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Chemical Education
The ''Journal of Chemical Education'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal available in both print and electronic versions. It is published by the Division of Chemical Education of the American Chemical Society The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all ... and was established in 1924 by Neil Gordon. The journal covers research on chemical education, and its target audience includes instructors of chemistry from middle school through graduate school and some scientists in commerce, industry, and government. References External links * Chemical education journals American Chemical Society academic journals Monthly journals Academic journals established in 1924 English-language journals {{chemistry-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |