|
Patterned Vegetation
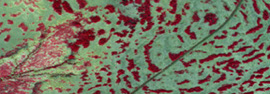
Patterned vegetation is a vegetation community that exhibits distinctive and repetitive patterns. Examples of patterned vegetation include fir waves, tiger bush, and string bog. The patterns typically arise from an interplay of phenomena that differentially encourage plant growth or mortality. A coherent pattern arises because there is a strong directional component to these phenomena, such as wind in the case of fir waves, or surface runoff in the case of tiger bush. Patterns can include relatively evenly spaced patches, parallel bands, or some intermediate between those two. These patterns in the vegetation can appear without any underlying pattern in soil types, and are thus said to "self-organize" rather than be determined by the environment. Mechanisms Several of the mechanisms underlying patterning of vegetation have been known and studied since at least the middle of the 20th century, however, mathematical models replicating them have only been produced much more recentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
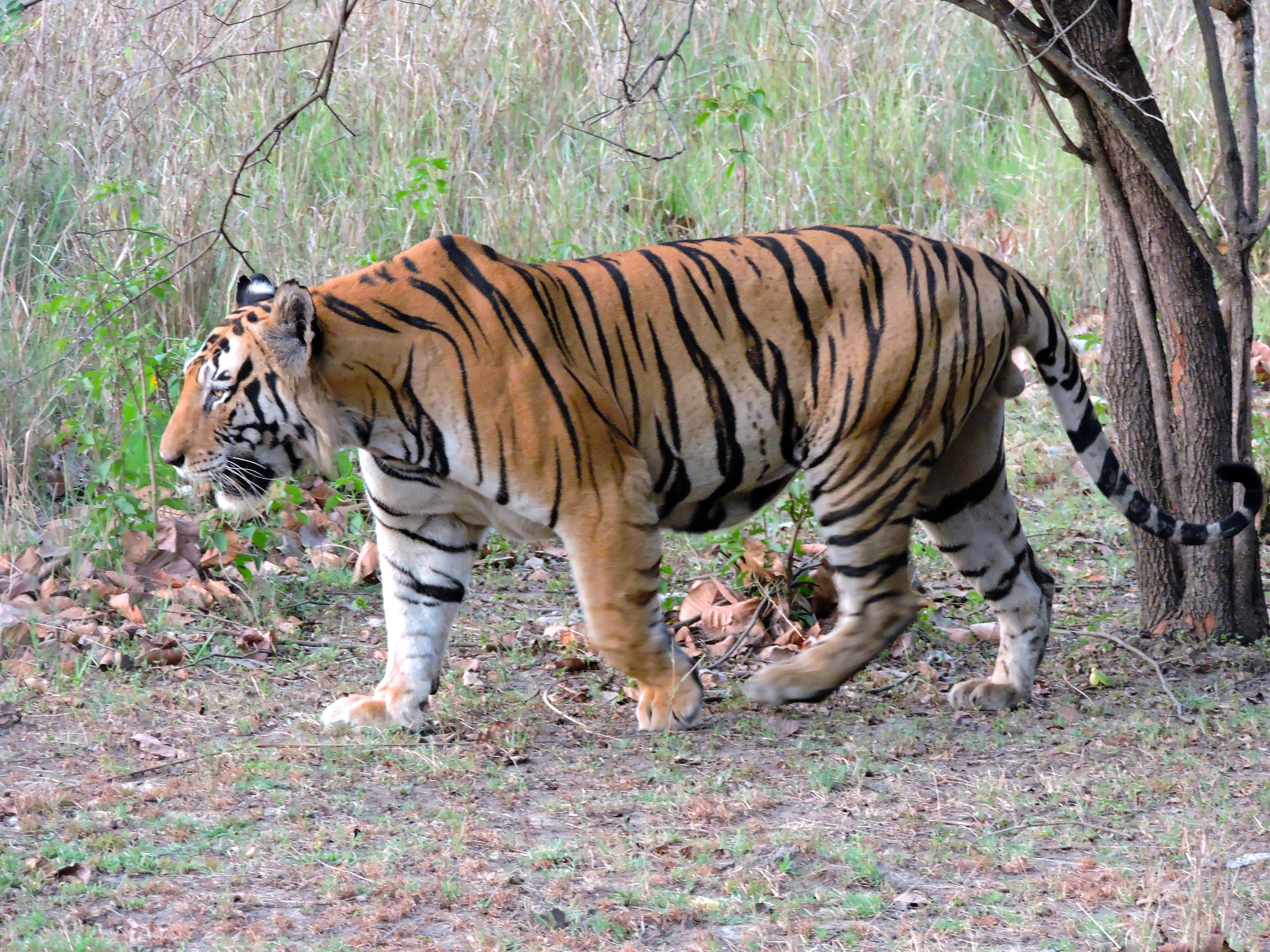
Tiger Bush HAPEX-Sahel
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is a large Felidae, cat and a member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Asia. It has a powerful, muscular body with a large head and paws, a long tail and orange fur with black, mostly vertical stripes. It is traditionally classified into nine Holocene, recent subspecies, though some recognise only two subspecies, mainland Asian tigers and the island tigers of the Sunda Islands. Throughout the tiger's range, it inhabits mainly forests, from coniferous and temperate broadleaf and mixed forests in the Russian Far East and Northeast China to tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests on the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. The tiger is an apex predator and preys mainly on ungulates, which it takes by ambush. It lives a mostly solitary life and occupies home ranges, defending these from individuals of the same sex. The range of a male tiger overlaps with that of multiple females with whom he mates. Females give birth to usually two or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Patterns
The Turing pattern is a concept introduced by English mathematician Alan Turing in a 1952 paper titled "The Chemical Basis of Morphogenesis" which describes how patterns in nature, such as stripes and spots, can arise naturally and autonomously from a homogeneous, uniform state. The pattern arises due to Turing instability which in turn arises due to the interplay between differential diffusion of chemical species and chemical reaction. The instability mechanism is surprising because a pure diffusion, such as molecular diffusion, would be expected to have a stabilizing influence on the system (i.e., complete mixing). Overview In his paper, Turing examined the behaviour of a system in which two diffusible substances interact with each other, and found that such a system is able to generate a spatially periodic pattern even from a random or almost uniform initial condition. Prior to the discovery of this instability mechanism arising due to unequal diffusion coefficients of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patterns In Nature
Patterns in nature are visible regularities of form found in the natural world. These patterns recur in different contexts and can sometimes be modelled mathematically. Natural patterns include symmetries, trees, spirals, meanders, waves, foams, tessellations, cracks and stripes. Early Greek philosophers studied pattern, with Plato, Pythagoras and Empedocles attempting to explain order in nature. The modern understanding of visible patterns developed gradually over time. In the 19th century, the Belgian physicist Joseph Plateau examined soap films, leading him to formulate the concept of a minimal surface. The German biologist and artist Ernst Haeckel painted hundreds of marine organisms to emphasise their symmetry. Scottish biologist D'Arcy Thompson pioneered the study of growth patterns in both plants and animals, showing that simple equations could explain spiral growth. In the 20th century, the British mathematician Alan Turing predicted mechanisms of morp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Formation
The science of pattern formation deals with the visible, (statistically) orderly outcomes of self-organization and the common principles behind similar patterns in nature. In developmental biology, pattern formation refers to the generation of complex organizations of cell fate determination, cell fates in space and time. The role of genes in pattern formation is an aspect of morphogenesis, the creation of diverse anatomy, anatomies from similar genes, now being explored in the science of evolutionary developmental biology or evo-devo. The mechanisms involved are well seen in the anterior-posterior patterning of embryos from the model organism ''Drosophila melanogaster'' (a fruit fly), one of the first organisms to have its morphogenesis studied, and in the eyespot (mimicry), eyespots of butterflies, whose development is a variant of the standard (fruit fly) mechanism. Patterns in nature Examples of pattern formation can be found in biology, physics, and science, and can readily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Succession
Ecological succession is the process of how species compositions change in an Community (ecology), ecological community over time. The two main categories of ecological succession are primary succession and secondary succession. Primary succession occurs after the initial Colonisation (biology), colonization of a newly created habitat with no living organisms. Secondary succession occurs after a Disturbance (ecology), disturbance such as fire, habitat destruction, or a natural disaster destroys a pre-existing community. Both consistent patterns and variability are observed in ecological succession. Theories of ecological succession identify different factors that help explain why plant communities change the way they do. Succession was among the first theories advanced in ecology. Ecological succession was first documented in the Indiana Dunes of Northwest Indiana by Henry Chandler Cowles during the late 19th century and remains a main Ecology, ecological topic of study. Over ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disturbance (ecology)
In ecology, a disturbance is a change in environmental conditions that causes a pronounced change in an ecosystem. Disturbances often act quickly and with great effect, to alter the physical structure or arrangement of biotic component, biotic and abiotic elements. A disturbance can also occur over a long period of time and can impact the biodiversity within an ecosystem. Ecological disturbances include fires, flooding, storms, insect outbreaks, trampling, Human impact on the environment, human presence, earthquakes, plant diseases, infestations, volcanic eruptions, impact events, etc. Not only invasive species can have a profound effect on an ecosystem, native species can also cause disturbance by their behavior. Disturbance forces can have profound immediate effects on ecosystems and can, accordingly, greatly alter the Biocoenosis, natural community’s population size or species richness. Because of these and the impacts on populations, disturbance determines the future shifts i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonia Kéfi
Sonia Kéfi is a network scientist and systems ecologist who studies ecosystem dynamics and the resilience of ecosystems to climate change and human land use. She works for the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) in the Institut des Sciences de l’Evolution de Montpellier, associated with the University of Montpellier, and is also affiliated as an external professor with the Santa Fe Institute. Education and career Kéfi earned her Ph.D. in 2008 from Utrecht University Utrecht University (UU; , formerly ''Rijksuniversiteit Utrecht'') is a public university, public research university in Utrecht, Netherlands. Established , it is one of the oldest universities in the Netherlands. In 2023, it had an enrollment of ... in the Netherlands, and then did postdoctoral research as a Humboldt Fellow at Technische Universität Darmstadt in Germany before joining CNRS in 2011. Recognition Kéfi won the 2011 of the Koninklijke Hollandsche Maatschappij der Wetensch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
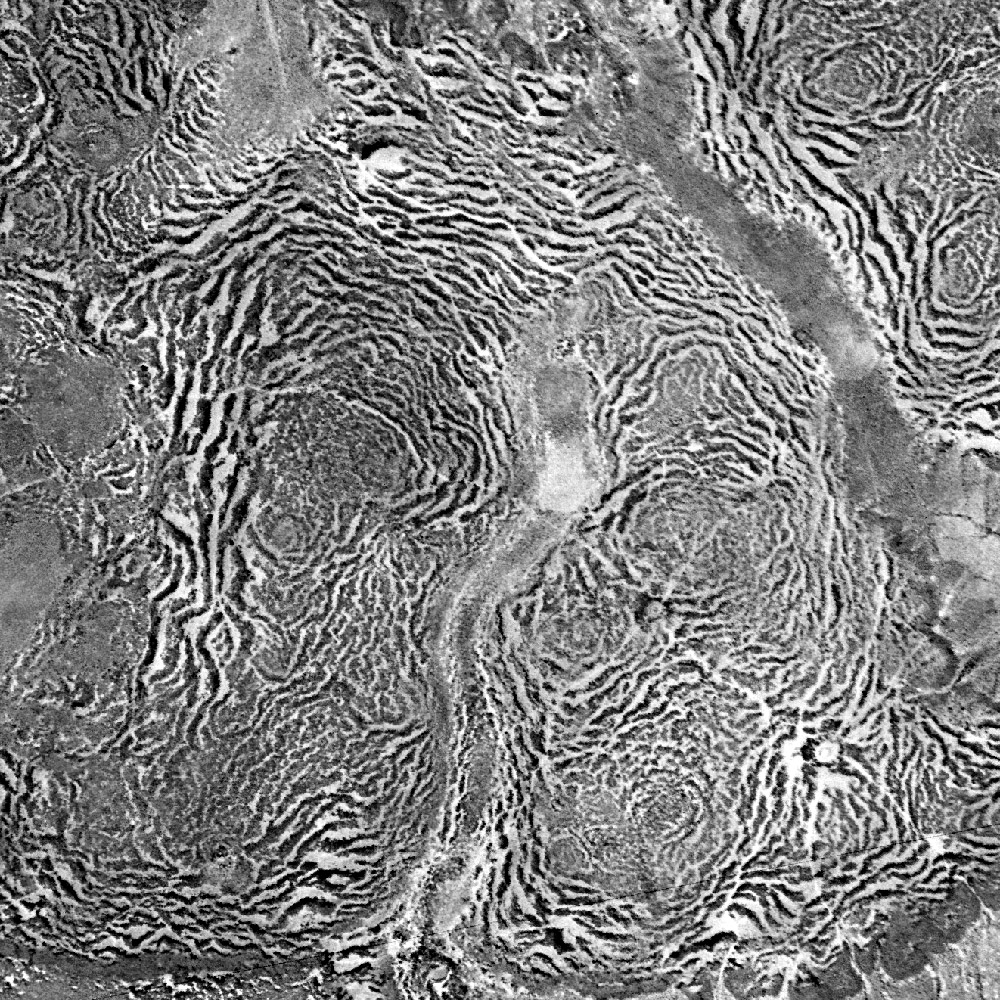
Fir Waves
A fir wave is a set of alternating bands of fir trees in sequential stages of development, observed in forests on exposed mountain slopes in several areas, including northeastern North America and Japan. Fir waves develop by wave-regeneration following wind disturbance, and is one of various types of patterned vegetation. Formation Fir waves form by the ecological process of wave-regeneration. When a tree falls, a gap in the canopy is formed. This exposes trees at the leeward edge of the gap to greater wind. These trees are thus more likely to die from damage and desiccation than windward trees. These leeward trees eventually die, gradually expanding the gap downwind. At the same time, young trees start to grow in the wind shadow in the windward portion of the gap, protected from the high winds by the surviving trees. The combination of dying trees at the leeward edge and regenerating trees at the windward edge results in the propagation of the fir waves in the direction of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Formation
The science of pattern formation deals with the visible, (statistically) orderly outcomes of self-organization and the common principles behind similar patterns in nature. In developmental biology, pattern formation refers to the generation of complex organizations of cell fate determination, cell fates in space and time. The role of genes in pattern formation is an aspect of morphogenesis, the creation of diverse anatomy, anatomies from similar genes, now being explored in the science of evolutionary developmental biology or evo-devo. The mechanisms involved are well seen in the anterior-posterior patterning of embryos from the model organism ''Drosophila melanogaster'' (a fruit fly), one of the first organisms to have its morphogenesis studied, and in the eyespot (mimicry), eyespots of butterflies, whose development is a variant of the standard (fruit fly) mechanism. Patterns in nature Examples of pattern formation can be found in biology, physics, and science, and can readily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-organization
Self-organization, also called spontaneous order in the social sciences, is a process where some form of overall order and disorder, order arises from local interactions between parts of an initially disordered system. The process can be spontaneous when sufficient energy is available, not needing control by any external agent. It is often triggered by seemingly random Statistical fluctuations, fluctuations, amplified by positive feedback. The resulting organization is wholly decentralized, :wikt:distribute, distributed over all the components of the system. As such, the organization is typically Robustness, robust and able to survive or self-healing material, self-repair substantial perturbation theory, perturbation. Chaos theory discusses self-organization in terms of islands of predictability in a sea of chaotic unpredictability. Self-organization occurs in many physics, physical, chemistry, chemical, biology, biological, robotics, robotic, and cognitive systems. Examples of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Runoff
Surface runoff (also known as overland flow or terrestrial runoff) is the unconfined flow of water over the ground surface, in contrast to ''channel runoff'' (or ''stream flow''). It occurs when excess rainwater, stormwater, meltwater, or other sources, can no longer sufficiently rapidly infiltrate in the soil. This can occur when the soil is #Saturation excess overland flow, saturated by water to its full capacity, and the rain arrives #Infiltration excess overland flow, more quickly than the soil can absorb it. Surface runoff often occurs because wikt:impervious#Adjective, impervious areas (such as roofs and Road surface, pavement) do not allow water to soak into the ground. Furthermore, runoff can occur either through natural or human-made processes. Surface runoff is a major component of the water cycle. It is the primary agent of Soil erosion#Rainfall and runoff, soil erosion by water. The land area producing runoff that drains to a common point is called a drainage basin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |