|
Pashto Dialects
Pashto dialects ( də Pəx̌tó žәbgóṭi) can be divided into two large varieties: Northern Pashto and Southern Pashto. Each of the two varieties of Pashto is further divided into a number of dialects. Northern Pashto is spoken in eastern Afghanistan, and central, northern and eastern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (including Peshawar). Southern Pashto is spoken to the south of it, in southern and western Afghanistan (including Kandahar), southern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and northern Balochistan (including Quetta). 'Ethnologue' divides Pashto into Northern, Southern and Central Pashto, and Wanetsi. Overview According to David Neil MacKenzie, a consonant shift took place in the northern parts of Pashtunistan in several phases in the medieval era. During the shift, the retroflex fricative ''ṣ̌'' changed to ''x̌'' or to ''x'' , while ''ẓ̌'' changed to ''ǵ'' or to ''g'' . That is supported by the linguist Georg Morgenstierne's assertion that the Pashto script developed in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
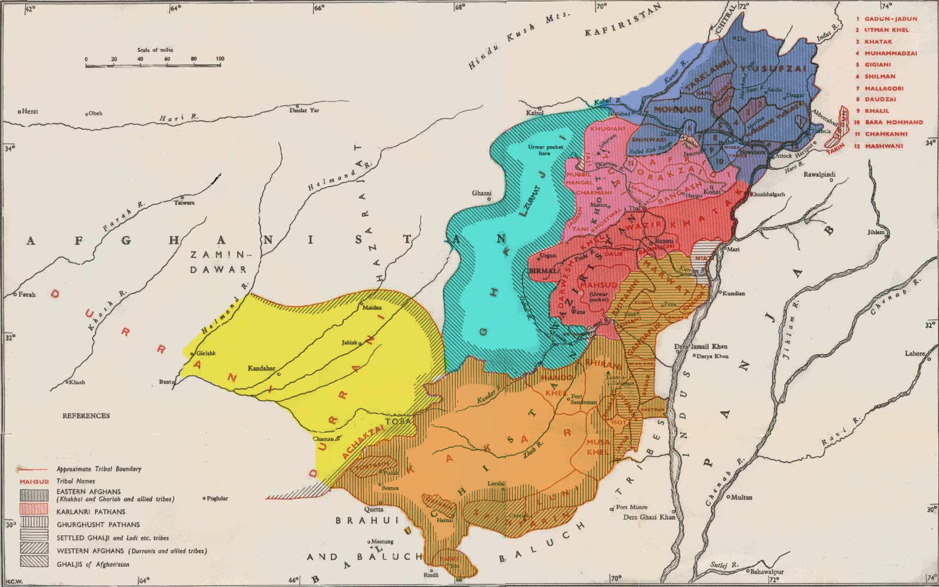
Pashto Dialect Map
Pashto ( , ; , ) is an eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family, natively spoken in northwestern Pakistan and southern and eastern Afghanistan. It has official status in Afghanistan and the Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani (). Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official languages of Afghanistan alongside Dari,Constitution of Afghanistan �''Chapter 1 The State, Article 16 (Languages) and Article 20 (Anthem)''/ref> and it is the second-largest provincial language of Pakistan, spoken mainly in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and the northern districts of Balochistan. Likewise, it is the primary language of the Pashtun diaspora around the world. The total number of Pashto-speakers is at least 40 million, (40 million) although some estimates place it as high as 60 million. Pashto is "one of the primary markers of ethnic identity" amongst Pashtuns. Geographic distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashto
Pashto ( , ; , ) is an eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family, natively spoken in northwestern Pakistan and southern and eastern Afghanistan. It has official status in Afghanistan and the Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani (). Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official languages of Afghanistan alongside Dari, Constitution of Afghanistan �''Chapter 1 The State, Article 16 (Languages) and Article 20 (Anthem)''/ref> and it is the second-largest provincial language of Pakistan, spoken mainly in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and the northern districts of Balochistan. Likewise, it is the primary language of the Pashtun diaspora around the world. The total number of Pashto-speakers is at least 40 million, (40 million) although some estimates place it as high as 60 million. Pashto is "one of the primary markers of ethnic identity" amongst Pashtuns. Geograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waziristan
Waziristan (Persian language, Persian, Pashto, Ormuri, , ) is a mountainous region of the Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. The Waziristan region administratively splits among three districts: North Waziristan, Lower South Waziristan District, and Upper South Waziristan District. Waziristan region, consisted of three districts, covers around and is mainly populated by the Burki, Wazir (Pashtun tribe), Mehsud, The Wolves, & Wazir Pashtun tribe, who speak the Waziri dialect of the Pashto language. Etymology The name "Waziristan" is associated with the ancestor of the Pashtun tribes, Mahsud, Mehsud (The Wolves), named Wazir. Both tribes descended from him and are predominantly settled in the Waziristan region. Overview and history Waziristan lies between the Tochi River, Kurram River and the Gomal River. It borders the Kurram Agency in the north, Bannu District, Bannu in the northeast, Tank, Pakistan, Tank in the east, Frontier Region Dera Ismail Khan, Dera Ismail Kha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdialect
Subdialect (from Latin , "under", and Ancient Greek , ''diálektos'', "discourse") is a linguistic term designating a dialectological category between the levels of dialect and idiolect. Subdialects are basic subdivisions of a dialect. Subdialects can be divided further, ultimately down to idiolects. Subdialects of one dialect are generally quite close to each other, differing mainly in pronunciation and certain local words. See also * Accent (dialect) * Variety (linguistics) In sociolinguistics, a variety, also known as a lect or an isolect, is a specific form of a language or language cluster. This may include languages, dialects, registers, styles, or other forms of language, as well as a standard variety.Meec ... * Language cluster * Dubrovnik subdialect * Laško subdialect * Lwów subdialect * Supradialect References Literature * Joseph R. Applegate, "Phonological Rules of a Subdialect of English", Word, vol. 17/2 (1961), p. 186-193. * Asta Les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) is an alphabetic system of phonetic notation based primarily on the Latin script. It was devised by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century as a standard written representation for the sounds of speech. The IPA is used by linguists, lexicography, lexicographers, foreign language students and teachers, speech–language pathology, speech–language pathologists, singers, actors, constructed language creators, and translators. The IPA is designed to represent those qualities of speech that are part of lexical item, lexical (and, to a limited extent, prosodic) sounds in oral language: phone (phonetics), phones, Intonation (linguistics), intonation and the separation of syllables. To represent additional qualities of speechsuch as tooth wikt:gnash, gnashing, lisping, and sounds made with a cleft lip and cleft palate, cleft palatean extensions to the International Phonetic Alphabet, extended set of symbols may be used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pashto Alphabet
The Pashto alphabet () is the right-to-left script, right-to-left abjad-based alphabet developed from the Persian alphabet, Perso-Arabic script, used for the Pashto, Pashto language in Pakistan and Afghanistan. It originated in the 16th century through the works of Pir Roshan. Form Pashto is written in the Arabic Naskh (script), Naskh. Pashto uses all 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet, and shares 3 letters (, , and ) with Persian alphabet, Persian in the additional letters. Differences from Persian alphabet Pashto has several letters which do not appear in the Persian alphabet, which are shown in the table below: All the additional characters are derived from existing Arabic letters by adding diacritics; for example, the consonants ''x̌īn/ṣ̌īn'' and ''ǵe/ẓ̌e'' look like Arabic's ''sīn'' and ''re'' respectively with a dot above and beneath. Similarly, the letters representing retroflex consonants are written with a small circle (known as a "panḍak", "ğaṛw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tani District
Tani District (, شيتک تني) is situated in the southern part of Khost Province, Afghanistan. Where most of Shitakzai Taniwal or Tani live. It borders Spera District to the west, Nadir Shah Kot and Mando Zayi to the north, Gurbuz District to the east and Pakistan Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ... to the south. The population is 52,800 (2006) people. The district center is the village of Tani, situated in the northeastern part of the district. Taniwal or Tani tribe of Shitak or Shitakzai is settled here. Shitak (Tani) is the Brother Tribe of Shitakzai (Bannuchi now live in Bannu & Dawar or Dour of Tochi Valley Waziristan) The language spoken in Taniwal or Tani District is Pashto language close relation with Dawari or Baniswola Pashto. External links AI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bannu District
Bannu District (, ) is a district in the Bannu Division of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. Its status as a district was formally recorded in 1861 during the British Raj. This district constitutes one of the 26 districts that collectively form the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province. It borders North Waziristan to the northwest, Karak to the northeast, Lakki Marwat and Bettani to the southeast, and South Waziristan to the southwest. It is represented in the provincial assembly by four MPAs. Cloth weaving, sugar mills and the manufacturing of cotton fabrics, machinery and equipment are the major industries in Bannu. It is also known for its weekly ''Jumma'' fair. The district forms a basin drained by the Kurram and Gambila (or Tochi) rivers, which originate in the hills of Waziristan. Although Bannu is surrounded by rugged and dry mountains, it is a fertile place, and early English visitors had been known to refer to it as a "paradise" – see the description by Edwarde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karlani
Karlāṇī or Karrani () is a Pashtun tribal confederacy. They primarily inhabit the FATA region of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan and certain parts of eastern Afghanistan. In the 16th century the Karlani founded the Karrani dynasty, the last dynasty to rule the Bengal Sultanate. . Origins Karlani itself means "adopted". The 17th century Mughal scribe Nimat Allah al-Harawi does not mention Karlani tribes in his '' Makhzan-i-Afghani''. According to a legend, Karlan was the adopted son of Qais Abdur Rasheed, the eponymous ancestor of Pashtuns. In another variant of the tradition, Karlan was adopted in exchange of a cooking pot, and was found by two Ormur brothers in an empty field where an army had encamped previous night. The childless brother then exchanged baby for a pot. This suggests that Karlanis are adopted tribes of non-Pashtun origins unlike the rest of the tribes. The exact genesis of Karlani Pashtuns remains disputed, with Karlani tribes like Afridis and Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiced Retroflex Sibilant
The voiced retroflex sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some Speech communication, spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is z`. Like all the retroflex consonants, the IPA symbol is formed by adding a rightward-pointing hook extending from the bottom of a ''z'' (the letter used for the corresponding alveolar consonant). Features Features of the voiced retroflex sibilant: Occurrence In the following transcriptions, diacritics may be used to distinguish between apical consonant, apical and laminal consonant, laminal . The commonality of cross-linguistically is 2% in a phonological analysis of 2155 languages.Phoible.org. (2018). PHOIBLE Online – Segments. [online] Available at: http://phoible.org/parameters. Voiced retroflex non-sibilant fricative Features Features of the voiced retroflex non-sibilant fricative: Occurrence Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Retroflex Sibilant
The voiceless retroflex sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is which is a Latin letter s combined with a retroflex hook. Like all the retroflex consonants, the IPA letter is formed by adding a rightward-pointing hook to the bottom of (the letter used for the corresponding alveolar consonant). A distinction can be made between laminal, apical, and sub-apical articulations. Only one language, Toda, appears to have more than one voiceless retroflex sibilant, and it distinguishes subapical palatal from apical postalveolar retroflex sibilants; that is, both the tongue articulation and the place of contact on the roof of the mouth are different. Some scholars also posit the voiceless retroflex approximant distinct from the fricative. The approximant may be represented in the IPA as . Features Features of the voiceless retroflex fricative: Occurrence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakhi Language
Wakhi (, , IPA: ikwɔr zik is an Indo-European language in the Eastern Iranian branch of the language family spoken today in Wakhan District, Northern Afghanistan, and neighboring areas of Tajikistan, Pakistan and China. Classification and distribution Wakhi is one of several languages that belong to the areal Pamir language group. It is believed to be a descendant of the Scytho-Khotanese language once spoken in the Kingdom of Khotan. The Wakhi people are occasionally called Pamiris and Guhjali. It is spoken by the inhabitants of the Wakhan Corridor of Afghanistan, parts of Gilgit-Baltistan (the former NAs) of Pakistan, the Gorno-Badakhshan region of Tajikistan, and Xinjiang in Western China. The Wakhi use the self-appellation 'X̌ik' (ethnic) and suffix it with 'wor'/'war' to denote their language as 'X̌ik-wor' themselves. The noun 'X̌ik' comes from ''*waxša-ī̆ka-'' (an inhabitant of ''*Waxša-'' 'Oxus', for Wakhan, in Wakhi 'Wux̌.' There are other equivalents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |