|
Pascal's Identity
In mathematics, Pascal's rule (or Pascal's formula) is a combinatorics, combinatorial identity (mathematics), identity about binomial coefficients. The binomial coefficients are the numbers that appear in Pascal's triangle. Pascal's rule states that for natural number, positive integers ''n'' and ''k'', + = , where \tbinom is the binomial coefficient, namely the coefficient of the term in the polynomial expansion, expansion of . There is no restriction on the relative sizes of and ; in particular, the above identity remains valid when since \tbinom = 0 whenever . Together with the boundary conditions \tbinom = \tbinom= 1 for all nonnegative integers ''n'', Pascal's rule determines that \binom = \frac, for all integers . In this sense, Pascal's rule is the recurrence relation that defines the binomial coefficients. Pascal's rule can also be generalized to apply to multinomial coefficients. Combinatorial proof Blaise Pascal, Pascal's rule has an intuitive combinatorial me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal's Rule 4c1 Plus 4c2 Equals 5c2
Pascal, Pascal's or PASCAL may refer to: People and fictional characters * Pascal (given name), including a list of people with the name * Pascal (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters with the name ** Blaise Pascal, French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, writer and theologian Places * Pascal (crater), a lunar crater * Pascal Island (Antarctica) * Pascal Island (Western Australia) Science and technology * Pascal (unit), the SI unit of pressure * Pascal (programming language), a programming language developed by Niklaus Wirth **Microsoft Pascal **Turbo Pascal * PASCAL (database), a bibliographic database maintained by the Institute of Scientific and Technical Information * Pascal (microarchitecture), codename for a microarchitecture developed by Nvidia Other uses * (1895–1911) * (1931–1942) * Pascal and Maximus, fictional characters in ''Tangled'' * Pascal blanc, a French white wine grape * Pascal College, secondary education schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinatorics
Combinatorics is an area of mathematics primarily concerned with counting, both as a means and as an end to obtaining results, and certain properties of finite structures. It is closely related to many other areas of mathematics and has many applications ranging from logic to statistical physics and from evolutionary biology to computer science. Combinatorics is well known for the breadth of the problems it tackles. Combinatorial problems arise in many areas of pure mathematics, notably in algebra, probability theory, topology, and geometry, as well as in its many application areas. Many combinatorial questions have historically been considered in isolation, giving an ''ad hoc'' solution to a problem arising in some mathematical context. In the later twentieth century, however, powerful and general theoretical methods were developed, making combinatorics into an independent branch of mathematics in its own right. One of the oldest and most accessible parts of combinatorics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hockey-stick Identity
In combinatorics, the hockey-stick identity, Christmas stocking identity, boomerang identity, Fermat's identity or Chu's Theorem, states that if n \geq r \ge 0 are integers, then : \binom + \binom + \binom + \cdots + \binom = \binom. The name stems from the graphical representation of the identity on Pascal's triangle: when the addends represented in the summation and the sum itself are highlighted, the shape revealed is vaguely reminiscent of those objects (see hockey stick, Christmas stocking). Formulations Using sigma notation, the identity states : \sum^n_= \qquad \text n,r\in\mathbb, \quad n\geq r or equivalently, the mirror-image by the substitution j\to i-r, and by using the identify =: : \sum^_=\sum^_= \qquad \text n,r\in\mathbb, \quad n\geq r. Proofs Inductive and algebraic proofs The inductive and algebraic proofs both make use of Pascal's identity: :=+. Inductive proof This identity can be proven by mathematical induction on n. Base case Let n=r; :\sum^n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative integers. The set (mathematics), set of all integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the set of natural numbers, the set of integers \mathbb is Countable set, countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fraction, fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , 5/4, and Square root of 2, are not. The integers form the smallest Group (mathematics), group and the smallest ring (mathematics), ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set (mathematics)
In mathematics, a set is a collection of different things; the things are '' elements'' or ''members'' of the set and are typically mathematical objects: numbers, symbols, points in space, lines, other geometric shapes, variables, or other sets. A set may be finite or infinite. There is a unique set with no elements, called the empty set; a set with a single element is a singleton. Sets are ubiquitous in modern mathematics. Indeed, set theory, more specifically Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, has been the standard way to provide rigorous foundations for all branches of mathematics since the first half of the 20th century. Context Before the end of the 19th century, sets were not studied specifically, and were not clearly distinguished from sequences. Most mathematicians considered infinity as potentialmeaning that it is the result of an endless processand were reluctant to consider infinite sets, that is sets whose number of members is not a natural number. Specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subset
In mathematics, a Set (mathematics), set ''A'' is a subset of a set ''B'' if all Element (mathematics), elements of ''A'' are also elements of ''B''; ''B'' is then a superset of ''A''. It is possible for ''A'' and ''B'' to be equal; if they are unequal, then ''A'' is a proper subset of ''B''. The relationship of one set being a subset of another is called inclusion (or sometimes containment). ''A'' is a subset of ''B'' may also be expressed as ''B'' includes (or contains) ''A'' or ''A'' is included (or contained) in ''B''. A ''k''-subset is a subset with ''k'' elements. When quantified, A \subseteq B is represented as \forall x \left(x \in A \Rightarrow x \in B\right). One can prove the statement A \subseteq B by applying a proof technique known as the element argument:Let sets ''A'' and ''B'' be given. To prove that A \subseteq B, # suppose that ''a'' is a particular but arbitrarily chosen element of A # show that ''a'' is an element of ''B''. The validity of this technique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal (19June 162319August 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic Church, Catholic writer. Pascal was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. His earliest mathematical work was on projective geometry; he wrote a significant treatise on the subject of conic sections at the age of 16. He later corresponded with Pierre de Fermat on probability theory, strongly influencing the development of modern economics and social sciences, social science. In 1642, he started some pioneering work on calculating machines (called Pascal's calculators and later Pascalines), establishing him as one of the first two inventors of the mechanical calculator. Like his contemporary René Descartes, Pascal was also a pioneer in the natural and applied sciences. Pascal wrote in defense of the scientific method and produced several controversial results. He made important contributions to the study of fluids, and clari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multinomial Coefficient
In mathematics, the multinomial theorem describes how to expand a power of a sum in terms of powers of the terms in that sum. It is the generalization of the binomial theorem from binomials to multinomials. Theorem For any positive integer and any non-negative integer , the multinomial theorem describes how a sum with terms expands when raised to the th power: (x_1 + x_2 + \cdots + x_m)^n = \sum_ x_1^ \cdot x_2^ \cdots x_m^ where = \frac is a multinomial coefficient. The sum is taken over all combinations of nonnegative integer indices through such that the sum of all is . That is, for each term in the expansion, the exponents of the must add up to . In the case , this statement reduces to that of the binomial theorem. Example The third power of the trinomial is given by (a+b+c)^3 = a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + 3 a^2 b + 3 a^2 c + 3 b^2 a + 3 b^2 c + 3 c^2 a + 3 c^2 b + 6 a b c. This can be computed by hand using the distributive property of multiplication over additi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinatorics
Combinatorics is an area of mathematics primarily concerned with counting, both as a means and as an end to obtaining results, and certain properties of finite structures. It is closely related to many other areas of mathematics and has many applications ranging from logic to statistical physics and from evolutionary biology to computer science. Combinatorics is well known for the breadth of the problems it tackles. Combinatorial problems arise in many areas of pure mathematics, notably in algebra, probability theory, topology, and geometry, as well as in its many application areas. Many combinatorial questions have historically been considered in isolation, giving an ''ad hoc'' solution to a problem arising in some mathematical context. In the later twentieth century, however, powerful and general theoretical methods were developed, making combinatorics into an independent branch of mathematics in its own right. One of the oldest and most accessible parts of combinatorics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recurrence Relation
In mathematics, a recurrence relation is an equation according to which the nth term of a sequence of numbers is equal to some combination of the previous terms. Often, only k previous terms of the sequence appear in the equation, for a parameter k that is independent of n; this number k is called the ''order'' of the relation. If the values of the first k numbers in the sequence have been given, the rest of the sequence can be calculated by repeatedly applying the equation. In ''linear recurrences'', the th term is equated to a linear function of the k previous terms. A famous example is the recurrence for the Fibonacci numbers, F_n=F_+F_ where the order k is two and the linear function merely adds the two previous terms. This example is a linear recurrence with constant coefficients, because the coefficients of the linear function (1 and 1) are constants that do not depend on n. For these recurrences, one can express the general term of the sequence as a closed-form expression o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
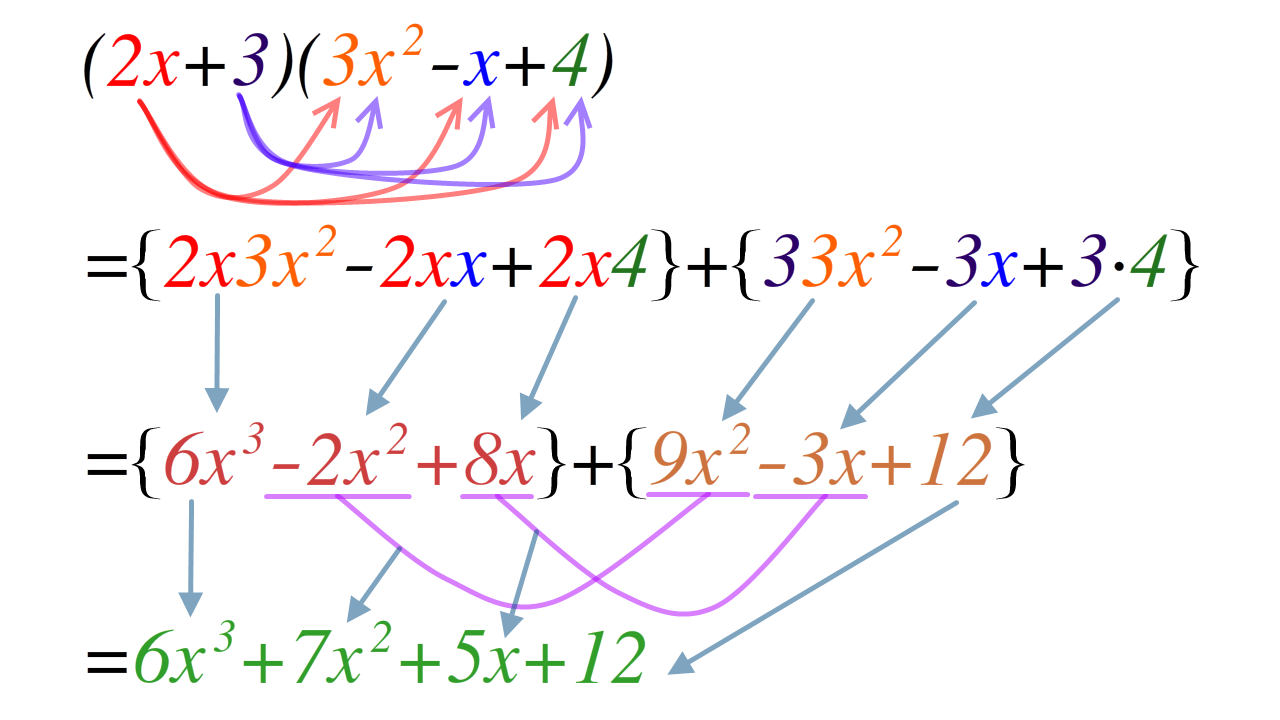
Polynomial Expansion
In mathematics, an expansion of a product of sums expresses it as a sum of products by using the fact that multiplication distributes over addition. Expansion of a polynomial expression can be obtained by repeatedly replacing subexpressions that multiply two other subexpressions, at least one of which is an addition, by the equivalent sum of products, continuing until the expression becomes a sum of (repeated) products. During the expansion, simplifications such as grouping of like terms or cancellations of terms may also be applied. Instead of multiplications, the expansion steps could also involve replacing powers of a sum of terms by the equivalent expression obtained from the binomial formula; this is a shortened form of what would happen if the power were treated as a repeated multiplication, and expanded repeatedly. It is customary to reintroduce powers in the final result when terms involve products of identical symbols. Simple examples of polynomial expansions are the wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |