|
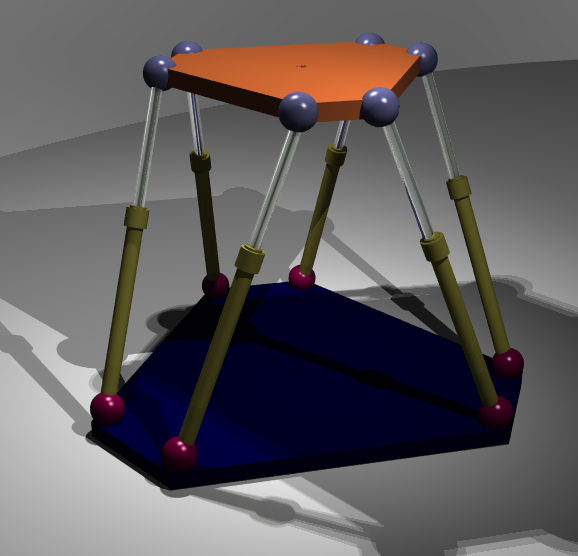
Parallel Manipulator
A parallel manipulator is a mechanical system that uses several computer-controlled serial chains to support a single platform, or end-effector. Perhaps, the best known parallel manipulator is formed from six linear actuators that support a movable base for devices such as flight simulators. This device is called a Stewart platform or the Gough-Stewart platform in recognition of the engineers who first designed and used them. Also known as parallel robots, or generalized Stewart platforms (in the Stewart platform, the actuators are paired together on both the basis and the platform), these systems are articulated robots that use similar mechanisms for the movement of either the robot on its base, or one or more manipulator arms. Their 'parallel' distinction, as opposed to a serial manipulator, is that the end effector (or 'hand') of this linkage (or 'arm') is directly connected to its base by a number of (usually three or six) separate and independent linkages working simu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexapod0a
Hexapod may refer to: Things with six limbs, e.g. a hexapod chair would have six not the traditional four limbs Biology * Hexapoda, a subphylum of arthropods including the insects * Hexapodidae, a family of crabs Technology * Hexapod (robotics), a mechanical vehicle that walks on six legs * Stewart platform, a machine platform supported by six struts, used in robotics * Hexapod-Telescope, a telescope in Chile mounted on a Stewart platform chassis frame See also * Tetrapod * Octopod {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pin-jointed Truss
A truss is an assembly of ''members'' such as beams, connected by ''nodes'', that creates a rigid structure. In engineering, a truss is a structure that "consists of two-force members only, where the members are organized so that the assemblage as a whole behaves as a single object". A ''two-force member'' is a structural component where force is applied to only two points. Although this rigorous definition allows the members to have any shape connected in any stable configuration, architectural trusses typically comprise five or more triangular units constructed with straight members whose ends are connected at joints referred to as '' nodes''. In this typical context, external forces and reactions to those forces are considered to act only at the nodes and result in forces in the members that are either tensile or compressive. For straight members, moments (torques) are explicitly excluded because, and only because, all the joints in a truss are treated as revolutes, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists since most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, including particle therapy for oncology, oncological purposes, Isotopes in medicine, radioisotope production for medical diagnostics, Ion implantation, ion implanters for the manufacturing of Semiconductor, semiconductors, and Accelerator mass spectrometry, accelerator mass spectrometers for measurements of rare isotopes such as radiocarbon. Large accelerators include the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York, and the largest accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider near Geneva, Switzerland, operated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Lens
thumb thumb A subtype of a magnetic lens ( quadrupole magnet) in the Maier-Leibnitz laboratory, Munich A magnetic lens is a device for the focusing or deflection of moving charged particles, such as electrons or ions, by use of the magnetic Lorentz force. Its strength can often be varied by usage of electromagnets. Magnetic lenses are used in diverse applications, from cathode ray tubes over electron microscopy to particle accelerators. Design A magnetic lens typically consists of several electromagnets arranged in a quadrupole (see quadrupole magnet), sextupole, or higher format; the electromagnetic coils are placed at the vertices of a square or another regular polygon. From this configuration a customized magnetic field can be formed to manipulate the particle beam. The passing particle is subjected to two vector forces H_Z (parallel to the core), and H_R (parallel to the radius of the lens). H_R causes the particle to spiral through the lens, and this spiraling expose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatic Lens
An electrostatic lens is a device that assists in the transport of charged particles. For instance, it can guide electrons emitted from a sample to an electron analyzer, analogous to the way an optical lens assists in the transport of light in an optical instrument. Systems of electrostatic lenses can be designed in the same way as optical lenses, so electrostatic lenses easily magnify or converge the electron trajectories. An electrostatic lens can also be used to focus an ion beam, for example to make a microbeam for irradiating individual cells. Cylinder lens A cylinder lens consists of several cylinders whose sides are thin walls. Each cylinder lines up parallel to the optical axis into which electrons enter. There are small gaps put between the cylinders. When each cylinder has a different voltage, the gap between the cylinders works as a lens. The magnification is able to be changed by choosing different voltage combinations. Although the magnification of two cylinder lense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight Simulator
A flight simulator is a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and the environment in which it flies, for pilot training, design, or other purposes. It includes replicating the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they react to applications of flight controls, the effects of other aircraft systems, and how the aircraft reacts to external factors such as air density, turbulence, wind shear, cloud, precipitation, etc. Flight simulation is used for a variety of reasons, including flight training (mainly of pilots), the design and development of the aircraft itself, and research into aircraft characteristics and control handling qualities. The term "flight simulator" may carry slightly different meaning in general language and technical documents. In past regulations, it referred specifically to devices which can closely mimic the behavior of aircraft throughout various procedures and flight conditions. In more recent definitions, this has been named "full fli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinematic Chain
In mechanical engineering, a kinematic chain is an assembly of rigid bodies connected by joints to provide constrained motion that is the mathematical model for a mechanical system. Reuleaux, F., 187''The Kinematics of Machinery,''(trans. and annotated by A. B. W. Kennedy), reprinted by Dover, New York (1963) As the word chain suggests, the rigid bodies, or links, are constrained by their connections to other links. An example is the simple open chain formed by links connected in series, like the usual chain, which is the kinematic model for a typical robot manipulator.J. M. McCarthy and G. S. Soh, 2010''Geometric Design of Linkages,''Springer, New York. Mathematical models of the connections, or joints, between two links are termed kinematic pairs. Kinematic pairs model the hinged and sliding joints fundamental to robotics, often called ''lower pairs'' and the surface contact joints critical to cams and gearing, called ''higher pairs.'' These joints are generally modele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of the moment often form a loop or hysteresis curve, where there are different values of one variable depending on the direction of change of another variable. This history dependence is the basis of memory in a hard disk drive and the remanence that retains a record of the Earth's magnetic field magnitude in the past. Hysteresis occurs in ferromagnetic and ferroelectricity, ferroelectric materials, as well as in the deformation (mechanics), deformation of rubber bands and shape-memory alloys and many other natural phenomena. In natural systems, it is often associated with irreversible process, irreversible thermodynamic change such as phase transitions and with internal friction; and dissipation is a common side effect. Hysteresis can be fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexapod Positioner Aka Stewart Platform X2
{{disambiguation ...
Hexapod may refer to: Things with six limbs, e.g. a hexapod chair would have six not the traditional four limbs Biology * Hexapoda, a subphylum of arthropods including the insects * Hexapodidae, a family of crabs Technology * Hexapod (robotics), a mechanical vehicle that walks on six legs * Stewart platform, a machine platform supported by six struts, used in robotics * Hexapod-Telescope, a telescope in Chile mounted on a Stewart platform chassis frame See also * Tetrapod * Octopod An octopus (: octopuses or octopodes) is a soft-bodied, eight-limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, and nautiloids. Like other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |