|
Pandanus Amaryllifolius
''Pandanus'' is a genus of monocots with about 578 accepted species. They are palm-like, dioecious trees and shrubs native to the Old World tropics and subtropics. Common names include pandan, screw palm and screw pine. The genus is classified in the order Pandanales, family Pandanaceae, and is the largest in the family. Description The species vary in size from small shrubs less than tall, to medium-sized trees tall, typically with a broad canopy, heavy fruit, and moderate growth rate. The trunk is stout, wide-branching, and ringed with many leaf scars. Mature plants can have branches. Depending on the species, the trunk can be smooth, rough, or warty. The roots form a pyramidal tract to hold the trunk. They commonly have many thick stilt roots near the base, which provide support as the tree grows top-heavy with leaves, fruit, and branches. These roots are adventitious and often branched. The top of the plant has one or more crowns of strap-shaped leaves that may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
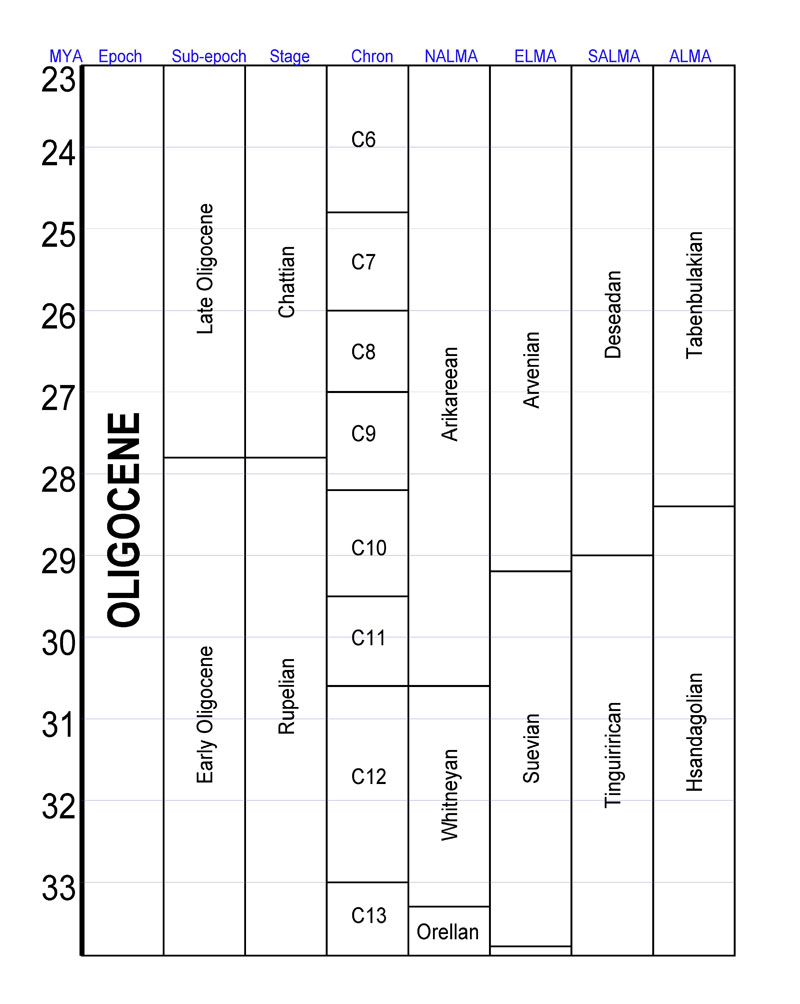
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Miocene Climatic Optimum
The Middle Miocene Climatic Optimum (MMCO), sometimes referred to as the Middle Miocene Thermal Maximum (MMTM), was an interval of warm climate during the Miocene epoch, specifically the Burdigalian and Langhian stages. Duration Based on the magnetic susceptibility of Miocene sedimentary stratigraphic sequences in the Huatugou section in the Qaidam Basin, the MMCO lasted from 17.5 to 14.5 Ma; rocks deposited during this interval have a high magnetic susceptibility due to the production of superparamagnetic and single domain magnetite amidst the warm and humid conditions at the time that defines the MMCO. Estimates derived from Mg/Ca palaeothermometry in the benthic foraminifer ''Oridorsalis umbonatus'' suggest the onset of the MMCO occurred at 16.9 Ma, peak warmth at 15.3 Ma, and the end of the MMCO at 13.8 Ma. Climate Global mean surface temperatures during the MMCO were approximately 18.4 °C, about 3 °C warmer than today and 4 °C warmer than preindustri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicified
In geology, silicification is a process in which silica-rich fluids seep into the voids of Earth materials, e.g., rocks, wood, bones, shells, and replace the original materials with silica (SiO2). Silica is a naturally existing and abundant compound found in organic and inorganic materials, including Earth's crust and mantle. There are a variety of silicification mechanisms. In silicification of wood, silica permeates into and occupies cracks and voids in wood such as vessels and cell walls. The original organic matter is retained throughout the process and will gradually decay through time. In the silicification of carbonates, silica replaces carbonates by the same volume. Replacement is accomplished through the dissolution of original rock minerals and the precipitation of silica. This leads to a removal of original materials out of the system. Depending on the structures and composition of the original rock, silica might replace only specific mineral components of the rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Fruit
Multiple fruits, also called collective fruits, are fruiting bodies formed from a cluster of flowers, the ''inflorescence''. Each flower in the inflorescence produces a fruit, but these mature into a single mass. After flowering, the mass is called an infructescence. Examples are the ficus, fig, pineapple, mulberry, osage orange, and jackfruit. In contrast, an aggregate fruit such as a raspberry develops from multiple ovary (botany), ovaries of a single flower. In languages other than English, the meanings of "multiple" and "aggregate" fruit are reversed, so that multiple fruits merge several pistils within a single flower. In some cases, the infructescences are similar in appearance to simple fruits. One example is pineapple (''Ananas''), which is formed from the Adnation, fusion of the berry (botany), berries with Receptacle (botany), receptacle tissues and bracts. As shown in the photograph of the noni, stages of flowering and fruit development in the noni or Indian mulberr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drupe
In botany, a drupe (or stone fruit) is a type of fruit in which an outer fleshy part (exocarp, or skin, and mesocarp, or flesh) surrounds a single shell (the ''pip'' (UK), ''pit'' (US), ''stone'', or ''pyrena'') of hardened endocarp with a seed (''kernel'') inside. Drupes do not split open to release the seed, i.e., they are dehiscence (botany), indehiscent. These fruits usually develop from a single carpel, and mostly from flowers with Superior ovary, superior ovaries (polypyrenous drupes are exceptions). The definitive characteristic of a drupe is that the hard, woody (lignified) stone is derived from the Ovary (botany), ovary wall of the flower. In an aggregate fruit, which is composed of small, individual drupes (such as a raspberry), each individual is termed a drupelet, and may together form an aggregate fruit. Such fruits are often termed ''berries'', although botanists use a Berry (botany), different definition of ''berry''. Other fleshy fruits may have a stony enclosur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adventitiousness
Important structures in plant development are buds, shoots, roots, leaves, and flowers; plants produce these tissues and structures throughout their life from meristems located at the tips of organs, or between mature tissues. Thus, a living plant always has embryonic tissues. By contrast, an animal embryo will very early produce all of the body parts that it will ever have in its life. When the animal is born (or hatches from its egg), it has all its body parts and from that point will only grow larger and more mature. However, both plants and animals pass through a phylotypic stage that evolved independently and that causes a developmental constraint limiting morphological diversification. According to plant physiologist A. Carl Leopold, the properties of organization seen in a plant are emergent properties which are more than the sum of the individual parts. "The assembly of these tissues and functions into an integrated multicellular organism yields not only the characterist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandanus Sp
''Pandanus'' is a genus of monocots with about 578 accepted species. They are palm-like, dioecious trees and shrubs native to the Old World tropics and subtropics. Common names include pandan, screw palm and screw pine. The genus is classified in the order Pandanales, family Pandanaceae, and is the largest in the family. Description The species vary in size from small shrubs less than tall, to medium-sized trees tall, typically with a broad canopy, heavy fruit, and moderate growth rate. The trunk is stout, wide-branching, and ringed with many leaf scars. Mature plants can have branches. Depending on the species, the trunk can be smooth, rough, or warty. The roots form a pyramidal tract to hold the trunk. They commonly have many thick stilt roots near the base, which provide support as the tree grows top-heavy with leaves, fruit, and branches. These roots are adventitiousness, adventitious and often branched. The top of the plant has one or more crowns of strap-shaped leav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Science
''Pacific Science'' is a quarterly multidisciplinary peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the biological and physical sciences of the Pacific basin, focusing especially on biogeography, ecology, evolution, geology and volcanology, oceanography, palaeontology, and systematics. It is published by the University of Hawaii Press and was established in 1947. It is the official journal of the Pacific Science Association. The founding editor-in-chief was A. Grove Day. Leonard D. Tuthill served as editor of vols. 2-7 (1948–1953); William A. Gosline edited vols. 8-10 (1954–1956) and vols. 22-25 (1968–1971); and O. A. Bushnell edited vols. 11-21 (1957–1967). The longest-serving editor was E. Alison Kay, who edited vols. 26-54 (1972–2000), stepping down only after she retired. Gerald D. Carr edited vols. 55-58 (2001–2004) and from vol. 59 (2005) was succeeded by Curtis C. Daehler. All editors have been faculty of the University of Hawaii. The journal's first electronic ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Botany
Economic botany is the study of the relationship between people (individuals and cultures) and plants. Economic botany intersects many fields including established disciplines such as agronomy, anthropology, archaeology, chemistry, economics, ethnobotany, ethnology, forestry, genetic resources, geography, geology, horticulture, medicine, microbiology, nutrition, pharmacognosy, and pharmacology. This link between botany and anthropology explores the ways humans use plants for food, medicines, and commerce. History In a 1958 essay at the conference that founded the Society for Economic Botany, David J. Rogers wrote, "A current viewpoint is that economic botany should concern itself with basic botanical, phytochemical and ethnological studies of plants known to be useful or those which may have potential uses so far underdeveloped. Economic botany is, then, a composite of those sciences working specifically with plants of importance to eople" Closely allied with economic botany is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandanaceae
Pandanaceae is a family of flowering plants native to the tropics and subtropics of the Old World, from West Africa to the Pacific. It contains 982 known species in five genera, of which the type genus, ''Pandanus'', is the most important, with species like '' Pandanus amaryllifolius'' and karuka (''Pandanus julianettii'') being important sources of food. The family likely originated during the Late Cretaceous. Characteristics Pandanaceae includes trees, shrubs, lianas, vines, epiphytes, and perennial herbs. Stems may be simple or bifurcately branched, and may have aerial prop roots. The stems bear prominent leaf scars. The leaves are very long and narrow, sheathing, simple, undivided, with parallel veins; the leaf margins and abaxial midribs are often prickly. The plants are dioecious. The inflorescences are terminally borne racemes, spikes or umbels, with subtended spathes, which may be brightly colored. The flowers are minute and lack perianths. Male flowers contain numero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |