|
PSA TU Engine
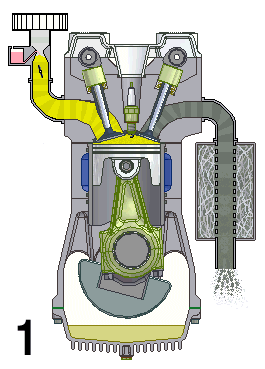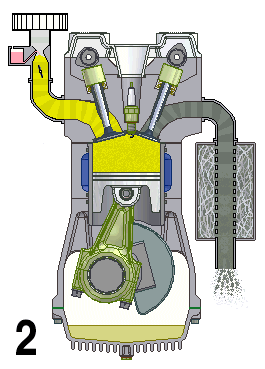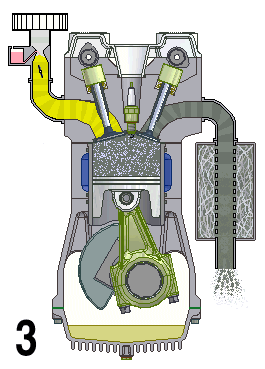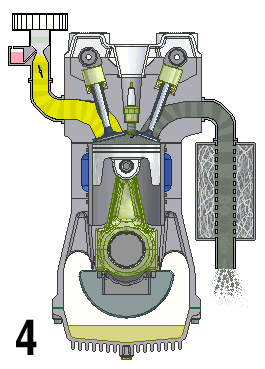
The TU family of small Straight-four engine, inline-four Reciprocating engine, piston engines by PSA Peugeot Citroën were introduced in 1986 and used in the Peugeot and Citroën range of cars. It was first installed in the Citroën AX in October 1986, replacing the PSA X engine, X family, although it shared many components with its predecessor. The TU is available in either petrol or a naturally aspirated Diesel engine, diesel variant, the latter called TUD. The TU engine is distantly related to the older X-Type engine — sharing a similar overhead camshaft architecture, but the key differences are the belt driven camshaft (the X is chain driven), and that the TU is mounted in a conventional upright position with a separate, end-on mounted transmission and unequal length drive shafts. The X engine, by comparison, had an integral transmission mounted on the side of the crankcase (giving rise to its popular nickname the "suitcase engine"), sharing a common oil supply and was moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturally Aspirated
A naturally aspirated engine, also known as a normally aspirated engine, and abbreviated to N/A or NA, is an internal combustion engine in which air intake depends solely on atmospheric pressure and does not have forced induction through a turbocharger or a supercharger. Description In a naturally aspirated engine, air for combustion (Diesel cycle in a diesel engine or specific types of Otto cycle in petrol engines, namely Gasoline direct injection, petrol direct injection) or an air/fuel mixture (traditional Otto cycle petrol engines), is drawn into the engine's cylinder (engine), cylinders by atmospheric pressure acting against a Vacuum, partial vacuum that occurs as the piston travels downwards toward Dead centre (engineering), bottom dead centre during the intake stroke (engine), stroke. Owing to innate restriction in the engine's inlet tract, which includes the Inlet manifold, intake manifold, a small pressure drop occurs as air is drawn in, resulting in a volumetric effici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Bosch GmbH
Robert Bosch GmbH (; ), commonly known as Bosch (styled BOSCH), is a German multinational engineering and technology company headquartered in Gerlingen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The company was founded by Robert Bosch in Stuttgart in 1886. Bosch is 94% owned by the Robert Bosch Stiftung, a charitable institution. Although the charity is funded by owning the vast majority of shares, it has no voting rights and is involved in health and social causes unrelated to Bosch's business. Bosch's core operating areas are spread across four business sectors: mobility (hardware and software), consumer goods (including household appliances and power tools), industrial technology (including drive and control) and energy and building technology. In terms of revenue, Bosch is the largest automotive supplier. History 1886–1920 The company started in a backyard in Stuttgart-West as the (Workshop for Precision Mechanics and Electrical Engineering) on 15 November 1886. The next ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Camshaft
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine in which the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion chamber in the engine block. ''Single overhead camshaft'' (SOHC) engines have one camshaft per cylinder bank, bank of cylinders. ''Dual overhead camshaft'' (DOHC, also known as "twin-cam") engines have two camshafts per bank. The first production car to use a DOHC engine was built in 1910. Use of DOHC engines slowly increased from the 1940s, leading to many automobiles by the early 2000s using DOHC engines. Design In an OHC engine, the camshaft is located at the top of the engine, above the combustion chamber. This contrasts the earlier overhead valve engine (OHV) and flathead engine configurations, where the camshaft is located down in the engine block. The valves in both OHC and OHV engines are located above the combustion chamber; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSA X Engine
The PSA X engine is a family of internal combustion engines used in Citroën, Peugeot, Talbot and Renault automobiles. The X family was mainly used in superminis and the entry-level models of midsize vehicles. It was designed and manufactured by the company "Française de Mécanique", a joint venture created by Peugeot (as predecessor to Groupe PSA) and Renault in 1969, and built in Douvrin in northern France. It is commonly called the "Suitcase" engine, the "Douvrin" nickname being commonly used for the bigger 2.0–2.2-liter J-Type engine, which was also built in Douvrin. The X design was introduced in 1972 with the Peugeot 104. It was an all-aluminium alloy SOHC inline-four design with two valves per cylinder driven by a chain, using petrol as fuel. It was applied transversely in front wheel drive vehicles only, tilted by an almost horizontal attitude of 72 degrees. The integral transmission is mounted on the rear side of the crankcase (thus appearing to be underneath th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citroën AX
The Citroën AX is a supermini which was built by the French manufacturer Citroën from 1986 to 1998. It was launched at the 1986 Paris Motor Show to replace the Citroën Visa and Citroën LNA. Overview Development of this model started in 1983, and it was initially also going to form the basis of a sister model from Talbot to replace the Samba; however, the falling popularity of the Talbot brand - coupled with the huge success of the new Peugeot 205 - had led to Peugeot deciding to axe it by the time the Citroën AX was launched, and so the Talbot version never made it into production. The car was available on the left-hand drive continental markets from its launch on 2 October 1986, as a three-door hatchback with 1.0, 1.1 and 1.4 L TU-series belt driven OHC engines. A range of five-door models was added in 1987 and a 1.4 L diesel engine was introduced in 1988. The latter was replaced by a 1.5 L unit in September 1994. The right-hand drive version for the UK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citroën
Citroën ()The double-dot diacritic over the 'e' is a diaeresis () indicating the two vowels are sounded separately, and not as a diphthong. is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded on 4 June 1919 by André Citroën. Citroën has been owned by Stellantis since 2021 and previously was part of the PSA Group after Peugeot acquired 89.95% share in 1976. Citroën's head office is located in the Stellantis Poissy Plant in Saint-Ouen-sur-Seine since 2021 (previously in Rueil-Malmaison) and its offices studies and research in Vélizy-Villacoublay, Poissy (CEMR), Carrières-sous-Poissy and Sochaux-Montbéliard. In 1934, the firm established its reputation for innovative technology with the Citroën Traction Avant, Traction Avant. This was the world's first car to be mass-produced with front-wheel drive and four-wheel independent suspension, as well as unibody construction, omitting a separate chassis, and instead using the body of the car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peugeot
Peugeot (, , ) is a French automobile brand owned by Stellantis. The family business that preceded the current Peugeot companies was established in 1810, making it the oldest car company in the world. On 20 November 1858, Émile Peugeot applied for the lion trademark. Armand Peugeot (1849–1915) built the company's first vehicle, a Steam car, steam-powered tricycle. In 1886, the company collaborated with Léon Serpollet, followed by the development of an internal combustion car in 1890, which used a Panhard-Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft, Daimler engine. The Peugeot family and company are originally from Sochaux, where Peugeot still operates a large manufacturing facility and the Musée de l'Aventure Peugeot, Peugeot Museum. Peugeot vehicles have received numerous international accolades, including six European Car of the Year awards. The brand also boasts over a century of success in motorsport, with victories including the Indianapolis 500 in 1913, 1916, and 1919. Peugeot Spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocating Engine
A reciprocating engine, more often known as a piston engine, is a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles Common features in all types There may be one or more pistons. Each piston is inside a cylinder, into which a gas is introduced, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter part is an vehicle emissions control, exhaust emission control device which converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalysis, catalyzing a redox chemical reaction, reaction. Catalytic converters are usually used with internal combustion engines fueled by gasoline or diesel fuel, diesel, including lean-burn engines, and sometimes on kerosene heaters and stoves. The first widespread introduction of catalytic converters was in the United States automobile market. To comply with the United States Environmental Protection Agency, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's stricter regulation of exhaust emissions, most gasoline-powered vehicles starting with the 1975 model year are equipped with catalytic converters. These "two-way" oxidation converters combine oxygen with carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). "Three-way" conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
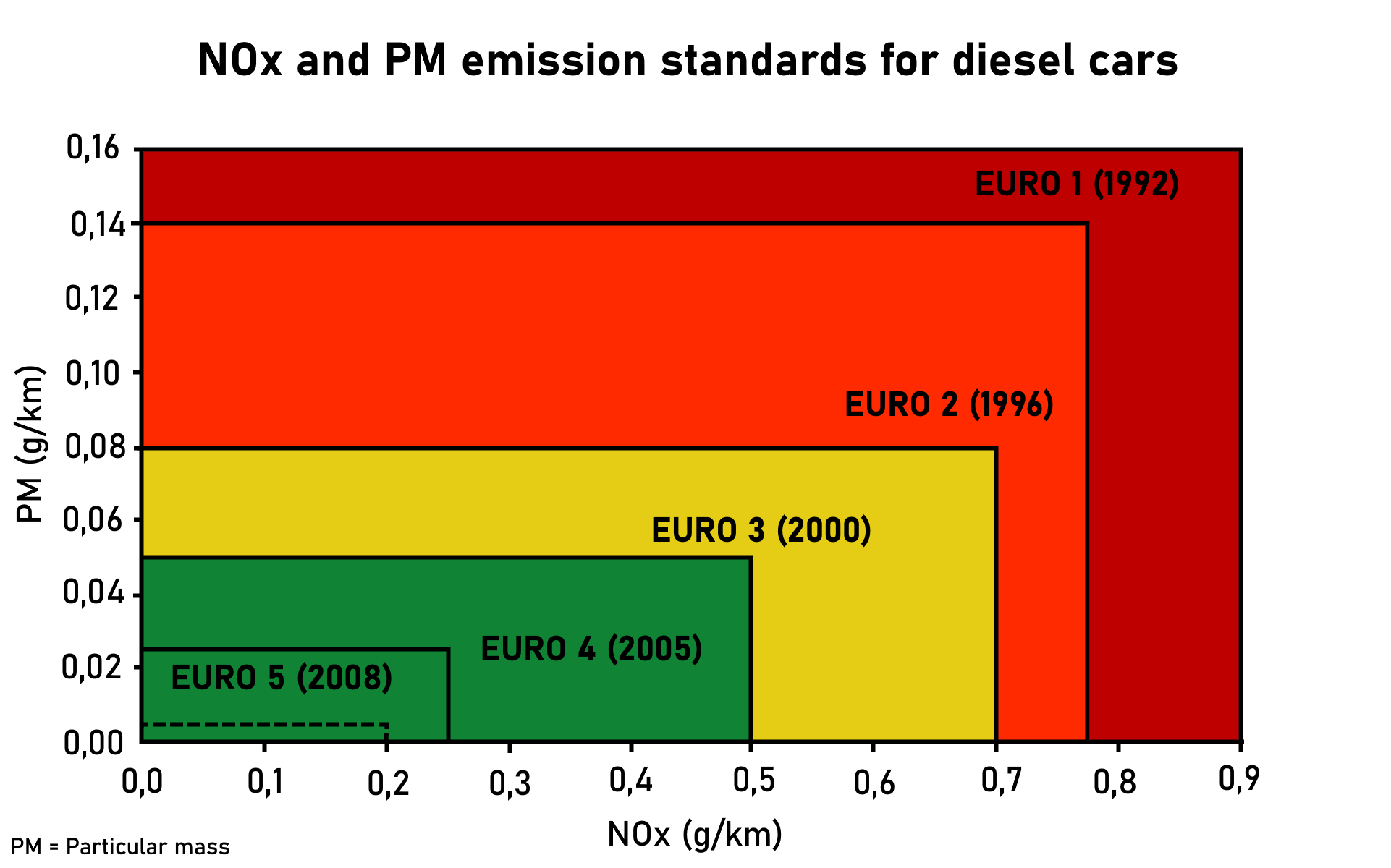
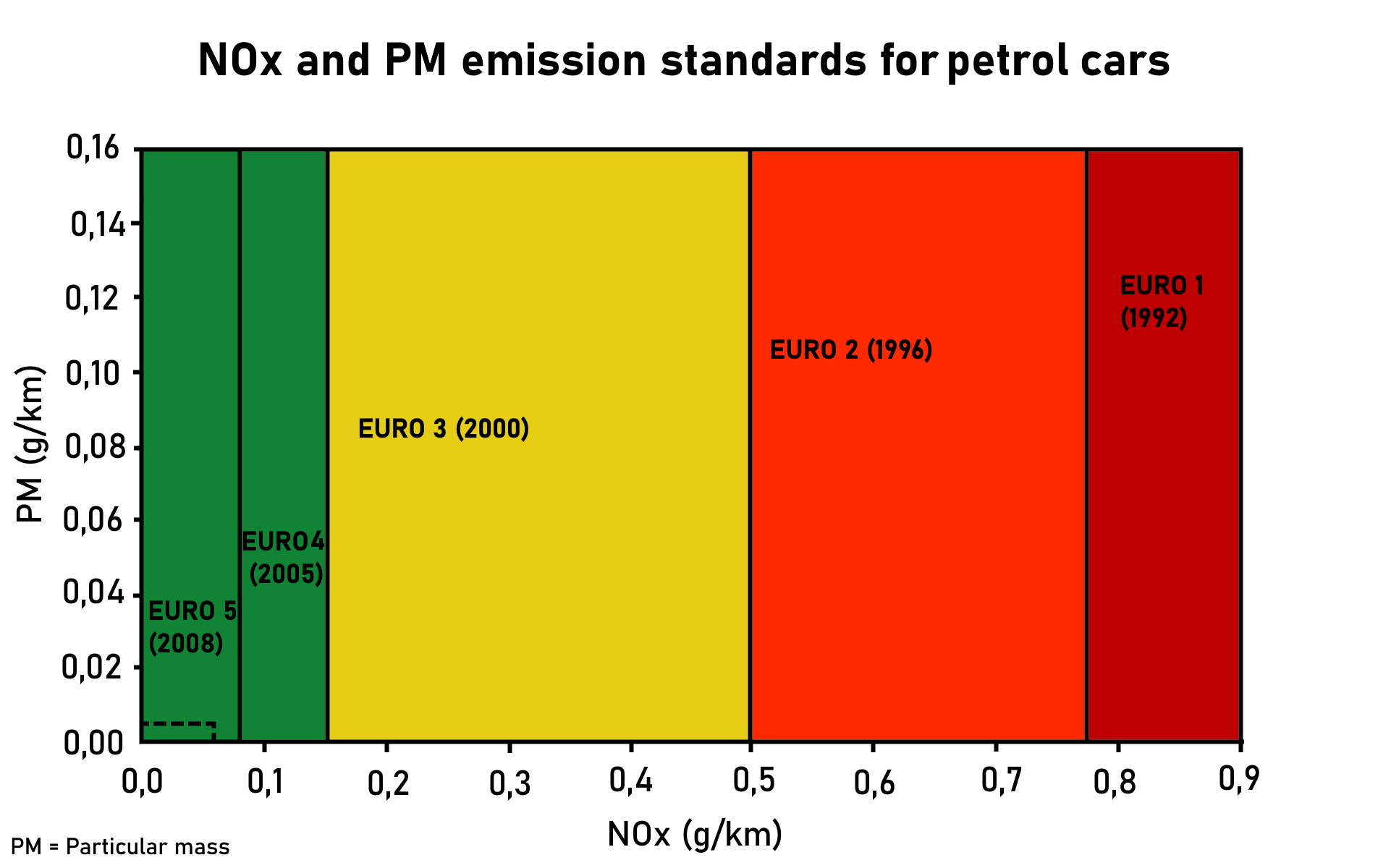
Euro IV
The European emission standards are vehicle emission standards that regulate pollution from the use of new land surface vehicles sold in the European Union and European Economic Area member states and the United Kingdom, and ships in European territorial waters. These standards target air pollution from exhaust gases, brake dust, and tyre rubber pollution, and are defined through a series of European Union directives that progressively introduce stricter limits to reduce environmental impact. Euro 7, agreed in 2024 and due to come into force in 2026, includes non-exhaust emissions such as particulates from tyres and brakes. Until 2030 fossil fueled vehicles are allowed to have dirtier brakes than electric vehicles. Background In the European Union, emissions of nitrogen oxides (), total hydrocarbon (THC), non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHC), carbon monoxide (CO) and particulate matter (PM) are regulated for most vehicle types, including cars, trucks (lorries), loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euro III
The European emission standards are vehicle emission standards that regulate pollution from the use of new land surface vehicles sold in the European Union and European Economic Area member states and the United Kingdom, and ships in European territorial waters. These standards target air pollution from exhaust gases, brake dust, and tyre rubber pollution, and are defined through a series of European Union directives that progressively introduce stricter limits to reduce environmental impact. Euro 7, agreed in 2024 and due to come into force in 2026, includes non-exhaust emissions such as particulates from tyres and brakes. Until 2030 fossil fueled vehicles are allowed to have dirtier brakes than electric vehicles. Background In the European Union, emissions of nitrogen oxides (), total hydrocarbon (THC), non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHC), carbon monoxide (CO) and particulate matter (PM) are regulated for most vehicle types, including cars, trucks (lorries), locomoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Valve Timing
Variable valve timing (VVT) is the process of altering the timing of a Poppet valve, valve lift event in an internal combustion engine, and is often used to improve performance, fuel economy or emissions. It is increasingly being used in combination with variable valve lift systems. There are many ways in which this can be achieved, ranging from mechanical devices to electro-hydraulic and camless systems. Increasingly strict emissions regulations are causing many automotive manufacturers to use VVT systems. Two-stroke cycle, Two-stroke engines use a Two-stroke power valve system, power valve system to get similar results to VVT. Background theory The valves within an internal combustion engine are used to control the flow of the intake and exhaust gases into and out of the combustion chamber. The timing, duration and lift of these valve events has a significant impact on engine performance. Without variable valve timing (variable valve lift), the valve timing is the same for all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |