|
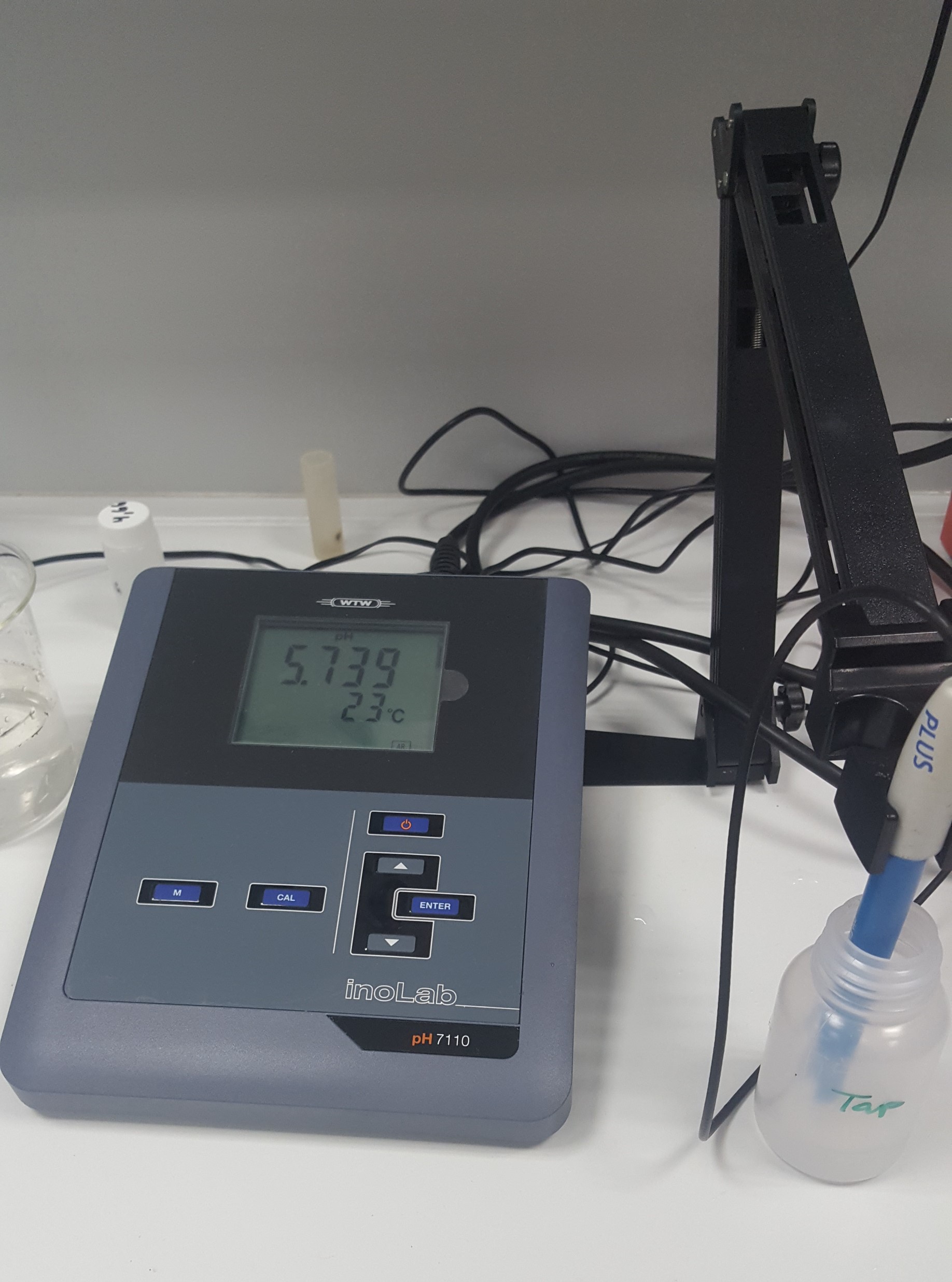
PH Meter
A pH meter is a scientific instrument that measures the hydrogen-ion activity in water-based solutions, indicating its acidity or alkalinity expressed as pH. The pH meter measures the difference in electrical potential between a pH electrode and a reference electrode, and so the pH meter is sometimes referred to as a "potentiometric pH meter". The difference in electrical potential relates to the acidity or pH of the solution. Testing of pH via pH meters (pH-metry) is used in many applications ranging from laboratory experimentation to quality control. Applications The rate and outcome of chemical reactions taking place in water often depends on the acidity of the water, and it is therefore useful to know the acidity of the water, typically measured by means of a pH meter. Knowledge of pH is useful or critical in many situations, including chemical laboratory analyses. pH meters are used for soil measurements in agriculture, water quality for municipal water supplies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beckman Model M PH Meter 2006
Beckman may refer to: *Beckman (surname) *Arnold Orville Beckman, chemist and entrepreneur *Beckman Coulter, a biomedical laboratory instruments company founded by Arnold O. Beckman *Beckman Coulter Life Sciences, a life sciences company focused on research instruments and reagents for enabling new discoveries *3737 Beckman, an asteroid * Institutes and research centers supported by the Arnold and Mabel Beckman Foundation ** Beckman Center for Molecular and Genetic Medicine at Stanford University, Stanford, California ** Beckman Institute at Caltech, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California *** Beckman Institute Laser Resource Center (BILRC) at Caltech ** Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ** Beckman Laser Institute, University of California, Irvine, in Irvine, California ** Beckman Research Institute (BRI) at the City of Hope National Medical Center in Duarte, California, United States * Schools **Arn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipal Water
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. These systems are what supply drinking water to populations around the globe. Aspects of service quality include continuity of supply, water quality and water pressure. The institutional responsibility for water supply is arranged differently in different countries and regions (urban versus rural). It usually includes issues surrounding policy and regulation, service provision and standardization. The cost of supplying water consists, to a very large extent, of fixed costs (capital costs and personnel costs) and only to a small extent of variable costs that depend on the amount of water consumed (mainly energy and chemicals). Almost all service providers in the world charge tariffs to recover part of their costs. Water supply is a separate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony Electrode
The antimony electrode has been investigated for its ability to function as a pH electrode.Bates, Roger G. ''Determination of pH: theory and practice''. Wiley, 1973, pp 300-304 The electrode is made of elemental antimony. The electrochemical process can be formulated as :Sb2O3 + 6 H+ + 6 e- 2Sb + 3 H2O The oxide, Sb2O3, is present on the surface of the electrode. Although this electrode does not give measurements of high accuracy, its rapid response, simplicity and rugged construction make it useful for continuous industrial pH monitoring. It can be used at elevated temperatures. In an unusual application, an antimony electrode was used to measure pH inside the human stomach. The simplicity of construction meant that the electrode could be made small enough to be swallowed. Thin copper wires were attached to the electrode and one terminal on a pH meter. The subject's foot was placed in a saline solution. A calomel reference electrode was also placed in this solution and was connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Electrode
A reference electrode is an electrode that has a stable and well-known electrode potential. The overall chemical reaction taking place in a cell is made up of two independent half-reactions, which describe chemical changes at the two electrodes. To focus on the reaction at the working electrode, the reference electrode is standardized with constant (buffered or saturated) concentrations of each participant of the redox reaction. There are many ways reference electrodes are used. The simplest is when the reference electrode is used as a half-cell to build an electrochemical cell. This allows the potential of the other half cell to be determined. An accurate and practical method to measure an electrode's potential in isolation ( absolute electrode potential) has yet to be developed. Aqueous reference electrodes Common reference electrodes and potential with respect to the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE): * Standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) (E = 0.000 V) activity of H+ = 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Electrode
A glass electrode is a type of ion-selective electrode made of a doped glass membrane that is sensitive to a specific ion. The most common application of ion-selective glass electrodes is for the measurement of pH. The pH electrode is an example of a glass electrode that is sensitive to hydrogen ions. Glass electrodes play an important part in the instrumentation for chemical analysis, and physicochemical studies. The voltage of the glass electrode, relative to some reference value, is sensitive to changes in the activity of certain types of ions. History The first studies of glass electrodes (GE) found different sensitivities of different glasses to change the medium's acidity ( pH), due to the effects of the alkali metal ions. In 1906, M. Cremer, the father of Erika Cremer, determined that the electric potential that arises between parts of the fluid, located on opposite sides of the glass membrane, is proportional to the concentration of acid (hydrogen ion concentration). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potentiometric
A potentiometer is a three- terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat. The measuring instrument called a potentiometer is essentially a voltage divider used for measuring electric potential (voltage); the component is an implementation of the same principle, hence its name. Potentiometers are commonly used to control electrical devices such as volume controls on audio equipment. It is also used in speed control of fans. Potentiometers operated by a mechanism can be used as position transducers, for example, in a joystick. Potentiometers are rarely used to directly control significant power (more than a watt), since the power dissipated in the potentiometer would be comparable to the power in the controlled load. Nomenclature Some terms in the electronics industry used to describe certain types of potentiometers are: * Pot: abbre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Garcelon Using Beckman PH Meter 2004
George may refer to: Names * George (given name) * George (surname) People * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Papagheorghe, also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George, son of Andrew I of Hungary Places South Africa * George, South Africa, a city ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa, a city * George, Missouri, a ghost town * George, Washington, a city * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Computing * George (algebraic compiler) also known as 'Laning and Zierler system', an algebraic compiler by Laning and Zierler in 1952 * GEORGE (computer), early computer built by Argonne National Laboratory in 1957 * GEORGE (operating system), a range of operating systems (George 1–4) for the ICT 1900 range of computers in the 1960s * GEORGE (programming language), an autocode system invented by Charles Leonard Ham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living Cells
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miniaturized
Miniaturization ( Br.Eng.: ''miniaturisation'') is the trend to manufacture ever-smaller mechanical, optical, and electronic products and devices. Examples include miniaturization of mobile phones, computers and vehicle engine downsizing. In electronics, the exponential scaling and miniaturization of silicon MOSFETs (MOS transistors) leads to the number of transistors on an integrated circuit chip doubling every two years, an observation known as Moore's law. This leads to MOS integrated circuits such as microprocessors and memory chips being built with increasing transistor density, faster performance, and lower power consumption, enabling the miniaturization of electronic devices. Electronic circuits The history of miniaturization is associated with the history of information technology based on the succession of switching devices, each smaller, faster, and cheaper than its predecessor. During the period referred to as the Second Industrial Revolution (), miniatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detection
{{Unreferenced, date=March 2018 In general, detection is the action of accessing information without specific cooperation from with the sender. In the history of radio communications, the term "detector" was first used for a device that detected the simple presence or absence of a radio signal, since all communications were in Morse code. The term is still in use today to describe a component that extracts a particular signal from all of the electromagnetic waves present. Detection is usually based on the frequency of the carrier signal, as in the familiar frequencies of radio broadcasting, but it may also involve filtering a faint signal from noise, as in radio astronomy, or reconstructing a hidden signal, as in steganography. In optoelectronics, "detection" means converting a received optical input to an electrical output. For example, the light signal received through an optical fiber is converted to an electrical signal in a detector such as a photodiode. In steganography, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high-tech, but it is most commonly applied to industrial design, in which raw materials from the primary sector are transformed into finished goods on a large scale. Such goods may be sold to other manufacturers for the production of other more complex products (such as aircraft, household appliances, furniture, sports equipment or automobiles), or distributed via the tertiary industry to end users and consumers (usually through wholesalers, who in turn sell to retailers, who then sell them to individual customers). Manufacturing engineering is the field of engineering that designs and optimizes the manufacturing process, or the steps through which raw materials are transformed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |