|
Pd-l1
Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) also known as cluster of differentiation 274 (CD274) or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CD274'' gene. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a 40kDa type 1 transmembrane protein that has been speculated to play a major role in suppressing the adaptive arm of immune systems during particular events such as pregnancy, tissue allografts, autoimmune disease and other disease states such as hepatitis. Normally the adaptive immune system reacts to antigens that are associated with immune system activation by exogenous or endogenous danger signals. In turn, clonal expansion of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells and/or CD4+ helper cells is propagated. The binding of PD-L1 to the inhibitory checkpoint molecule PD-1 transmits an inhibitory signal based on interaction with phosphatases ( SHP-1 or SHP-2) via Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-Based Switch Motif (ITSM). This reduces the proliferation of antigen-specific T-cells in l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PD-1
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1), (CD279 cluster of differentiation 279). PD-1 is a protein encoded in humans by the ''PDCD1'' gene. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor on T cells and B cells that has a role in regulating the immune system's response to the cells of the human body by down-regulating the immune system and promoting self-tolerance by suppressing T cell inflammatory activity. This prevents autoimmune diseases, but it can also prevent the immune system from killing cancer cells. PD-1 is an immune checkpoint and guards against autoimmunity through two mechanisms. First, it promotes apoptosis (programmed cell death) of antigen-specific T-cells in lymph nodes. Second, it reduces apoptosis in regulatory T cells (anti-inflammatory, suppressive T cells). PD-1 inhibitors, a new class of drugs that block PD-1, activate the immune system to attack tumors and are used to treat certain types of cancer. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor that belongs to the immunoglobulin superf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
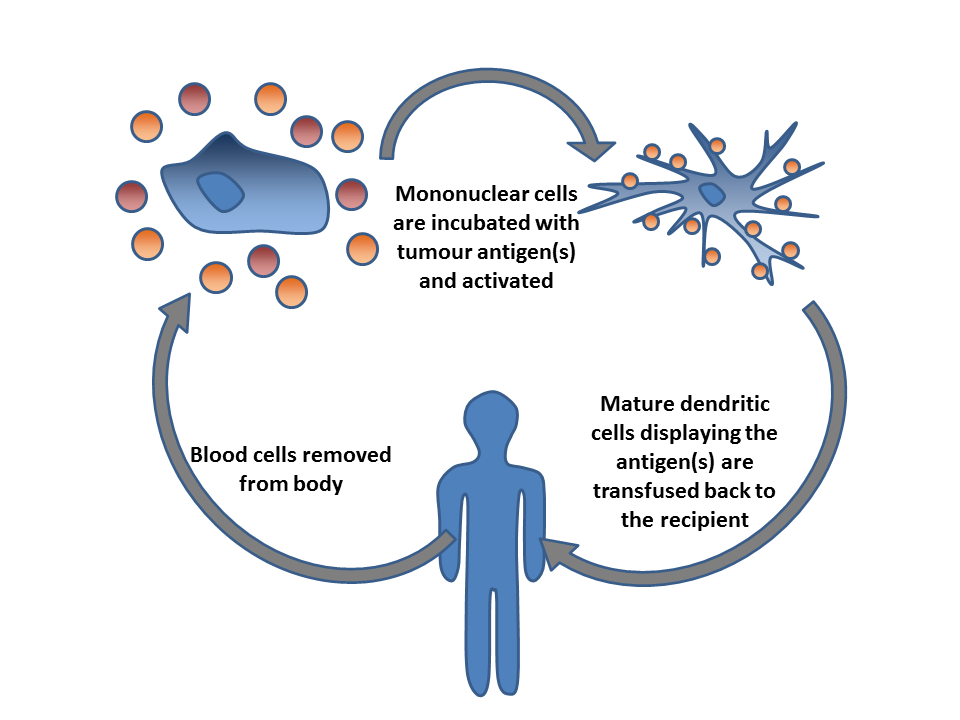
Cancer Immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncotherapy) is the stimulation of the immune system to treat cancer, improving the immune system's natural ability to fight the disease. It is an application of the basic research, fundamental research of cancer immunology (immuno-oncology) and a growing subspecialty of oncology. Cancer immunotherapy exploits the fact that cancer cells often have tumor antigens, molecules on their surface that can bind to antibody proteins or T-cell receptors, triggering an immune system response. The tumor antigens are often proteins or other macromolecules (e.g., carbohydrates). Normal antibodies bind to external pathogens, but the modified immunotherapy antibodies bind to the tumor antigens marking and identifying the cancer cells for the immune system to inhibit or kill. The clinical success of cancer immunotherapy is highly variable between different forms of cancer; for instance, certain subtypes of gastric cancer react well to the approach whereas immunothera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CTLA-4
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4, (CTLA-4) also known as CD152 ( cluster of differentiation 152), is a protein receptor that functions as an immune checkpoint and downregulates immune responses. CTLA-4 is constitutively expressed in regulatory T cells but only upregulated in conventional T cells after activation – a phenomenon which is particularly notable in cancers. It acts as an "off" switch when bound to CD80 or CD86 on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. It is encoded by the gene ''CTLA4'' in humans. The CTLA-4 protein is encoded by the ''Ctla-4'' gene in mice. History CTLA-4 was first identified in 1991 as a second receptor for the T cell costimulation ligand B7. In November 1995, the labs of Tak Wah Mak and Arlene Sharpe independently published their findings on the discovery of the function of CTLA-4 as a negative regulator of T-cell activation, by knocking out the gene in mice. Previous studies from several labs had used methods which could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
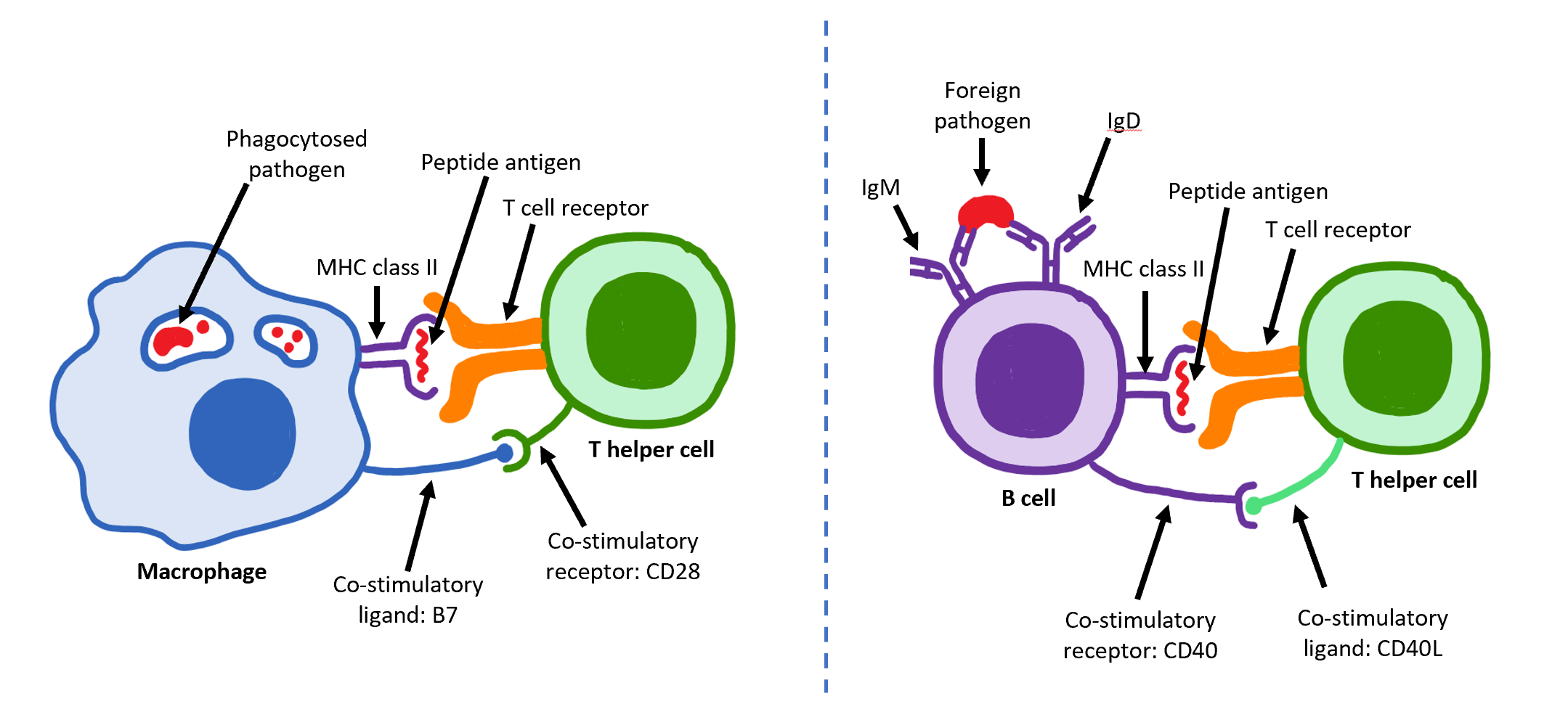
CD80
The Cluster of differentiation 80 (also CD80 and B7-1) is a B7, type I membrane protein in the immunoglobulin superfamily, with an extracellular immunoglobulin constant-like domain and a variable-like domain required for receptor binding. It is closely related to CD86, another B7 protein (B7-2), and often works in tandem. Both CD80 and CD86 interact with Co-stimulation, costimulatory receptors CD28, CTLA-4 (CD152) and the p75 neurotrophin receptor. Structure CD80 is a member of the B7 (protein), B7 family, which consists of molecules present at Antigen-presenting cell, APCs and their receptors present on the T cell, T-cells. CD80 is present specifically on Dendritic cell, DC, activated B cell, B-cells, and macrophages, but also T cell, T-cells. CD80 is also a Transmembrane protein, transmembrane glycoprotein and a member of the Immunoglobulin superfamily, Ig superfamily. It is composed of 288 amino acids, and its mass is 33 Dalton (unit), kDa. It consists of two Ig-like extracel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costimulator
Co-stimulation is a secondary signal which immune cells rely on to activate an immune response in the presence of an antigen-presenting cell. In the case of T cells, two stimuli are required to fully activate their immune response. During the activation of lymphocytes, co-stimulation is often crucial to the development of an effective immune response. Co-stimulation is required in addition to the antigen-specific signal from their antigen receptors. T cell co-stimulation T cells require two signals to become fully activated. A first signal, which is antigen-specific, is provided through the T cell receptor (TCR) which interacts with peptide- MHC molecules on the membrane of an antigen presenting cell (APC). A second signal, the co-stimulatory signal, is antigen nonspecific and is provided by the interaction between co-stimulatory molecules expressed on the membrane of the APC and the T cell. This interaction promotes and enhances the TCR signaling, but can also be bi-directiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Helper Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell Immunoglobulin class switching, antibody class switching, breaking Cross-presentation, cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express Receptor (biochemistry), receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory T Cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain immune tolerance, tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppression, immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulation and upregulation, downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same cell lineage, lineage as naïve T helper cell, CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine Transforming growth factor beta, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD28
CD28 (Cluster of Differentiation 28) is a protein expressed on T cells that provides essential co-stimulation, co-stimulatory signals required for T cell activation and survival. When T cells are stimulated through CD28 in conjunction with the T-cell receptor (T cell receptor, TCR), it enhances the production of various interleukins, particularly interleukin 6, IL-6. CD28 serves as a receptor for CD80 (B7.1) and CD86 (B7.2), proteins found on antigen-presenting cells (APCs). CD28 is the only B7 (protein), B7 receptor consistently expressed on naive T cells. In the absence of CD28:B7 interaction, a naive T cell's TCR engagement with an Major histocompatibility complex, MHC:antigen complex leads to anergy. CD28 is also expressed on bone marrow stromal cells, plasma cells, neutrophils, and eosinophils, although its function in these cells is not fully understood. Typically, CD28 is expressed on about 50% of CD8, CD8+ T cells and more than 80% of CD4, CD4+ T cells in humans. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD86
Cluster of Differentiation 86 (also known as CD86 and B7-2) is a protein constitutively expressed on dendritic cells, Langerhans cells, macrophages, B-cells (including memory B-cells), and on other antigen-presenting cells. Along with CD80, CD86 provides costimulatory signals necessary for T cell activation and survival. Depending on the ligand bound, CD86 can signal for self-regulation and cell-cell association, or for attenuation of regulation and cell-cell disassociation. The ''CD86'' gene encodes a type I membrane protein that is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Alternative splicing results in two transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Additional transcript variants have been described, but their full-length sequences have not been determined. Structure CD86 belongs to the B7 family of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is a 70 kDa glycoprotein made up of 329 amino acids. Both CD80 and CD86 share a conserved amino acid motif that forms their l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanomolar
Molar concentration (also called molarity, amount concentration or substance concentration) is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. Specifically, It is a measure of the concentration of a chemical species, in particular, of a solute in a solution, in terms of amount of substance per unit volume of solution. In chemistry, the most commonly used unit for molarity is the number of moles per liter, having the unit symbol mol/L or mol/ dm3 (1000 mol/ m3) in SI units. A solution with a concentration of 1 mol/L is said to be 1 molar, commonly designated as 1 M or 1 M. Molarity is often depicted with square brackets around the substance of interest; for example, the molarity of the hydrogen ion is depicted as + Definition Molar concentration or molarity is most commonly expressed in units of moles of solute per litre of solution. For use in broader applications, it is defined as amount of substance of solute per unit volume of solution, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociation Constant
In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant (''K''D) is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate (dissociate) reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex falls apart into its component molecules, or when a salt splits up into its component ions. The dissociation constant is the inverse of the association constant. In the special case of salts, the dissociation constant can also be called an ionization constant. For a general reaction: : A_\mathit B_\mathit \mathit A + \mathit B in which a complex \ce_x \ce_y breaks down into ''x'' A subunits and ''y'' B subunits, the dissociation constant is defined as : K_\mathrm = \frac where and ''x'' B''y''are the equilibrium concentrations of A, B, and the complex A''x'' B''y'', respectively. One reason for the popularity of the dissociation constant in biochemistry and pharmacology is that in the frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |