|
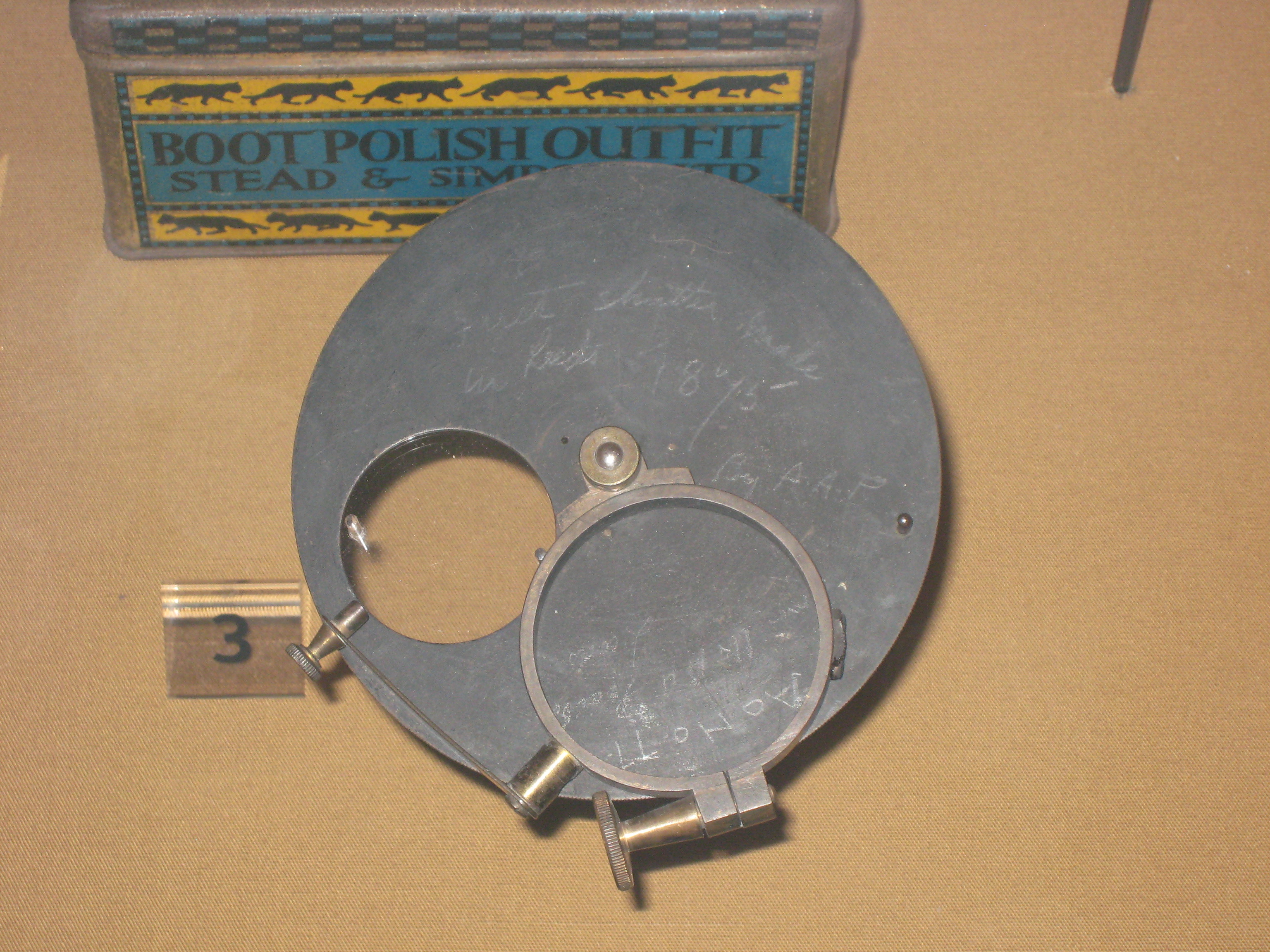
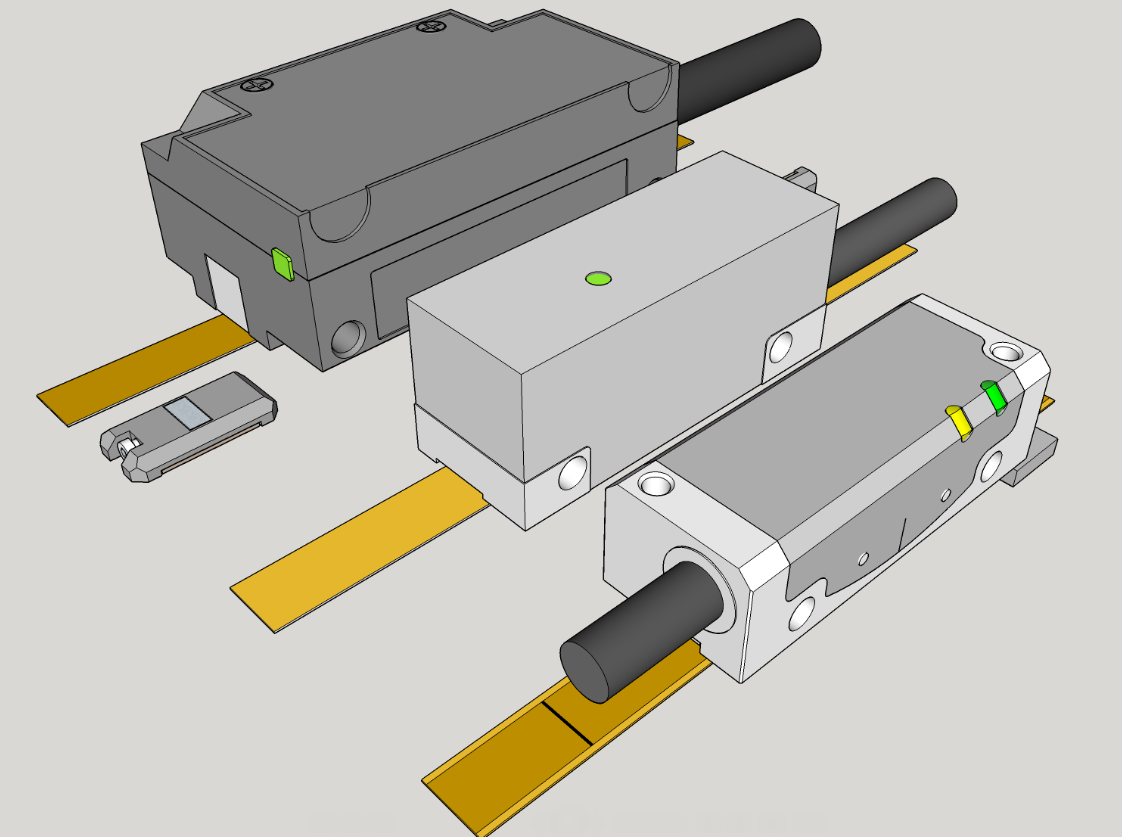
Optical Chopper
An optical chopper is a device which periodically interrupts a light beam. Three types are available: variable frequency rotating disc choppers, fixed frequency tuning fork choppers, and optical shutters. A rotating disc chopper was famously used in 1849 by Hippolyte Fizeau in the first non-astronomical measurement of the speed of light. Use in science laboratories Optical choppers, usually rotating disc mechanical shutters, are widely used in science labs in combination with lock-in amplifiers. The chopper is used to modulate the intensity of a light beam, and a lock-in amplifier is used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio. To be effective, an optical chopper should have a stable rotating speed. In cases where the 1/f noise is the main problem, one would like to select the maximum chopping frequency possible. This is limited by the motor speed and the number of slots in the rotating disc, which is in turn limited by the disc radius and the beam diameter. Examples Optical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chopper Wheels
Chopper may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Chopper'' (comics), a horror comic book mini-series * ''Chopper'' (film), a 2000 Australian film by and about Mark "Chopper" Read * Chopper (''Judge Dredd''), a character in British comics anthologies ''2000 AD'' and ''Judge Dredd'' * ''Chopper'' (video game), a 2009 iOS video game * '' Chopper I'', a 1988 video game developed by SNK Playmore * Tony Tony Chopper, a character from the manga and anime ''One Piece'' People * Christopher Hope (journalist) (born 1971), British journalist * Mark "Chopper" Read (1954–2013), Australian criminal, author and recording artist Transportation * Chopper (motorcycle), a type of customized motorcycle * Chopper bicycle, a customized bicycle modeled after the motorcycle * Raleigh Chopper, a model of bicycles * A colloquialism for helicopter * A nickname for the British Rail Class 20 diesel-electric locomotive * Chopper coupler Other * Chopper (archaeology), a stone tool * Chopper (elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Encoder
A linear encoder is a sensor, transducer or readhead paired with a scale that encodes position. The sensor reads the scale in order to convert the encoded position into an analog or digital signal, which can then be decoded into position by a digital readout (DRO) or motion controller. The encoder can be either ''incremental'' or ''absolute.'' In an incremental system, position is determined by motion over time; in contrast, in an absolute system, motion is determined by position over time. Linear encoder technologies include optical, magnetic, inductive, capacitive and eddy current. Optical technologies include shadow, self imaging and interferometric. Linear encoders are used in metrology instruments, motion systems, inkjet printers and high precision machining tools ranging from digital calipers and coordinate measuring machines to stages, CNC mills, manufacturing gantry tables and semiconductor steppers. Physical principle Linear encoders are transducers that exploit many d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-emitting Diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Encoder
A rotary encoder, also called a shaft encoder, is an electro-mechanical device that converts the angular position or motion of a shaft or axle to analog or digital output signals. There are two main types of rotary encoder: absolute and incremental. The output of an absolute encoder indicates the current shaft position, making it an angle transducer. The output of an incremental encoder provides information about the ''motion'' of the shaft, which typically is processed elsewhere into information such as position, speed and distance. Rotary encoders are used in a wide range of applications that require monitoring or control, or both, of mechanical systems, including industrial controls, robotics, photographic lenses, computer input devices such as optomechanical mice and trackballs, controlled stress rheometers, and rotating radar platforms. Technologies * Mechanical: Also known as conductive encoders. A series of circumferential copper tracks etched onto a PCB is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Lamp
Signal lamp training during World War II A signal lamp (sometimes called an Aldis lamp or a Morse lamp) is a semaphore system using a visual signaling device for optical communication, typically using Morse code. The idea of flashing dots and dashes from a lantern was first put into practice by Captain Philip Howard Colomb, of the Royal Navy, in 1867. Colomb's design used limelight for illumination, and his original code was not the same as Morse code. During World War I, German signalers used optical Morse transmitters called ', with a range of up to 8 km (5 miles) at night, using red filters for undetected communications. Modern signal lamps produce a focused pulse of light, either by opening and closing shutters mounted in front of the lamp, or by tilting a concave mirror. They continue to be used to the present day on naval vessels and for aviation light signals in air traffic control towers, as a backup device in case of a complete failure of an aircraft's radio. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
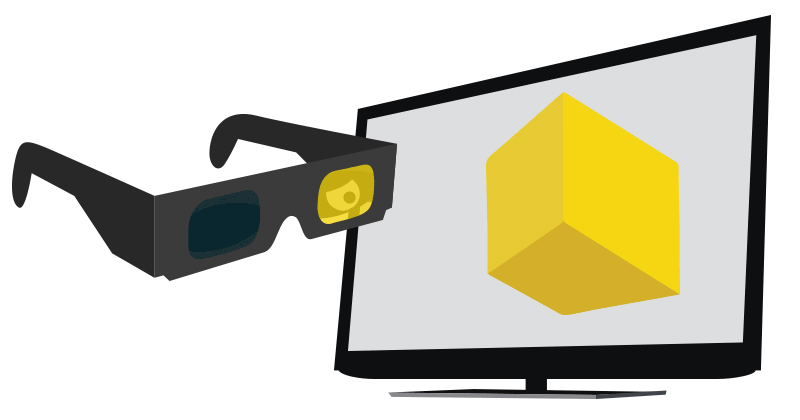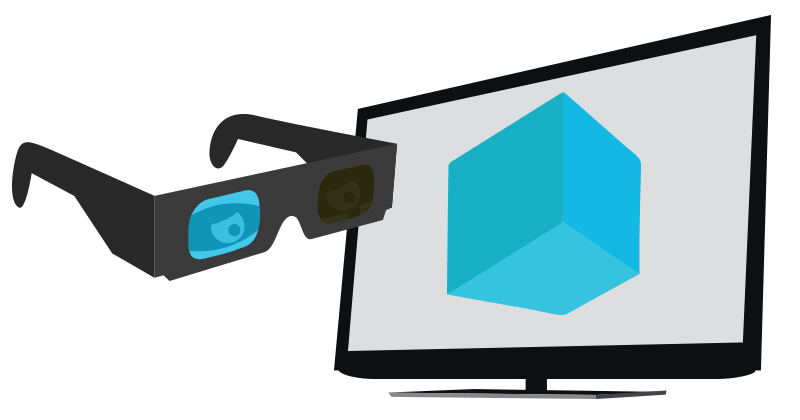
Liquid Crystal Shutter Glasses
An active shutter 3D system (a.k.a. alternate frame sequencing, alternate image, AI, alternating field, field sequential or eclipse method) is a technique of displaying stereoscopic 3D images. It works by only presenting the image intended for the left eye while blocking the right eye's view, then presenting the right-eye image while blocking the left eye, and repeating this so rapidly that the interruptions do not interfere with the perceived fusion of the two images into a single 3D image. Modern active shutter 3D systems generally use liquid crystal shutter glasses (also called "LC shutter glasses" or "active shutter glasses"). Each eye's glass contains a liquid crystal layer which has the property of becoming opaque when voltage is applied, being otherwise transparent. The glasses are controlled by a timing signal that allows the glasses to alternately block one eye, and then the other, in synchronization with the refresh rate of the screen. The timing synchronization to the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Movement
The term Beta movement is used for the optical illusion of apparent motion in which the very short projection of one figure and a subsequent very short projection of a more or less similar figure in a different location are experienced as one figure that moves. The illusion of motion caused by animation and film is sometimes believed to rely on beta movement, as an alternative to the older explanation known as persistence of vision. However, there are notable differences between the short-range apparent motion that occurs in film (with little differences between successive images) and the long-range apparent motion originally described as beta movement (with bigger differences between positions of successive images). Examples of use The beta movement effect has been widely used in news ticker technology and is commonly seen in LED displays. History Observations of apparent motion through quick succession of images go back to the 19th century. In 1833, Joseph Plateau introd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movie Projector
A movie projector is an opto-mechanical device for displaying motion picture film by projecting it onto a screen. Most of the optical and mechanical elements, except for the illumination and sound devices, are present in movie cameras. Modern movie projectors are specially built video projectors. (see also digital cinema) Many projectors are specific to a particular film gauge and not all movie projectors are film projectors since the use of film is required. Predecessors The main precursor to the movie projector was the magic lantern. In its most common setup it had a concave mirror behind a light source to help direct as much light as possible through a painted glass picture slide and a lens, out of the lantern onto a screen. Simple mechanics to have the painted images moving were probably implemented since Christiaan Huygens introduced the apparatus around 1659. Initially candles and oil lamps were used, but other light sources, such as the argand lamp and lime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shutter (photography)
In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period, exposing photographic film or a photosensitive digital sensor to light in order to capture a permanent image of a scene. A shutter can also be used to allow pulses of light to pass outwards, as seen in a movie projector or a signal lamp. A shutter of variable speed is used to control exposure time of the film. The shutter is constructed so that it automatically closes after a certain required time interval. The speed of the shutter is controlled by a ring outside the camera, on which various timings are marked. Camera shutter Camera shutters can be fitted in several positions: * Leaf shutters are usually fitted within a lens assembly (''central shutter''), or more rarely immediately behind (''behind-the-lens shutter'') or, even more rarely, in front of a lens, and shut off the beam of light where it is narrow. * Focal-plane shutters are mounted near the focal plane and move to uncover the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest point in an all points addressable display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software. Each pixel is a sample of an original image; more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original. The intensity of each pixel is variable. In color imaging systems, a color is typically represented by three or four component intensities such as red, green, and blue, or cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. In some contexts (such as descriptions of camera sensors), ''pixel'' refers to a single scalar element of a multi-component representation (called a ''photosite'' in the camera sensor context, although '' sensel'' is sometimes used), while in yet other contexts (like MRI) it may refer to a set of component intensities for a spatial position. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LCD Television
Liquid-crystal-display televisions (LCD TVs) are television sets that use liquid-crystal displays to produce images. They are, by far, the most widely produced and sold television display type. LCD TVs are thin and light, but have some disadvantages compared to other display types such as high power consumption, poorer contrast ratio, and inferior color gamut. LCD TVs rose in popularity in the early years of the 21st century, surpassing sales of cathode ray tube televisions worldwide in 2007. Sales of CRT TVs dropped rapidly after that, as did sales of competing technologies such as plasma display panels and rear-projection television. History Early efforts Passive matrix LCDs first became common as portable computer displays in the 1980s, competing for market share with plasma displays. The LCDs had very slow refresh rates that blurred the screen even with scrolling text, but their light weight and low cost were major benefits. Screens using reflective LCDs required no intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
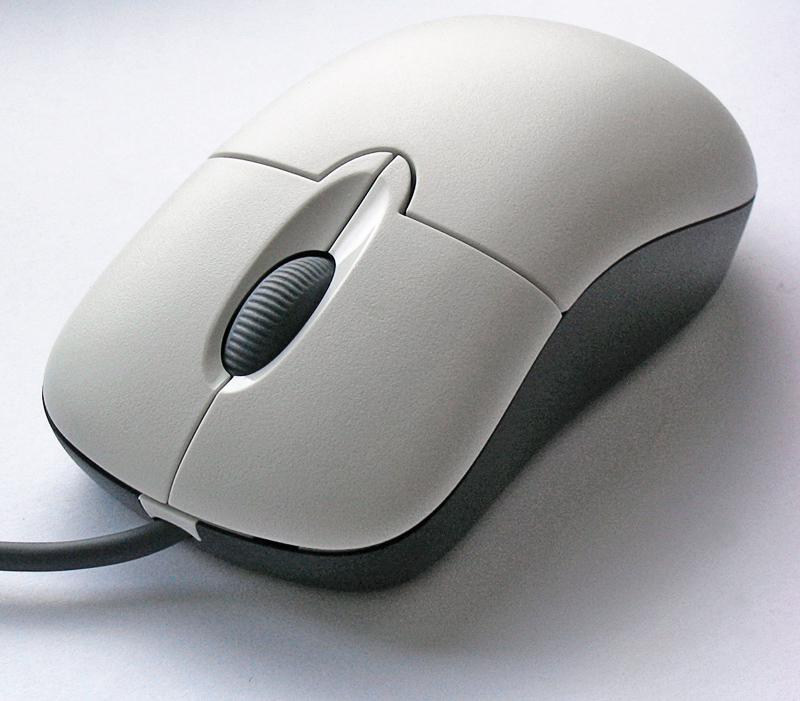
Mouse (computing)
A computer mouse (plural mice, sometimes mouses) is a hand-held pointing device that detects two-dimensional motion relative to a surface. This motion is typically translated into the motion of a pointer on a display, which allows a smooth control of the graphical user interface of a computer. The first public demonstration of a mouse controlling a computer system was in 1968. Mice originally used two separate wheels to track movement across a surface: one in the X-dimension and one in the Y. Later, the standard design shifted to utilize a ball rolling on a surface to detect motion. Most modern mice use optical sensors that have no moving parts. Though originally all mice were connected to a computer by a cable, many modern mice are cordless, relying on short-range radio communication with the connected system. In addition to moving a cursor, computer mice have one or more buttons to allow operations such as the selection of a menu item on a display. Mice often also feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |